
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Volume 2
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781337553582
Author: Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 35, Problem 20P
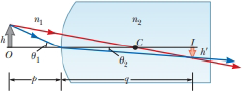
Figure P35.20 (page 958) shows a curved surface separating a material with index of refraction n1 from a material with index n2. The surface forms an image I of object O. The ray shown in red passes through the surface along a radial line. Its angles of incidence and refraction are both zero, so its direction does not change at the surface. For the ray shown in blue, the direction changes according to Snell’s law, n1 sin θ1 = n2 sin θ2. For paraxial rays, we assume θ1, and θ2 are small, so we may write n1 tan θ1 = n2 tan θ2. The magnification is defined as M = h′/h. Prove that the magnification is given by M = −n1q/n2p.
Figure P35.20
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
Make sure to draw a Free Body Diagram as well
Make sure to draw a Free Body Diagram as well
Make sure to draw a Free Body Diagram please as well
Chapter 35 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Volume 2
Ch. 35.1 - You are standing approximately 2 m away from a...Ch. 35.2 - You wish to start a fire by reflecting sunlight...Ch. 35.2 - Consider the image in the mirror in Figure 35.14....Ch. 35.3 - Prob. 35.4QQCh. 35.3 - Prob. 35.5QQCh. 35.4 - What is the focal length of a pane of window...Ch. 35.6 - Two campers wish to start a fire during the day....Ch. 35 - (a) Does your bathroom mirror show you older or...Ch. 35 - Two flat mirrors have their reflecting surfaces...Ch. 35 - A periscope (Fig. P35.3) is useful for viewing...
Ch. 35 - Two plane mirrors stand facing each other, 3.00 m...Ch. 35 - An object is placed 50.0 cm from a concave...Ch. 35 - An object is placed 20.0 cm from a concave...Ch. 35 - An object of height 2.00 cm is placed 30.0 cm from...Ch. 35 - Why is the following situation impossible? At a...Ch. 35 - A large hall in a museum has a niche in one wall....Ch. 35 - A concave spherical mirror has a radius of...Ch. 35 - An object 10.0 cm tall is placed at the zero mark...Ch. 35 - You are training to become an opticians assistant....Ch. 35 - A certain Christmas tree ornament is a silver...Ch. 35 - Review. A ball is dropped at t = 0 from rest 3.00...Ch. 35 - You unconsciously estimate the distance to an...Ch. 35 - A convex spherical mirror has a focal length of...Ch. 35 - One end of a long glass rod (n = 1.50) is formed...Ch. 35 - Prob. 18PCh. 35 - Prob. 19PCh. 35 - Figure P35.20 (page 958) shows a curved surface...Ch. 35 - To dress up your dorm room, you have purchased a...Ch. 35 - You are working for a solar energy company. Your...Ch. 35 - An object located 32.0 cm in front of a lens forms...Ch. 35 - An objects distance from a converging lens is 5.00...Ch. 35 - A contact lens is made of plastic with an index of...Ch. 35 - A converging lens has a focal length of 10.0 cm....Ch. 35 - A converging lens has a focal length of 10.0 cm....Ch. 35 - Suppose an object has thickness dp so that it...Ch. 35 - An object is placed 10.0 cm from a diverging lens...Ch. 35 - In Figure P35.30, a thin converging lens of focal...Ch. 35 - You are working for an electronics company that...Ch. 35 - Prob. 32PCh. 35 - Two rays traveling parallel to the principal axis...Ch. 35 - Josh cannot see objects clearly beyond 25.0 cm...Ch. 35 - Figure 35.34 diagrams a cross section of a camera....Ch. 35 - The refracting telescope at the Yerkes Observatory...Ch. 35 - The distance between the eyepiece and the...Ch. 35 - What are (a) the maximum angular magnification...Ch. 35 - A patient has a near point of 45.0 cm and far...Ch. 35 - The intensity I of the light reaching the CCD in a...Ch. 35 - A certain childs near point is 10.0 cm; her far...Ch. 35 - Astronomers often take photographs with the...Ch. 35 - A simple model of the human eye ignores its lens...Ch. 35 - A real object is located at the zero end of a...Ch. 35 - The distance between an object and its upright...Ch. 35 - Prob. 46APCh. 35 - Andy decides to use an old pair of eyeglasses to...Ch. 35 - Two converging lenses having focal lengths of f1 =...Ch. 35 - Two lenses made of kinds of glass having different...Ch. 35 - Prob. 50APCh. 35 - An object is placed 12.0 cm to the left of a...Ch. 35 - An object is placed a distance p to the left of a...Ch. 35 - In a darkened room, a burning candle is placed...Ch. 35 - In many applications, it is necessary to expand or...Ch. 35 - Why is the following situation impossible?...Ch. 35 - A zoom lens system is a combination of lenses that...Ch. 35 - Consider the lensmirror arrangement shown in...Ch. 35 - A floating strawberry illusion is achieved with...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- please answer this asap!!!!arrow_forwardRT = 4.7E-30 18V IT = 2.3E-3A+ 12 38Ω ли 56Ω ли r5 27Ω ли r3 28Ω r4 > 75Ω r6 600 0.343V 75.8A Now figure out how much current in going through the r4 resistor. |4 = unit And then use that current to find the voltage drop across the r resistor. V4 = unitarrow_forward7 Find the volume inside the cone z² = x²+y², above the (x, y) plane, and between the spheres x²+y²+z² = 1 and x² + y²+z² = 4. Hint: use spherical polar coordinates.arrow_forward
- ганм Two long, straight wires are oriented perpendicular to the page, as shown in the figure(Figure 1). The current in one wire is I₁ = 3.0 A, pointing into the page, and the current in the other wire is 12 4.0 A, pointing out of the page. = Find the magnitude and direction of the net magnetic field at point P. Express your answer using two significant figures. VO ΜΕ ΑΣΦ ? Figure P 5.0 cm 5.0 cm ₁ = 3.0 A 12 = 4.0 A B: μΤ You have already submitted this answer. Enter a new answer. No credit lost. Try again. Submit Previous Answers Request Answer 1 of 1 Part B X Express your answer using two significant figures. ΜΕ ΑΣΦ 0 = 0 ? below the dashed line to the right P You have already submitted this answer. Enter a new answer. No credit lost. Try again.arrow_forwardAn infinitely long conducting cylindrical rod with a positive charge λ per unit length is surrounded by a conducting cylindrical shell (which is also infinitely long) with a charge per unit length of −2λ and radius r1, as shown in the figure. What is σinner, the surface charge density (charge per unit area) on the inner surface of the conducting shell? What is σouter, the surface charge density on the outside of the conducting shell? (Recall from the problem statement that the conducting shell has a total charge per unit length given by −2λ.)arrow_forwardA small conducting spherical shell with inner radius aa and outer radius b is concentric with a larger conducting spherical shell with inner radius c and outer radius d (Figure 1). The inner shell has total charge +2q, and the outer shell has charge −2q. What's the total charge on the inner surface of the small shell? What's the total charge on the outer surface of the small shell? What's the total charge on the inner surface of the large shell? What's the total charge on the outer surface of the large shell?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Convex and Concave Lenses; Author: Manocha Academy;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=CJ6aB5ULqa0;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY