
Concept explainers
A telephoto lens consists of a positive lens of focal length +3.5 cm placed 2.0 cm in front of a negative lens of focal length –1.8 cm. (a) Locate the image of a very distant object. (b) Determine the focal length of the single lens that would form as large an image of a distant object as is formed by this lens combination.
(a)
The distance of the image of an object, which is very far away from the telephoto lens, if it has a positive focal length of
Answer to Problem 33SP
Solution:
A real image at a distance of
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
The focal length of the negative lens is
The focal length of the positive lens is
The positive lens is placed
Formula used:
The expression for the thin lens formula is written as
Here,
Sign convention:
Explanation:
Draw the diagram according to the problem.
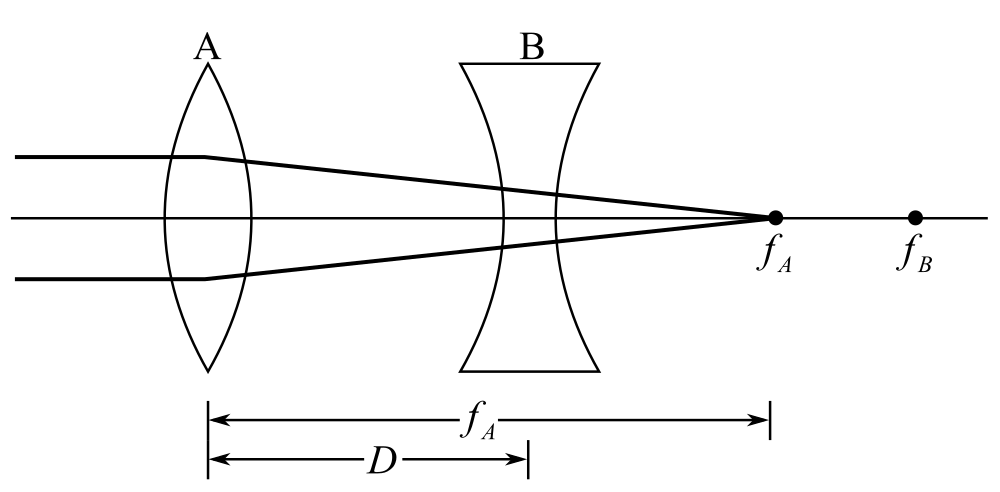
Here,
Understand that for the given diagram, the image of the object at very distant formed at the focus of the positive lens, which works as an object for the negative lens. So, the distance of the object from the negative lens will be the difference between its focal length and the distance between both the lenses.
The expression for the distance of the object from a negative lens is
Substitute
Also, the object will be at right side for negative lens. So, its distance will be negative according to the sign convention. Therefore,
Write the expression for the lens formula for a thin lens:
Substitute
The positive sign of the distance of the image shows that a real image is formed
Conclusion:
Hence, the image formed of a very distant object from the telephoto is real and
(b)
The focal length of a single lens that will form as large image of distant object as formed by the combination of a positive lens of focal length
Answer to Problem 33SP
Solution:
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
The focal length of the positive lens is
The focal length of the negative lens is
The positive lens is placed
Formula used:
The expression for the resultant focal length of a combination of lenses is written as
Explanation:
Recall the expression for the resultant focal length of a combination of lenses:
Substitute
Conclusion:
The focal length of the single lens will be
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 39 Solutions
Schaum's Outline of College Physics, Twelfth Edition (Schaum's Outlines)
- Solve and answer the question correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forward་ The position of a particle is described by r = (300e 0.5t) mm and 0 = (0.3t²) rad, where t is in seconds. Part A Determine the magnitude of the particle's velocity at the instant t = 1.5 s. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. v = Value Submit Request Answer Part B ? Units Determine the magnitude of the particle's acceleration at the instant t = 1.5 s. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. a = Value A ? Unitsarrow_forwardSolve and answer the question correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forward
- Solve and answer the question correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forwardA spiral transition curve is used on railroads to connect a straight portion of the track with a curved portion. (Figure 1) Part A v = v₁ft/s 600 ft y = (106) x³ If the spiral is defined by the equation y = (106)³, where x and y are in feet, determine the magnitude of the acceleration of a train engine moving with a constant speed of v₁ = 30 ft/s when it is at point x = 600 ft. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. ? a = Value Unitsarrow_forwardsolve and answer the problem correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forward
- Solve and answer the question correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forwardSolve and answer the question correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forwardWhen the motorcyclist is at A, he increases his speed along the vertical circular path at the rate of = (0.3t) ft/s², where t is in seconds. Take p = 360 ft. (Figure 1) Part A 60° Ρ B If he starts from rest at A, determine the magnitude of his velocity when he reaches B. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. v = Value Submit Request Answer ་ Part B ? Units If he starts from rest at A, determine the magnitude of his acceleration when he reaches B. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. 11 ? a = Value Unitsarrow_forward
- The car starts from rest at s = 0 and increases its speed at a₁ = 7 m/s². (Figure 1) Part A = 40 m Determine the time when the magnitude of acceleration becomes 20 m/s². Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. ? t = Value Units Part B At what position s does this occur? Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. s = Value Submit Request Answer ? Unitsarrow_forwardSolve and answer the question correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forwardSolve and answer the question correctly please. Thank you!!arrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax
University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





