
To label: The urinary structures given in the figure.
Introduction: The urinary system is the drainage system of the body for removing wastes in the form of urine. For this process, the parts of the urinary system should work together in coordination. The mammalian urinary system includes kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra.
Explanation of Solution
Pictorial representation: The organs of the female urinary system are given in the Fig.1.
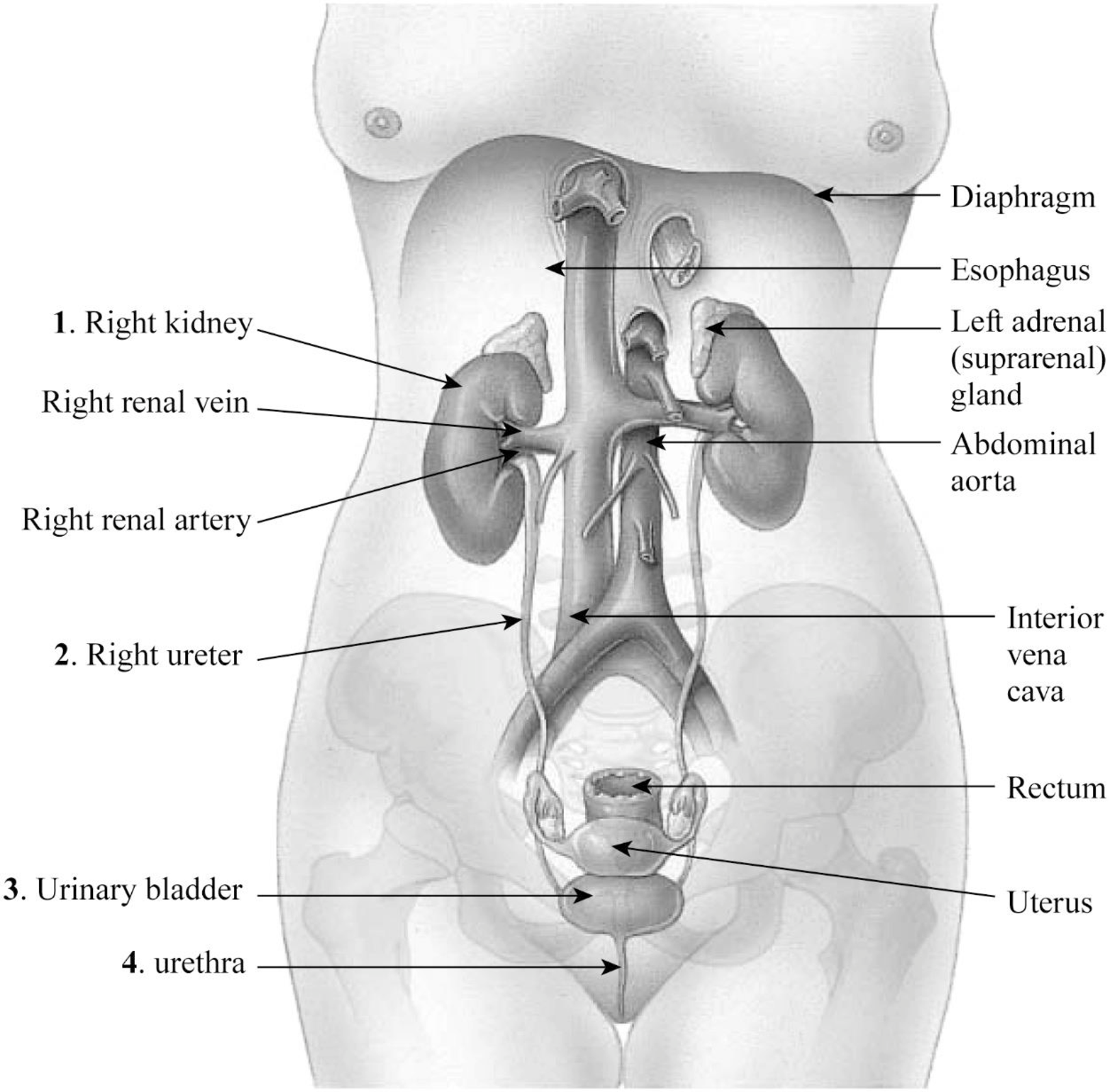
Fig.1: The organs of the female urinary system.
1. Right kidney: The kidney is an important organ of the excretory system. The right kidney is slightly longer than the left kidney.
2. Right ureter: The right ureter is located on the right side of the abdomen and is a long fibromuscular tube that transports urine from the right kidney to the urinary bladder. Urine makes the renal pelvis to contract in rhythm to drive urine through the ureters into the urinary bladder.
3. Urinary bladder: The wall of the urinary bladder has the detrusor muscle; it allows the storage of urine and contraction during urination and release of urine.
4. Urethra: Urethra is a tube that carries urine to the outside of the body. The bladder is joined to the urethra through the bladder neck that consists of internal sphincter muscles.
Pictorial representation: The location and coverings of the kidneys are given in Fig.2.
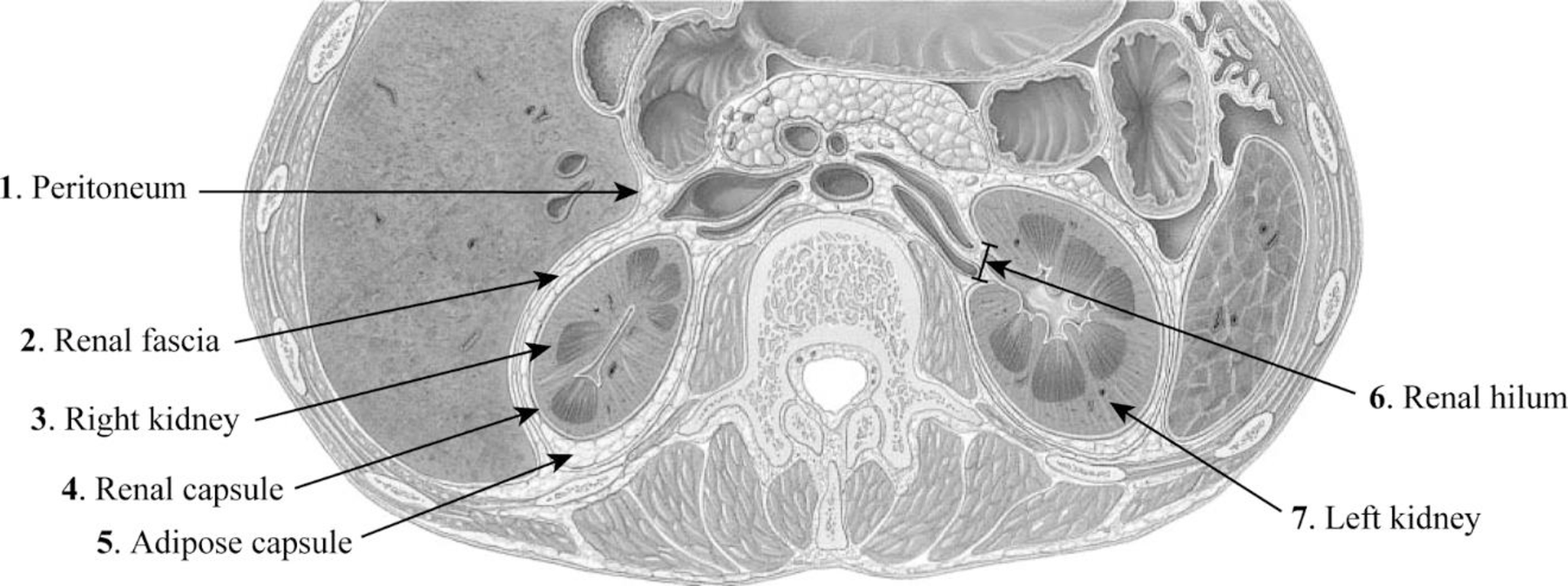
Fig.2: The location and coverings of the kidneys.
1. Peritoneum: The peritoneum is a sheet-like membrane that forms two layers and a space called the peritoneal cavity.
2. Renal fascia: The renal fascia is the layer of irregular connective tissue. This layer covers the adipose capsule and encapsulates the kidney. It passes anteriorly to the kidney, abdominal aorta, and renal vessels and posteriorly connects to the psoas fascia.
3. Right kidney: The right kidney is located on the right side of the abdomen and is connected to the right ureters through which urine reaches the urinary bladder.
4. Renal capsule: The fibrous capsule of the kidney is also known as the renal capsule. It is directly adhered to the external surface of the kidney.
5. Adipose capsule: The adipose capsule is the structure of the kidney that is located between the renal fascia and renal capsule. It is the perirenal fat that covers the renal capsule. This layer provides protection to the kidney from damage.
6. Renal hilum: The renal hilum is a depression in the surface of the kidney where blood vessels and nerves enter and exit.
7. Left kidney: The left kidney is located on the left side of the abdomen and is slightly shorter than the right kidney.
Pictorial representation: The internal structure of the kidney is given in Fig.3.
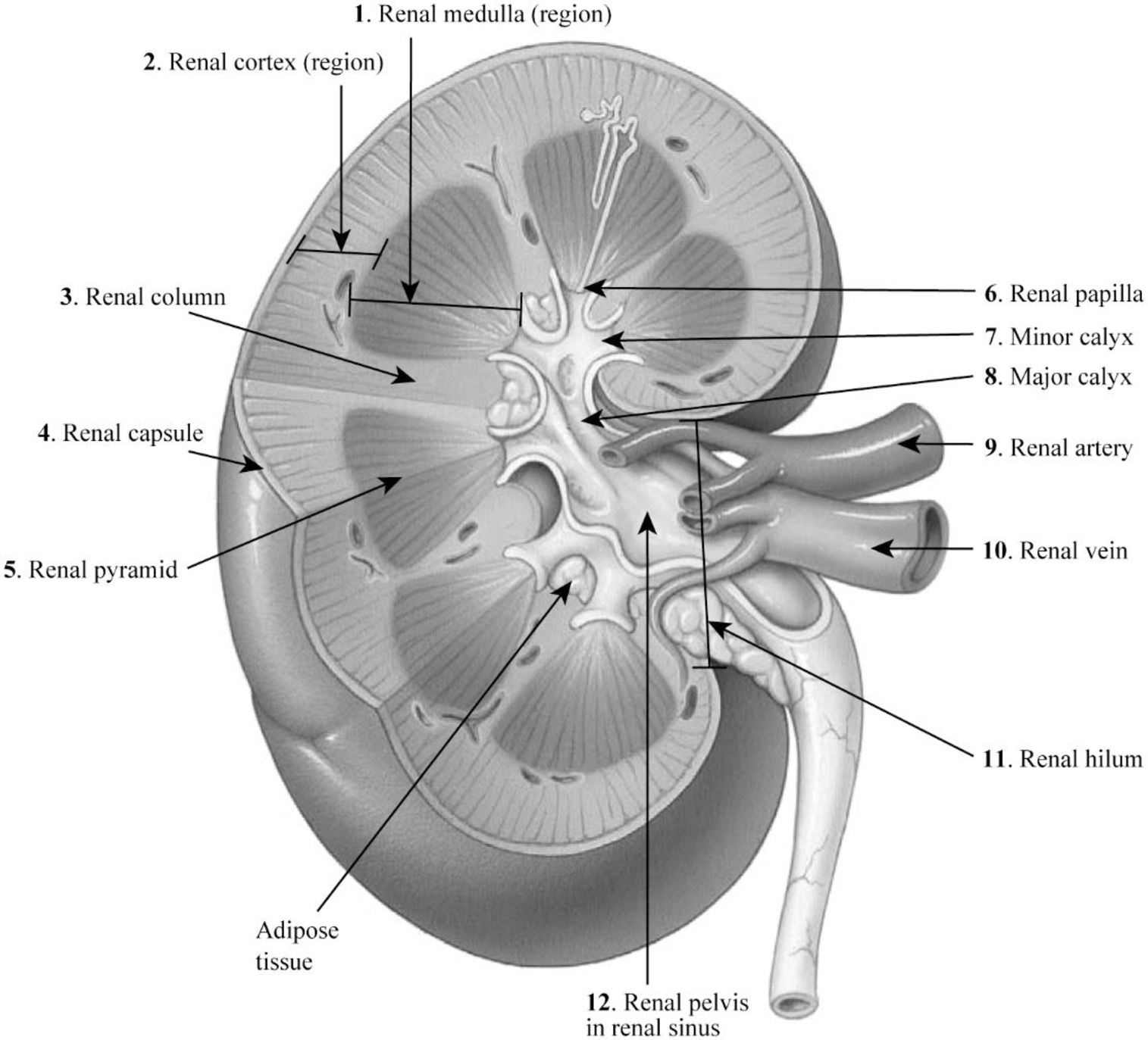
Fig.3: The internal structure of the kidney.
1. Renal medulla: The renal medulla is the deep region to the cortex of the kidney that contains 8–12 renal pyramids consisting of collecting ducts.
2. Renal cortex: The renal cortex is the outer portion of the kidney. It is a smooth outer zone present between the renal capsule and the renal medulla.
3. Renal column: The medullary renal cortex extensions present in between renal pyramids are called the renal column. This allows the renal cortex to be better attached, and each column consists of blood vessel and urinary tube lines.
4. Renal capsule: The renal capsule is composed of dense irregular connective tissue and maintains the kidney’s shape, protects from trauma, and prevents infectious pathogens from penetrating the kidney.
5. Renal pyramid: The renal pyramid is a cone-shaped tissue that consists of various tubules that transport located within the renal medulla. At the renal papilla, the renal pyramids drain urine into the minor calyx in the kidney.
6. Renal papilla: The renal papilla is the peak of the renal pyramid. At the renal papilla, the renal pyramids drain urine into the minor calyx in the kidney.
7. Minor calyx: The renal pelvis connects all the renal tubules and forms a cup-like region called calyces. The minor calyces surround the peak of the renal pyramids.
8. Major calyx: Two to three minor calyces unite to form the major calyx. Urine enters the papillary duct that is located within the renal papilla and then passes through the spaces (minor calyx, major calyx, and renal pelvis) within the renal sinus of the kidney.
9. Renal artery: The renal arteries carry a very large amount of blood from the heart to the kidneys for the process of filtration.
10. Renal vein: A large amount of blood enters the kidneys at the hilum through the renal artery and leaves the kidneys through the renal vein.
11. Renal hilum: A large amount of blood enters the kidneys at the hilum through the renal artery and leaves the kidneys through the renal vein.
12. Renal pelvis in renal sinus: The renal pelvis in the renal sinus connects all the renal tubules and forms a cup-like region called calyces. The minor calyces surround the peak of the renal pyramids. At the renal papilla, the renal pyramids drain urine into the minor calyx in the kidney.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 36 Solutions
Laboratory Manual for Anatomy and Physiology, 6e WileyPLUS (next generation) + Loose-leaf
- , if one of the archaeological specimens lacked the celiac disease-causing epitope, how could PCR be used to identify the allele in a contemporary germplasm collection of wild wheats, and to assist in transferring the allele to modern wheat varieties?arrow_forwardNow you will consider the composition of lipoproteins, including where they are synthesized, how they circulate, and where the various lipid and protein components are located within the lipoprotein molecule. Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets.arrow_forwardThe Oregon Wolfe Barley mapping population is unique in having 12 easily-scored morphological markers, each showing monogenic inheritance. Do you consider these markers useful? Briefly defend your answer, pointing out advantages and disadvantages of morphological vs. molecular markers.arrow_forward
- Biopharmaceutics and Pharmacokinetics:Two-Compartment Model Instant Absorption Questions Calculate these : a) B1, b) B2, c) hybrid rate constant (1) d) hybrid rate constant (2) e) t1/2,dist f) t1/2,elim g) k10 h) k12 i) k21 j) initial concentration (C0) k) central compartment volume (V1) l) steady-state volume (Vss) m) clearance (CL) AUC (0→10 min) using trapezoidal rule n) AUC (20→30 min) using trapezoidal rule o) AUCtail (AUC360→∞) p) total AUC (using short cut method) q) volume from AUC (VAUC)arrow_forwardIn a population of Jackalopes (pictured below), horn length will vary between 0.5 and 2 feet, with the mean length somewhere around 1.05 feet. You pick Jackalopes that have horn lengths around 1.75 feet to breed as this appears to be the optimal length for battling other Jackalopes for food. After a round of breeding, you measure the offsprings' mean horn length is 1.67. What is the heritability of horns length (h2)? Is Jackalope horn length a heritable trait? (4 pts)? 12pt v R Paragraph V BIU A श्र > Barrow_forwardThere are many differences between DNA replication happening during mitosis in a Douglas fir tree growing in the Oregon Cascade Mountains and DNA replication happening during a PCR reaction in a forestry research lab at Oregon State University where the laboratory is amplifying a Simple Sequence Repeat. Complete the following table that compares the two DNA replication events in terms of the primers, the nucleotides, the polymerase, and the target sequence. Additionally, give a general value for the number of copies of the template DNA after one S phase in one cell and after the lab has completed the PCR reaction. Tree SSR Type your answer here: Primers Nucleotides Polymerase Target sequence Number of copiesarrow_forward
- Describe how insulin binding to its receptor induces glucose uptake in healthy individuals. Please specifyeach step in the cascade and use a diagram to illustrate the answer.arrow_forwardThere is a patient with breast cancer, after staining the breast tissue with H&E, state the molecular subtype of the tumour extracted. Results of H&E staining are down belowarrow_forwardBiopharmaceutics and Pharmacokinetics:Two-Compartment Model Instant Absorption Questions Calculate these : a) B1, b) B2, c) hybrid rate constant (1) d) hybrid rate constant (2) e) t1/2,dist f) t1/2,elim g) k10 h) k12 i) k21 j) initial concentration (C0) k) central compartment volume (V1) l) steady-state volume (Vss) m) clearance (CL) AUC (0→10 min) using trapezoidal rule n) AUC (20→30 min) using trapezoidal rule o) AUCtail (AUC360→∞) p) total AUC (using short cut method) q) volume from AUC (VAUC)arrow_forward
- Use the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation for a propanoic acid solution (CH₂CH₂CO₂H, pK₁ = 4.874) to calculate the quotient [A-]/[HA] at three different pH values. pH = 4.479 [A-] [HA] [A-] pH = 4.874 [HA] = pH = 5.220 [A-] = [HA]arrow_forwardIn order to establish the expiration date of perishable food, growth curve data must be collected. Once the microbial load is so high that it poses a hazard to human health, the food item is no longer considered safe (expired). Generally a load of x50,000 bacteria/gram is considered unsafe. Your task is to determine the microbial growth curves for MicroYo, a new brand of yogurt. The growth is determined by sampling the yogurt and growing the bacterial isolates in broth culture which is then serially diluted by a total of x10,000 and inoculated onto standard petri plates of nutrient agar. The following colony counts are measured: Time (days) MicroYo colony count# 1 1 4 1 12 2 16 20 4 7 What day should you recommend expiring the yogurt (the last possible date before the microbial load is unsafe). 12 4 20 16arrow_forward9. Chicken combs in chickens is an example where you see interactions between genes. See potential genotypes and phenotypes below. Which genotype, when mated to a rose comb chicken, will produce progeny that are 50% walnut comb and 50% pea comb? walnut (RRPP) walnut (RrPP) pea (rrPP) walnut (RRPP) walnut (RrPp) pea (rrPp) rose rose single (RRPP) (Rrpp) (rrpp)arrow_forward
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education





