
Concept explainers
Fill in the blanks in the table below summarizing the interspecific interactions in a community.
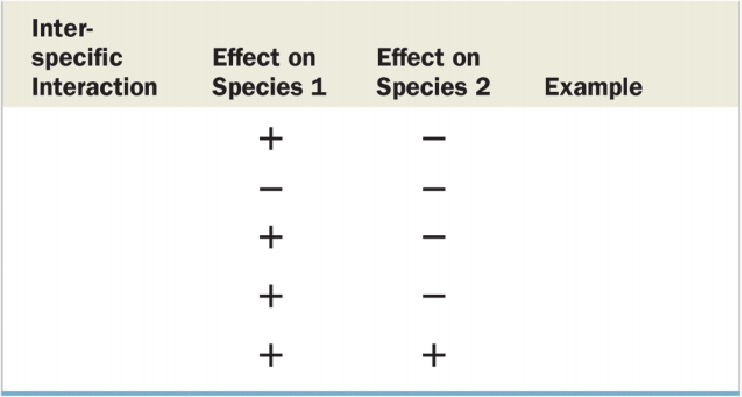
To complete: The blanks summarizing the interspecific interactions in a community.
Introduction: While surviving in an ecosystem, many species interact with each other. These interactions can be mutually beneficial or harmful for one or the other. There are five main types of interspecific interactions, namely, predation, competition, herbivory, parasitism, and mutualism.
Answer to Problem 1CC
Tabular representation: Table 1 represents the interspecific interactions in a community as follows:
| Interspecific interactions | Effect on species 1 | Effect on species 2 | Examples |
| Predation | + | - | Osprey/fish |
| Competition | - | - | Hyenas/vultures |
| Herbivory | + | - | Deer/shrub |
| Parasitism | + | - | Tapeworm/horse |
| Mutualism | + | + | Clown fish/anemone |
Table 1 Depicts the interspecific interactions in a community.
Explanation of Solution
The five types of interspecific interactions are as follows:
Predation: In predative interspecific interactions, one species preys on the other species for food or territory. It is a type of +/- interaction where one species benefits and the other species does not benefit. For example: interaction between a deer and a lion is predation.
Competition: It is the competitive interspecific interaction where two different types of species are competing for the same resource. Neither of them benefits from this, so it is a type of -/- interaction. For example: the interaction between vulture and hyenas.
Herbivory: It is the interaction between the herbivores and the plants. This interaction is a type of +/- interaction where the deer is benefited while the plant is not. For example: an interaction between deer and grass is herbivory.
Parasitism: It is parasitic form of interspecific interaction that involves one organism using the other for food and shelter. One organism such as the tapeworm inhabits the gut or any other part of the other organism such as the horse. This interaction is a +/- interactions, where only one is benefitted.
Mutualism: In this interaction, the organisms that are interacting are mutually beneficial for each other. One species provides one factor, while the other species provides another factor, for example, in the case of mycorrhiza, the fungus is in mutual interaction with the roots of the gymnosperm tree. The fungal element provides minerals and water from the soil, while the tree provides the nutrients. It is a +/+ form of interaction as both the organisms are benefitted.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 37 Solutions
BSC 1005 PKG-W/MOD. MAST. ACCESS >CI<
- 18. Watch this short youtube video about SARS CoV-2 replication. SARS-CoV-2 Life Cycle (Summer 2020) - YouTube.19. What is the name of the receptor that SARS CoV-2 uses to enter cells? Which human cells express this receptor? 20. Name a few of the proteins that the SARS CoV-2 mRNA codes for. 21. What is the role of the golgi apparatus related to SARS CoV-2arrow_forwardState the five functions of Globular Proteins, and give an example of a protein for each function.arrow_forwardDiagram of check cell under low power and high powerarrow_forward
- a couple in which the father has the a blood type and the mother has the o blood type produce an offspring with the o blood type, how does this happen? how could two functionally O parents produce an offspring that has the a blood type?arrow_forwardWhat is the opening indicated by the pointer? (leaf x.s.) stomate guard cell lenticel intercellular space none of thesearrow_forwardIdentify the indicated tissue? (stem x.s.) parenchyma collenchyma sclerenchyma ○ xylem ○ phloem none of thesearrow_forward
- Where did this structure originate from? (Salix branch root) epidermis cortex endodermis pericycle vascular cylinderarrow_forwardIdentify the indicated tissue. (Tilia stem x.s.) parenchyma collenchyma sclerenchyma xylem phloem none of thesearrow_forwardIdentify the indicated structure. (Cucurbita stem l.s.) pit lenticel stomate tendril none of thesearrow_forward
- Identify the specific cell? (Zebrina leaf peel) vessel element sieve element companion cell tracheid guard cell subsidiary cell none of thesearrow_forwardWhat type of cells flank the opening on either side? (leaf x.s.) vessel elements sieve elements companion cells tracheids guard cells none of thesearrow_forwardWhat specific cell is indicated. (Cucurbita stem I.s.) vessel element sieve element O companion cell tracheid guard cell none of thesearrow_forward
 Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning





