
Concept explainers
Fill in the blanks in the table below summarizing the interspecific interactions in a community.
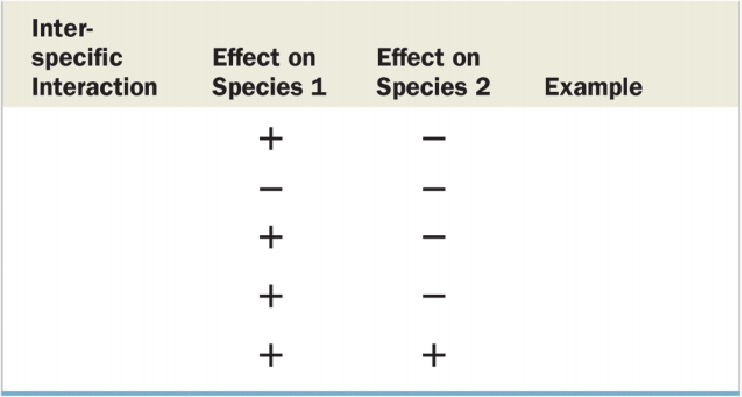
To complete: The blanks summarizing the interspecific interactions in a community.
Introduction: While surviving in an ecosystem, many species interact with each other. These interactions can be mutually beneficial or harmful for one or the other. There are five main types of interspecific interactions, namely, predation, competition, herbivory, parasitism, and mutualism.
Answer to Problem 1CC
Tabular representation: Table 1 represents the interspecific interactions in a community as follows:
| Interspecific interactions | Effect on species 1 | Effect on species 2 | Examples |
| Predation | + | - | Osprey/fish |
| Competition | - | - | Hyenas/vultures |
| Herbivory | + | - | Deer/shrub |
| Parasitism | + | - | Tapeworm/horse |
| Mutualism | + | + | Clown fish/anemone |
Table 1 Depicts the interspecific interactions in a community.
Explanation of Solution
The five types of interspecific interactions are as follows:
Predation: In predative interspecific interactions, one species preys on the other species for food or territory. It is a type of +/- interaction where one species benefits and the other species does not benefit. For example: interaction between a deer and a lion is predation.
Competition: It is the competitive interspecific interaction where two different types of species are competing for the same resource. Neither of them benefits from this, so it is a type of -/- interaction. For example: the interaction between vulture and hyenas.
Herbivory: It is the interaction between the herbivores and the plants. This interaction is a type of +/- interaction where the deer is benefited while the plant is not. For example: an interaction between deer and grass is herbivory.
Parasitism: It is parasitic form of interspecific interaction that involves one organism using the other for food and shelter. One organism such as the tapeworm inhabits the gut or any other part of the other organism such as the horse. This interaction is a +/- interactions, where only one is benefitted.
Mutualism: In this interaction, the organisms that are interacting are mutually beneficial for each other. One species provides one factor, while the other species provides another factor, for example, in the case of mycorrhiza, the fungus is in mutual interaction with the roots of the gymnosperm tree. The fungal element provides minerals and water from the soil, while the tree provides the nutrients. It is a +/+ form of interaction as both the organisms are benefitted.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 37 Solutions
CAMPBELL BIO: CONCEPTS&CONNECTIONS (LL)
- Which of the following best describes why it is difficult to develop antiviral drugs? Explain why. A. antiviral drugs are very difficult to develop andhave no side effects B. viruses are difficult to target because they usethe host cell’s enzymes and ribosomes tometabolize and replicate C. viruses are too small to be targeted by drugs D. viral infections usually clear up on their ownwith no problemsarrow_forwardThis question has 3 parts (A, B, & C), and is under the subject of Nutrition. Thank you!arrow_forwardThey got this question wrong the 2 previous times I uploaded it here, please make sure it's correvct this time.arrow_forward
- This question has multiple parts (A, B & C), and under the subject of Nutrition. Thank you!arrow_forwardCalculate the CFU/ml of a urine sample if 138 E. coli colonies were counted on a Nutrient Agar Plate when0.5 mls were plated on the NA plate from a 10-9 dilution tube. You must highlight and express your answerin scientific notatioarrow_forwardDon't copy off the other answer if there is anyarrow_forward
 Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning





