
EBK PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEER
9th Edition
ISBN: 8220100581557
Author: Jewett
Publisher: Cengage Learning US
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 37, Problem 37.75CP
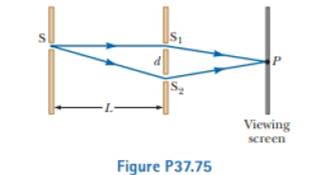
Monochromatic light of wavelength 620 nm passes through a very narrow slit S and then strikes a screen in which are two parallel slits. S1 and S2, as shown in Figure P37.75. Slit S1 is directly in line with S and at a distance of L = 1.20 in away from S, whereas S2, is displaced a distance d to one side. The light is detected at point /Jon a second screen, equidistant from S1 and S2. When either slit S1 or S2 is open, equal light intensities are measured at point P. When both slits are open, the intensity is three times larger. Find the minimum possible value for the slit separation d.
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
No chatgpt pls will upvote
Point charges of 6.50 μC and -2.50 μC are placed 0.300 m apart. (Assume the negative charge is located to the right of the positive charge. Include the sign of the value in your answers.)
(a) Where can a third charge be placed so that the net force on it is zero?
0.49
m to the right of the -2.50 μC charge
(b) What if both charges are positive?
0.49
xm to the right of the 2.50 μC charge
Find the electric field at the location of q, in the figure below, given that q₁ =9c9d = +4.60 nC, q = -1.00 nC, and the square is 20.0 cm on a side. (The +x axis is directed to the right.)
magnitude
direction
2500
x
What symmetries can you take advantage of? What charges are the same magnitude and the same distance away? N/C
226
×
How does charge sign affect the direction of the electric field? counterclockwise from the +x-axis
9a
9b
%
9
9d
Chapter 37 Solutions
EBK PHYSICS FOR SCIENTISTS AND ENGINEER
Ch. 37 - Which of the following causes the fringes in a...Ch. 37 - Using Figure 36.6 as a model, sketch the...Ch. 37 - One microscope slide is placed on top of another...Ch. 37 - While using a Michelson interferometer (shown in...Ch. 37 - Four trials of Young's double-slit experiment are...Ch. 37 - Suppose Youngs double-slit experiment is performed...Ch. 37 - Green light has a wavelength of 500 nm in air. (i)...Ch. 37 - A thin layer of oil (n = 1.25) is floating on...Ch. 37 - A monochromatic beam of light of wavelength .500...Ch. 37 - According to Table 35.1, the index of refraction...
Ch. 37 - Suppose you perform Youngs double-slit experiment...Ch. 37 - A plane monochromatic light wave is incident on a...Ch. 37 - A film of' oil on a puddle in a parking lot shows...Ch. 37 - Prob. 37.1CQCh. 37 - Prob. 37.2CQCh. 37 - Explain why two flashlights held close together do...Ch. 37 - A lens with outer radius of curvature R and index...Ch. 37 - Consider a dark fringe in a double-slit...Ch. 37 - Prob. 37.6CQCh. 37 - What is the necessary condition on the path length...Ch. 37 - In a laboratory accident, you spill two liquids...Ch. 37 - A theatrical smoke machine fills the space bet...Ch. 37 - Two slits are separated by 0.320 mm. A beam of...Ch. 37 - Light of wavelength 530 nm illuminates a pair of...Ch. 37 - A laser beam is incident on two slits with a...Ch. 37 - A Youngs interference experiment is performed with...Ch. 37 - Youngs double-slit experiment is performed with...Ch. 37 - Why is the following situation impossible? Two...Ch. 37 - Light of wavelength 620 nm falls on a double slit,...Ch. 37 - In a Youngs double-slit experiment, two parallel...Ch. 37 - pair of narrow, parallel slits separated by 0.250...Ch. 37 - Light with wavelength 442 nm passes through a...Ch. 37 - The two speakers of a boom box are 35.0 cm apart....Ch. 37 - Prob. 37.12PCh. 37 - Two radio antennas separated by d = 300 in as...Ch. 37 - A riverside warehouse has several small doors...Ch. 37 - A student holds a laser that emits light of...Ch. 37 - A student holds a laser that emits light of...Ch. 37 - Radio waves of wavelength 125 m from a galaxy...Ch. 37 - In Figure P36.10 (not to scale), let L = 1.20 m...Ch. 37 - Coherent light rays of wavelength strike a pair...Ch. 37 - Monochromatic light of wavelength is incident on...Ch. 37 - In the double-slit arrangement of Figure P36.13, d...Ch. 37 - Youngs double-slit experiment underlies the...Ch. 37 - Two slits are separated by 0.180 mm. An...Ch. 37 - Prob. 37.24PCh. 37 - In Figure P37.18, let L = 120 cm and d = 0.250 cm....Ch. 37 - Monochromatic coherent light of amplitude E0 and...Ch. 37 - The intensity on the screen at a certain point in...Ch. 37 - Green light ( = 546 nm) illuminates a pair of...Ch. 37 - Two narrow, parallel slits separated by 0.850 mm...Ch. 37 - A soap bubble (n = 1.33) floating in air has the...Ch. 37 - A thin film of oil (n = 1.25) is located on...Ch. 37 - A material having an index of refraction of 1.30...Ch. 37 - Prob. 37.33PCh. 37 - A film of MgF2 (n = 1.38) having thickness 1.00 ...Ch. 37 - A beam of 580-nm light passes through two closely...Ch. 37 - An oil film (n = 1.45) floating on water is...Ch. 37 - An air wedge is formed between two glass plates...Ch. 37 - Astronomers observe the chromosphere of the Sun...Ch. 37 - When a liquid is introduced into the air space...Ch. 37 - A lens made of glass (ng = 1.52) is coated with a...Ch. 37 - Two glass plates 10.0 cm long are in contact at...Ch. 37 - Mirror M1 in Figure 36.13 is moved through a...Ch. 37 - Prob. 37.43PCh. 37 - One leg of a Michelson interferometer contains an...Ch. 37 - Radio transmitter A operating at 60.0 MHz is 10.0...Ch. 37 - A room is 6.0 m long and 3.0 m wide. At the front...Ch. 37 - In an experiment similar to that of Example 36.1,...Ch. 37 - In the What If? section of Example 36.2, it was...Ch. 37 - An investigator finds a fiber at a crime scene...Ch. 37 - Raise your hand and hold it flat. Think of the...Ch. 37 - Two coherent waves, coming from sources at...Ch. 37 - In a Youngs interference experiment, the two slits...Ch. 37 - In a Youngs double-slit experiment using light of...Ch. 37 - Review. A flat piece of glass is held stationary...Ch. 37 - A certain grade of crude oil has an index of...Ch. 37 - The waves from a radio station can reach a home...Ch. 37 - Interference effects are produced at point P on a...Ch. 37 - Measurements are made of the intensity...Ch. 37 - Many cells are transparent anti colorless....Ch. 37 - Consider the double-slit arrangement shown in...Ch. 37 - Figure P36.35 shows a radio-wave transmitter and a...Ch. 37 - Figure P36.35 shows a radio-wave transmitter and a...Ch. 37 - In a Newtons-rings experiment, a plano-convex...Ch. 37 - Why is the following situation impossible? A piece...Ch. 37 - A plano-concave lens having index of refraction...Ch. 37 - A plano-convex lens has index of refraction n. The...Ch. 37 - Interference fringes are produced using Lloyds...Ch. 37 - Prob. 37.68APCh. 37 - Astronomers observe a 60.0-MHz radio source both...Ch. 37 - Figure CQ37.2 shows an unbroken soap film in a...Ch. 37 - Our discussion of the techniques for determining...Ch. 37 - The condition for constructive interference by...Ch. 37 - Both sides of a uniform film that has index of...Ch. 37 - Prob. 37.74CPCh. 37 - Monochromatic light of wavelength 620 nm passes...Ch. 37 - Prob. 37.76CP
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- would 0.215 be the answer for part b?arrow_forwardSuppose a toy boat moves in a pool at at a speed given by v=1.0 meter per second at t=0, and that the boat is subject to viscous damping. The damping on the boat causes the rate of speed loss to be given by the expression dv/dt=-2v. How fast will the boat be traveling after 1 second? 3 seconds? 10 seconds? Use separation of variables to solve this.arrow_forwardWhat functional form do you expect to describe the motion of a vibrating membrane without damping and why?arrow_forward
- If speed is tripled, how much larger will air drag become for an object? Show the math.arrow_forwardWhat does it tell us about factors on which air drag depends if it is proportional to speed squared?arrow_forwardWhat is the net charge on a sphere that has the following? x (a) 5.75 × 106 electrons and 8.49 × 106 protons 4.39e-13 What is the charge of an electron? What is the charge of a proton? C (b) 200 electrons and 109 protons 1.60e-10 What is the charge of an electron? What is the charge of a proton? Carrow_forward
- A spider begins to spin a web by first hanging from a ceiling by his fine, silk fiber. He has a mass of 0.025 kg and a charge of 3.5 μC. A second spider with a charge of 4.2 μC rests in her own web exactly 2.1 m vertically below the first spider. (a) What is the magnitude of the electric field due to the charge on the second spider at the position of the first spider? 8.57e3 N/C (b) What is the tension in the silk fiber above the first spider? 0.125 How does the electric field relate to the force? How do you calculate the net force? Narrow_forwardPoint charges of 6.50 μC and -2.50 μC are placed 0.300 m apart. (Assume the negative charge is located to the right of the positive charge. Include the sign of the value in your answers.) (a) Where can a third charge be placed so that the net force on it is zero? 0.49 m to the right of the -2.50 μC charge (b) What if both charges are positive? 0.185 xm to the right of the 2.50 μC chargearrow_forwardc = ad Find the electric field at the location of q, in the figure below, given that q₁ = 9₁ = 9₁ = +4.60 nC, q=-1.00 nC, and the square is 20.0 cm on a side. (The +x axis is directed to the right.) magnitude direction N/C ° counterclockwise from the +x-axis 9a % 9 9barrow_forward
- A spider begins to spin a web by first hanging from a ceiling by his fine, silk fiber. He has a mass of 0.025 kg and a charge of 3.5 μC. A second spider with a charge of 4.2 μC rests in her own web exactly 2.1 m vertically below the first spider. (a) What is the magnitude of the electric field due to the charge on the second spider at the position of the first spider? 8.57e3 N/C (b) What is the tension in the silk fiber above the first spider? 0.275 How does the electric field relate to the force? How do you calculate the net force? Narrow_forwardPlastic beads can often carry a small charge and therefore can generate electric fields. Three beads are oriented such that 92 is between 91 system of all three beads is zero. E field lines 91 92 93 X What charge does each bead carry? 91 = 92 = ?2.9 0 μC × What is the net charge of the system? What charges have to be equal? μC 93 2.9 με and 93. The sum of the charge on 91 and 92 is 91 +92 = -2.9 μC, and the net charge of thearrow_forwardAn electron has an initial speed of 5.26 x 100 m/s in a uniform 5.73 x 105 N/C strength electric field. The field accelerates the electron in the direction opposite to its initial velocity. (a) What is the direction of the electric field? opposite direction to the electron's initial velocity same direction as the electron's initial velocity not enough information to decide × What is the direction of the force on the electron? How does it compare to the direction of the electric field, considering the sign of the electron's charge? (b) How far does the electron travel before coming to rest? 0.0781 × What kinematic equation is relevant here? How do you calculate the force due to the electric field? m (c) How long does it take the electron to come to rest? 5.27e8 What is the final velocity of the electron? s (d) What is the electron's speed when it returns to its starting point? 5.26e6 m/sarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax
University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 3
Physics
ISBN:9781938168185
Author:William Moebs, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Spectra Interference: Crash Course Physics #40; Author: CrashCourse;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=-ob7foUzXaY;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY