
During a 3-month period, acute hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection was diagnosed in 9 residents of a nursing home. Serological testing of all residents revealed that 9 people had acute HBV infection, 2 had chronic infection, 5 had antibodies to HBV, and 58 were susceptible. Medical charts of residents were reviewed for history of medications and use of ancillary medical services. Infection control practices at the nursing home were assessed through interviews with personnel and direct observations of nursing procedures. A summary of the medical charts is shown below.
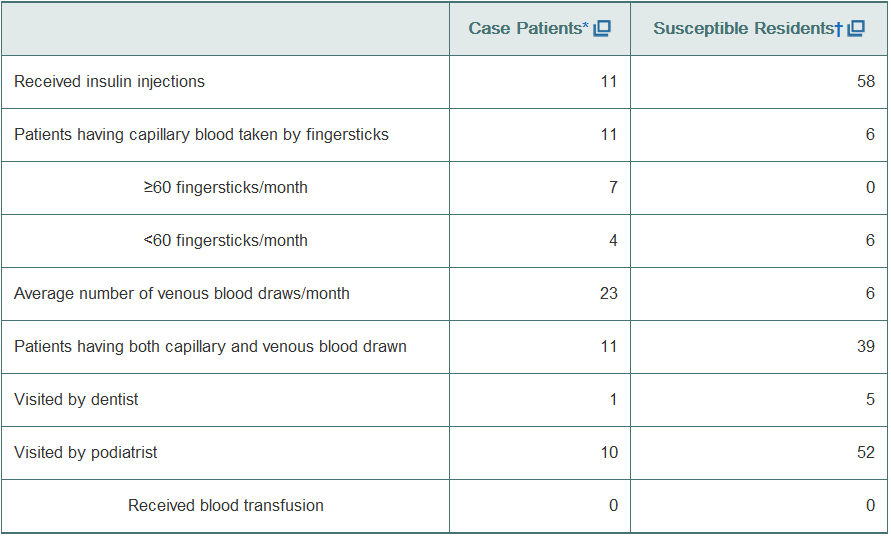
*A case patient has hepatitis B.
Susceptible residents live in the nursing home but do not have hepatitis B.
- What is the usual method of transmission for hepatitis B?
- What is the probable source of infection in hospitals?
- How was this infection transmitted?
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 39 Solutions
Laboratory Experiments in Microbiology (12th Edition) (What's New in Microbiology)
- How is the term enzyme related to the term proteinarrow_forwardCan very low temperatures cause proteins to denature? Explain why or why not?arrow_forwardHumans consider themselves amazingly clever and innovative, constantly developing "new" ways of altering the world around us. As material consumption has increased, many have turned to the ideas of recycling and reuse as a means to minimize some negative aspects of our modern consumerism. Mother Nature though is the ultimate innovator and, more importantly, the ultimate recycler.arrow_forward
- H gene assorts independently from the I gene. Both on autosomes. One man and one woman, both of HhIAIB genotype. Determine the blood type of progeny and fractions out of 16arrow_forwardAlleles at the P locus control seed color. Plants which are pp have white seeds, white flowers and no pigment in vegetative parts. Plants which are P_ have black seeds, purple flowers and may have varying degrees of pigment on stems and leaves. Seed color can be assessed, visually, based on if the seed is white or not white A gene for mold resistance has been reported and we want to determine its inheritance and whether it is linked to P. For the purposes of this exercise, we will assume that resistance is controlled by a single locus M, and M_ plants are resistant and mm plants are susceptible. Resistance can be measured, under greenhouse conditions, 2 weeks after planting, by injecting each seedling with a spore suspension. After two weeks, the seedlings can be rated as resistant or susceptible, based on whether or not tissue is actively sporulating. For this exercise we will use seed and data from the F10 generation of a recombinant inbred population produced using single seed…arrow_forwardLinkage in common bean Alleles at the P locus control seed color. Plants which are pp have white seeds, white flowers and no pigment in vegetative parts. Plants which are P_ have black seeds, purple flowers and may have varying degrees of pigment on stems and leaves. Seed color can be assessed, visually, based on if the seed is white or not white A gene for mold resistance has been reported and we want to determine its inheritance and whether it is linked to P. For the purposes of this exercise, we will assume that resistance is controlled by a single locus M, and M_ plants are resistant and mm plants are susceptible. Resistance can be measured, under greenhouse conditions, 2 weeks after planting, by injecting each seedling with a spore suspension. After two weeks, the seedlings can be rated as resistant or susceptible, based on whether or not tissue is actively sporulating. For this exercise we will use seed and data from the F10 generation of a recombinant inbred population…arrow_forward
- Alleles at the P locus control seed color. Plants which are pp have white seeds, white flowers and no pigment in vegetative parts. Plants which are P_ have black seeds, purple flowers and may have varying degrees of pigment on stems and leaves. Seed color can be assessed, visually, based on if the seed is white or not white A gene for mold resistance has been reported and we want to determine its inheritance and whether it is linked to P. For the purposes of this exercise, we will assume that resistance is controlled by a single locus M, and M_ plants are resistant and mm plants are susceptible. Resistance can be measured, under greenhouse conditions, 2 weeks after planting, by injecting each seedling with a spore suspension. After two weeks, the seedlings can be rated as resistant or susceptible, based on whether or not tissue is actively sporulating. For this exercise we will use seed and data from the F10 generation of a recombinant inbred population produced using single seed…arrow_forwardcan you help? I think its B but not surearrow_forwardSkip to main content close Homework Help is Here – Start Your Trial Now! arrow_forward search SEARCH ASK Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BUY Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition) 11th Edition ISBN: 9780134580999 Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn Publisher: PEARSON 1 The Human Body: An Orientation expand_moreChapter 1 : The Human Body: An Orientation Chapter Questions expand_moreSection: Chapter Questions Problem 1RQ: The correct sequence of levels forming the structural hierarchy is A. (a) organ, organ system,... format_list_bulletedProblem 1RQ: The correct sequence of levels forming the structural hierarchy is A. (a) organ, organ system,... See similar textbooks Bartleby Related Questions Icon Related questions Bartleby Expand Icon bartleby Concept explainers bartleby Question Draw a replication bubble with two replication forks.blue lines are DNA single strands and red lines are RNA single strands.indicate all 3' and 5’ ends on all DNA single…arrow_forward
- Provide an answerarrow_forwardQuestion 4 1 pts Which of the following would be most helpful for demonstrating alternative splicing for a new organism? ○ its proteome and its transcriptome only its transcriptome only its genome its proteome and its genomearrow_forwardIf the metabolic scenario stated with 100 mM of a sucrose solution, how much ATP would be made then during fermentation?arrow_forward
 Microbiology for Surgical Technologists (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781111306663Author:Margaret Rodriguez, Paul PricePublisher:Cengage LearningCase Studies In Health Information ManagementBiologyISBN:9781337676908Author:SCHNERINGPublisher:Cengage
Microbiology for Surgical Technologists (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781111306663Author:Margaret Rodriguez, Paul PricePublisher:Cengage LearningCase Studies In Health Information ManagementBiologyISBN:9781337676908Author:SCHNERINGPublisher:Cengage Comprehensive Medical Assisting: Administrative a...NursingISBN:9781305964792Author:Wilburta Q. Lindh, Carol D. Tamparo, Barbara M. Dahl, Julie Morris, Cindy CorreaPublisher:Cengage LearningEssentials of Pharmacology for Health ProfessionsNursingISBN:9781305441620Author:WOODROWPublisher:Cengage
Comprehensive Medical Assisting: Administrative a...NursingISBN:9781305964792Author:Wilburta Q. Lindh, Carol D. Tamparo, Barbara M. Dahl, Julie Morris, Cindy CorreaPublisher:Cengage LearningEssentials of Pharmacology for Health ProfessionsNursingISBN:9781305441620Author:WOODROWPublisher:Cengage





