
Concept explainers
To complete: The given map that reviews the genetic and environmental components of animal behavior and their relationship to learning.
Introduction:
The action of behavior is carried by the muscles that are in control of the nervous system in response to environmental stimulus. Thus, the behavior of animal is the response from internal and external environmental stimulus.
Explanation of Solution
Pictorial representation:
Fig.1 shows the completed map that reviews the genetic and environmental components of animal behavior and their relationship to learning.
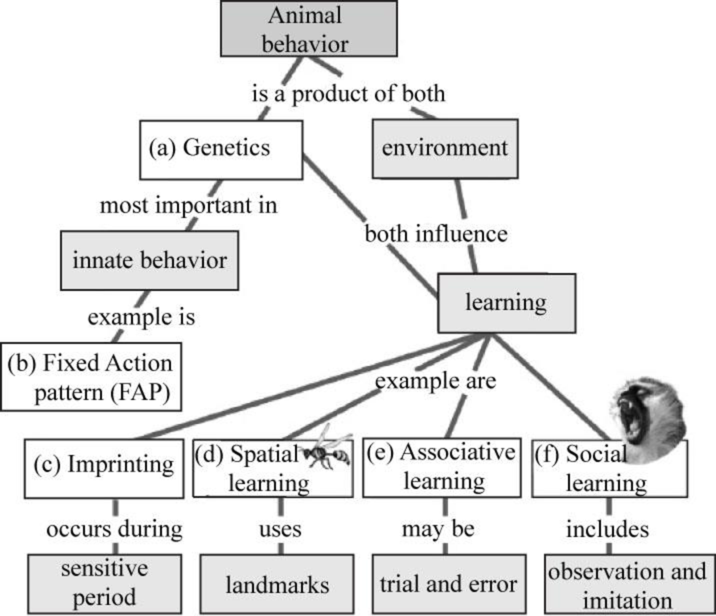
Fig.1: Components animal behavior and their relationship to learning.
(a)
Correct answer: Genetics.
The animal behavior is a combined effect of genetics and environment and both influence the learning in animals. However, genetics is the main cause of innate behaviors. Hence, the correct answer is genetics.
(b)
Correct answer: Fixed Action pattern (FAP).
FAP is an unchangeable series of action caused by a particular stimulus. Hence, the correct answer is FAP.
(c)
Correct answer: Imprinting.
Imprinting is the sensitive phase that occurs after the hatching of the young ones. The first person that the young ones see will imprint with them like the hatched newborns see their mother; so, they follow her in a straight line whenever she goes for a walk. Hence, the correct answer is imprinting.
(d)
Correct answer: Spatial learning.
Spatial learning is the memories of landmarks created by animals with in their environment. The landmarks include trees, water, and mountains to find their way to home. It helps them to find a mate, food, nest, and possible dangers. The landmarks include trees, water, and mountains to find their way to home. Hence, the correct answer is spatial learning
(e)
Correct answer: Associative learning.
Associative learning is the association of result with a particular action by animals like while training a dog an individual feeds them with treats on performing well in training so they associate the food with the behavior while they learn. Hence, the correct answer is associative learning.
(f)
Correct answer: Social learning.
Social learning is the learning from other’s behavior by just watching or observing them. In an experiment, many octopus were put through the maze, while one is going in the maze, the others were tend to watch and the next time when they perform, they remember the path and finish it within less time. This concludes that the animals watch and learn from other’s behavior for a particular situation. Hence, the correct answer is social learning.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 35 Solutions
CAMPBEL BIOLOGY:CONCEPTS & CONNECTIONS
- What is the structure and function of Eukaryotic cells, including their organelles? How are Eukaryotic cells different than Prokaryotic cells, in terms of evolution which form of the cell might have came first? How do Eukaryotic cells become malignant (cancerous)?arrow_forwardWhat are the roles of DNA and proteins inside of the cell? What are the building blocks or molecular components of the DNA and proteins? How are proteins produced within the cell? What connection is there between DNA, proteins, and the cell cycle? What is the relationship between DNA, proteins, and Cancer?arrow_forwardWhy cells go through various types of cell division and how eukaryotic cells control cell growth through the cell cycle control system?arrow_forward
- In one paragraph show how atoms and they're structure are related to the structure of dna and proteins. Talk about what atoms are. what they're made of, why chemical bonding is important to DNA?arrow_forwardWhat are the structure and properties of atoms and chemical bonds (especially how they relate to DNA and proteins).arrow_forwardThe Sentinel Cell: Nature’s Answer to Cancer?arrow_forward
- Molecular Biology Question You are working to characterize a novel protein in mice. Analysis shows that high levels of the primary transcript that codes for this protein are found in tissue from the brain, muscle, liver, and pancreas. However, an antibody that recognizes the C-terminal portion of the protein indicates that the protein is present in brain, muscle, and liver, but not in the pancreas. What is the most likely explanation for this result?arrow_forwardMolecular Biology Explain/discuss how “slow stop” and “quick/fast stop” mutants wereused to identify different protein involved in DNA replication in E. coli.arrow_forwardMolecular Biology Question A gene that codes for a protein was removed from a eukaryotic cell and inserted into a prokaryotic cell. Although the gene was successfully transcribed and translated, it produced a different protein than it produced in the eukaryotic cell. What is the most likely explanation?arrow_forward
 Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Comprehensive Medical Assisting: Administrative a...NursingISBN:9781305964792Author:Wilburta Q. Lindh, Carol D. Tamparo, Barbara M. Dahl, Julie Morris, Cindy CorreaPublisher:Cengage Learning
Comprehensive Medical Assisting: Administrative a...NursingISBN:9781305964792Author:Wilburta Q. Lindh, Carol D. Tamparo, Barbara M. Dahl, Julie Morris, Cindy CorreaPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning





