
Mathematical Ideas (13th Edition) - Standalone book
13th Edition
ISBN: 9780321977076
Author: Charles D. Miller, Vern E. Heeren, John Hornsby, Christopher Heeren
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 3.5, Problem 15E
Construct a valid argument based on the Euler diagram shown.
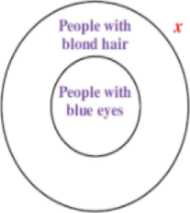
x represents Erin.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
https://www.hawkeslearning.com/Statistics/dbs2/datasets.html
Determine whether each function is an injection and determine whether each is a surjection.The notation Z_(n) refers to the set {0,1,2,...,n-1}. For example, Z_(4)={0,1,2,3}. f: Z_(6) -> Z_(6) defined by f(x)=x^(2)+4(mod6). g: Z_(5) -> Z_(5) defined by g(x)=x^(2)-11(mod5). h: Z*Z -> Z defined by h(x,y)=x+2y. j: R-{3} -> R defined by j(x)=(4x)/(x-3).
Determine whether each function is an injection and determine whether each is a surjection.
Chapter 3 Solutions
Mathematical Ideas (13th Edition) - Standalone book
Ch. 3.1 - Decide whether each is a statement or is not a...Ch. 3.1 - The ZIP code for Oscar, Louisiana, is 70762.Ch. 3.1 - 3. Listen, my children, and you shall hear of the...Ch. 3.1 - 4.Did you yield to oncoming traffic?Ch. 3.1 - 5.
Ch. 3.1 - 6.
Ch. 3.1 - 7 Some numbers are positive.
Ch. 3.1 - |8. Grover Cleveland was president of the United...Ch. 3.1 - Accidents are the main cause of deaths of children...Ch. 3.1 - 10 It is projected that in the United States...
Ch. 3.1 - Where are you going tomorrow?Ch. 3.1 - Behave yourself and sit down.Ch. 3.1 - Kevin Catfish" McCarthy once took a prolonged...Ch. 3.1 - 14 One gallon of milk weighs more than 3 pounds.
Ch. 3.1 - Decide whether each statement is compound. I read...Ch. 3.1 - My brother got married in Copenhagen.Ch. 3.1 - 17. Tomorrow is Saturday.
Ch. 3.1 - Jing is younger than 18 years of age, and so is...Ch. 3.1 - Prob. 19ECh. 3.1 - 20. The sign on the back of the car read "Canada...Ch. 3.1 - 21 If Lorri sells her quota, then Michelle will be...Ch. 3.1 - If Bobby is a politician, then Mitch is a crook.Ch. 3.1 - Write a negation for each statement.
23. Her...Ch. 3.1 - 24. No rain fell in southern California today.
Ch. 3.1 - Some books are longer than this book.Ch. 3.1 - 26. All students present will get another chance.
Ch. 3.1 - 27. No computer repairman can play blackjack.
Ch. 3.1 - 28. Some people have all the luck.
Ch. 3.1 - Everybody loves somebody sometime.Ch. 3.1 - Prob. 30ECh. 3.1 - The trash needs to be collectedCh. 3.1 - Prob. 32ECh. 3.1 - Give a negation of each inequality. Do not use a...Ch. 3.1 - Prob. 34ECh. 3.1 - 35.
Ch. 3.1 - Prob. 36ECh. 3.1 - Try to negate the sentence The exact number of...Ch. 3.1 - Prob. 38ECh. 3.1 - Let p represent the statement 'She has green eyes...Ch. 3.1 - 40.
Ch. 3.1 - Prob. 41ECh. 3.1 - 42.
Ch. 3.1 - pqCh. 3.1 - 44.
Ch. 3.1 - pqCh. 3.1 - pqCh. 3.1 - (pq)Ch. 3.1 - 48.
Ch. 3.1 - Tyler collects DVDs and Josh is not an art major.Ch. 3.1 - Tyler does not collect DVDs or Josh is not an art...Ch. 3.1 - Tyler does not collect DVDs or Josh is an art...Ch. 3.1 - Josh is an art major and Tyler does not collect...Ch. 3.1 - 53. Neither Tyler collects DVDs nor Josh is an art...Ch. 3.1 - 54. Either Josh is an art major or Tyler collects...Ch. 3.1 - Incorrect use of quantifiers often is heard in...Ch. 3.1 - Prob. 56ECh. 3.1 - Refer to the groups of art labeled A. B. and C,...Ch. 3.1 - 58. No picture has a frame.
Ch. 3.1 - 59. At least one picture does not have a frame
Ch. 3.1 - Not every picture has a frame.Ch. 3.1 - 61. At least one picture has a frame.
Ch. 3.1 - 62. No picture does not have a frame.
Ch. 3.1 - All pictures do not have frames.Ch. 3.1 - Not every picture does not have a frameCh. 3.1 - 65. Every whole number is an integer.
Ch. 3.1 - 66. Every integer is a whole number.
Ch. 3.1 - There exists a natural number that is not an...Ch. 3.1 - 68. There exists an integer that is not a natural...Ch. 3.1 - 69. All rational numbers are real numbers.
Ch. 3.1 - Prob. 70ECh. 3.1 - Some rational numbers are not integers.Ch. 3.1 - Some whole numbers are not rational numbers.Ch. 3.1 - 73. Each whole number is a positive number.
Ch. 3.1 - Each rational number is a positive number.Ch. 3.1 - 75. Explain the difference between the statements...Ch. 3.1 - Prob. 76ECh. 3.1 - 77. Write the following statement using “every”:...Ch. 3.1 - Prob. 78ECh. 3.1 - Refer to Example 5. If we let c represent cat and...Ch. 3.1 - 80. Use symbols to express the statements for...Ch. 3.2 - 1. If q is false, what must be the truth value of...Ch. 3.2 - If q is true, what must be the truth value of the...Ch. 3.2 - If the statement pq is true, and p is true, then q...Ch. 3.2 - If the statement pq is false, and p is false, then...Ch. 3.2 - 5. If is true, what must be the truth value of...Ch. 3.2 - If p(qr) is true, what must be the truth value of...Ch. 3.2 - If (pq) is true, what must be the truth values of...Ch. 3.2 - If (pq) is false, what must be the truth values of...Ch. 3.2 - pCh. 3.2 - qCh. 3.2 - 11.
Ch. 3.2 - 12.
Ch. 3.2 - 13.
Ch. 3.2 - 14.
Ch. 3.2 - pqCh. 3.2 - pqCh. 3.2 - 17.
Ch. 3.2 - 18.
Ch. 3.2 - [p(p)]Ch. 3.2 - [(pq)q]Ch. 3.2 - 21. Is the statement a conjunction or a...Ch. 3.2 - Prob. 22ECh. 3.2 - Let p represent a true statement, and let q and r...Ch. 3.2 - 24.
Ch. 3.2 - p(qr)Ch. 3.2 - 26
Ch. 3.2 - (pq)(rq)Ch. 3.2 - (rq)(rq)Ch. 3.2 - 29.
Ch. 3.2 - [r(qp)]Ch. 3.2 - [q(rp)]Ch. 3.2 - 32.
Ch. 3.2 - Let p represent the statement 168. let q represent...Ch. 3.2 - Prob. 34ECh. 3.2 - qrCh. 3.2 - Prob. 36ECh. 3.2 - (pq)rCh. 3.2 - Prob. 38ECh. 3.2 - (rq)pCh. 3.2 - Prob. 40ECh. 3.2 - Give the number of rows in the truth table for...Ch. 3.2 - Prob. 42ECh. 3.2 - 43.
Ch. 3.2 - 44.
Ch. 3.2 - 45.
Ch. 3.2 - [(pq)(rs)][(mn)(uv)]Ch. 3.2 - 47 If the truth table for a certain compound...Ch. 3.2 - Is it possible for the truth table of a compound...Ch. 3.2 - Construct a truth table for each compound...Ch. 3.2 - pqCh. 3.2 - 51.
Ch. 3.2 - pqCh. 3.2 - (qp)qCh. 3.2 - 54.
Ch. 3.2 - 55.
Ch. 3.2 - (pq)(pq)Ch. 3.2 - (pq)rCh. 3.2 - r(pq)Ch. 3.2 - 59.
Ch. 3.2 - (rp)(pq)Ch. 3.2 - Construct a truth table for each compound...Ch. 3.2 - (rs)(pq)Ch. 3.2 - Use one of De Morgan’s laws to write the negation...Ch. 3.2 - I am not going or she is going.Ch. 3.2 - It is summer and there is no snow.Ch. 3.2 - Prob. 66ECh. 3.2 - I said yes but she said noCh. 3.2 - Prob. 68ECh. 3.2 - Prob. 69ECh. 3.2 - 810or52Ch. 3.2 - Prob. 71ECh. 3.2 - 72. The lawyer and the client appeared in court.
Ch. 3.2 - Prob. 73ECh. 3.2 - Prob. 74ECh. 3.2 - There exists an integer n such that n0andn0 ..Ch. 3.2 - 76. For some integer .
Ch. 3.2 - Complete the truth table for exclusive disjunction...Ch. 3.2 - Prob. 78ECh. 3.2 - Prob. 79ECh. 3.2 - Prob. 80ECh. 3.2 - Prob. 81ECh. 3.2 - Prob. 82ECh. 3.2 - Prob. 83ECh. 3.2 - Prob. 84ECh. 3.2 - 85 De Morgan's law
can be stated verbally, "The...Ch. 3.3 - Rewrite each statement using the if . . . then...Ch. 3.3 - Rewrite each statement using the if then...Ch. 3.3 - Rewrite each statement using the if . . . then...Ch. 3.3 - No perfect square integers have units digit 2, 3,...Ch. 3.3 - Prob. 5ECh. 3.3 - Rewrite each statement using the if then...Ch. 3.3 - Prob. 7ECh. 3.3 - Rewrite each statement using the if then...Ch. 3.3 - Prob. 9ECh. 3.3 - Decide whether each statement is true or...Ch. 3.3 - Prob. 11ECh. 3.3 - Prob. 12ECh. 3.3 - Decide whether each statement is true or...Ch. 3.3 - Prob. 14ECh. 3.3 - Prob. 15ECh. 3.3 - Prob. 16ECh. 3.3 - |17. Explain why the statement “If , then ” is...Ch. 3.3 - Prob. 18ECh. 3.3 - Prob. 19ECh. 3.3 - Prob. 20ECh. 3.3 - Prob. 21ECh. 3.3 - Prob. 22ECh. 3.3 - Prob. 23ECh. 3.3 - Prob. 24ECh. 3.3 - Let s represent “She sings for a living,” let p...Ch. 3.3 - Let s represent She sings for a living, let p...Ch. 3.3 - Prob. 27ECh. 3.3 - Let s represent She sings for a living, let p...Ch. 3.3 - Prob. 29ECh. 3.3 - Let s represent “She sings for a living,” let p...Ch. 3.3 - Prob. 31ECh. 3.3 - Let b represent I take my ball, lets represent it...Ch. 3.3 - Prob. 33ECh. 3.3 - Let b represent I take my ball, lets represent it...Ch. 3.3 - Prob. 35ECh. 3.3 - Let b represent I take my ball, lets represent it...Ch. 3.3 - Prob. 37ECh. 3.3 - Find the truth value of each statement. Assume...Ch. 3.3 - Prob. 39ECh. 3.3 - Find the truth value of each statement. Assume...Ch. 3.3 - Prob. 41ECh. 3.3 - Find the truth value of each statement. Assume...Ch. 3.3 - Prob. 43ECh. 3.3 - Find the truth value of each statement. Assume...Ch. 3.3 - Prob. 45ECh. 3.3 - Find the truth value of each statement. Assume...Ch. 3.3 - Prob. 47ECh. 3.3 - Prob. 48ECh. 3.3 - Prob. 49ECh. 3.3 - Construct a truth table for each statement....Ch. 3.3 - Prob. 51ECh. 3.3 - Construct a truth table for each statement....Ch. 3.3 - Prob. 53ECh. 3.3 - Construct a truth table for each statement....Ch. 3.3 - Construct a truth table /breach statement....Ch. 3.3 - Construct a truth table /breach statement....Ch. 3.3 - Prob. 57ECh. 3.3 - Construct a truth table /breach statement....Ch. 3.3 - 59. What is the minimum number of Fs that must...Ch. 3.3 - Prob. 60ECh. 3.3 - Prob. 61ECh. 3.3 - Write the negation of each statement. Remember...Ch. 3.3 - Prob. 63ECh. 3.3 - Write the negation of each statement. Remember...Ch. 3.3 - Prob. 65ECh. 3.3 - Write the negation of each statement. Remember...Ch. 3.3 - Write each statement as an equivalent statement...Ch. 3.3 - Prob. 68ECh. 3.3 - Prob. 69ECh. 3.3 - Prob. 70ECh. 3.3 - Prob. 71ECh. 3.3 - Prob. 72ECh. 3.3 - Prob. 73ECh. 3.3 - Prob. 74ECh. 3.3 - Prob. 75ECh. 3.3 - Prob. 76ECh. 3.3 - Prob. 77ECh. 3.3 - Prob. 78ECh. 3.3 - Prob. 79ECh. 3.3 - Prob. 80ECh. 3.3 - Prob. 81ECh. 3.3 - Prob. 82ECh. 3.3 - Prob. 83ECh. 3.3 - Write a logical statement representing each of the...Ch. 3.3 - Write a logical statement representing each of the...Ch. 3.3 - Prob. 86ECh. 3.3 - Prob. 87ECh. 3.3 - Prob. 88ECh. 3.3 - Prob. 89ECh. 3.3 - Prob. 90ECh. 3.3 - Draw circuits representing the following...Ch. 3.3 - Prob. 92ECh. 3.3 - Prob. 93ECh. 3.3 - Draw circuits representing the following...Ch. 3.3 - Prob. 95ECh. 3.3 - Prob. 96ECh. 3.3 - Prob. 97ECh. 3.4 - For each given conditional statement (or statement...Ch. 3.4 - For each given conditional statement (or statement...Ch. 3.4 - If it aint broke, dont fix it. For each given...Ch. 3.4 - Prob. 4ECh. 3.4 - For each given conditional statement (or statement...Ch. 3.4 - 6, Milk contains calcium. For each given...Ch. 3.4 - For each given conditional statement (or statement...Ch. 3.4 - Prob. 8ECh. 3.4 - Prob. 9ECh. 3.4 - For each given conditional statement (or statement...Ch. 3.4 - Prob. 11ECh. 3.4 - Prob. 12ECh. 3.4 - Prob. 13ECh. 3.4 - Prob. 14ECh. 3.4 - Prob. 15ECh. 3.4 - Prob. 16ECh. 3.4 - 17 Discuss the equivalences that exist among a...Ch. 3.4 - Prob. 18ECh. 3.4 - Prob. 19ECh. 3.4 - Prob. 20ECh. 3.4 - Prob. 21ECh. 3.4 - Write each statement in the form if p, then q....Ch. 3.4 - Prob. 23ECh. 3.4 - Write each statement in the form “if p, then...Ch. 3.4 - Write each statement in the form “if p, then...Ch. 3.4 - 26. Being in Kalamazoo is sufficient for being in...Ch. 3.4 - Prob. 27ECh. 3.4 - Prob. 28ECh. 3.4 - Prob. 29ECh. 3.4 - 30. The economy will recover only if employment...Ch. 3.4 - Prob. 31ECh. 3.4 - No integers are irrational numbersCh. 3.4 - Prob. 33ECh. 3.4 - Prob. 34ECh. 3.4 - Prob. 35ECh. 3.4 - 36. A square is a rectangle with two adjacent...Ch. 3.4 - Prob. 37ECh. 3.4 - Prob. 38ECh. 3.4 - Prob. 39ECh. 3.4 - Prob. 40ECh. 3.4 - Prob. 41ECh. 3.4 - Prob. 42ECh. 3.4 - Prob. 43ECh. 3.4 - Prob. 44ECh. 3.4 - Prob. 45ECh. 3.4 - Prob. 46ECh. 3.4 - Prob. 47ECh. 3.4 - Prob. 48ECh. 3.4 - Prob. 49ECh. 3.4 - Prob. 50ECh. 3.4 - Prob. 51ECh. 3.4 - Prob. 52ECh. 3.4 - Prob. 53ECh. 3.4 - This number is positive. This same number is a...Ch. 3.4 - Prob. 55ECh. 3.4 - Prob. 56ECh. 3.4 - Exercises 57 and 58 refer to the chapter opener on...Ch. 3.4 - Exercises 57 and 58 refer to the chapter opener on...Ch. 3.5 - Decide whether each argument is valid or...Ch. 3.5 - 2. All disc jockeys play music.
Ch. 3.5 - All celebrities have problems....Ch. 3.5 - All Southerners speak with an accent....Ch. 3.5 - All dogs love to bury bones...Ch. 3.5 - 6 All vice presidents use cell phones.
Ch. 3.5 - 7 All residents of Colorado know how to breathe...Ch. 3.5 - Prob. 8ECh. 3.5 - Prob. 9ECh. 3.5 - 10. Some philosophers are absent minded.
Ch. 3.5 - Prob. 11ECh. 3.5 - Prob. 12ECh. 3.5 - Refer to Example 3. If the second premise and the...Ch. 3.5 - Prob. 14ECh. 3.5 - Construct a valid argument based on the Euler...Ch. 3.5 - x represents vaccinationsCh. 3.5 - As mentioned in the text, an argument can have a...Ch. 3.5 - All actors have cars....Ch. 3.5 - All chickens have beaks....Ch. 3.5 - All chickens have beaks....Ch. 3.5 - Prob. 21ECh. 3.5 - Prob. 22ECh. 3.5 - Prob. 23ECh. 3.5 - 24. A scalene triangle has a longest side.
Ch. 3.5 - In Exercises 25-30. the premises marked A, B and C...Ch. 3.5 - 26. Some people who live in a suburb drive.
Ch. 3.5 - Prob. 27ECh. 3.5 - Some people who contribute to air pollution live...Ch. 3.5 - Prob. 29ECh. 3.5 - Prob. 30ECh. 3.6 - Each argument either is valid by one of the forms...Ch. 3.6 - 2. If you use binoculars, then you get a glimpse...Ch. 3.6 - 3. If Marina works hard enough, she will get a...Ch. 3.6 - If Isaiahs ankle heals on time, hell play this...Ch. 3.6 - 5. If he doesn't have to get up at 3 00 a m., he's...Ch. 3.6 - A mathematician is a device for turning coffee...Ch. 3.6 - If Clayton pitches, the Dodgers win....Ch. 3.6 - If Josh plays, the opponent gets shut out....Ch. 3.6 - If youre going through hell, keep going. (quote...Ch. 3.6 - If you can't get rid of the skeleton in your...Ch. 3.6 - She uses e-commerce or she pays by credit card....Ch. 3.6 - 12 Mia kicks or Drew passes.
Ch. 3.6 - Use a truth table to determine whether the...Ch. 3.6 - pqp qCh. 3.6 - pqq pCh. 3.6 - Prob. 16ECh. 3.6 - 17.
Ch. 3.6 - 18.
Ch. 3.6 - 19.
Ch. 3.6 - 20.
Ch. 3.6 - 21. =
Ch. 3.6 - (pq)(pq)qpCh. 3.6 - (pq)(pq)p qCh. 3.6 - Prob. 24ECh. 3.6 - 25.
Ch. 3.6 - Prob. 26ECh. 3.6 - Earlier we showed how to analyze arguments using...Ch. 3.6 - Prob. 28ECh. 3.6 - Determine whether each argument is valid or...Ch. 3.6 - 30. If Hurricane Gustave hit that grove of trees,...Ch. 3.6 - 31. If Yoda is my favorite Star Wars character,...Ch. 3.6 - 32 Carne Underwood sings or Joe Jonas is not a...Ch. 3.6 - The Cowboys will make the playoffs if and only if...Ch. 3.6 - If I've got you under my skin. then you are deep...Ch. 3.6 - 35. If Dr. Hardy is a department chairman, then he...Ch. 3.6 - Prob. 36ECh. 3.6 - Prob. 37ECh. 3.6 - All men are mortal Socrates is a man Therefore,...Ch. 3.6 - A recent DirecTV commercial had the following...Ch. 3.6 - Molly made the following observation If I want to...Ch. 3.6 - Prob. 41ECh. 3.6 - 42. None of your sons can do logic.
Ch. 3.6 - Prob. 43ECh. 3.6 - Prob. 44ECh. 3.6 - Prob. 45ECh. 3.6 - Prob. 46ECh. 3.6 - Prob. 47ECh. 3.6 - Prob. 48ECh. 3.6 - Prob. 49ECh. 3.6 - Let p be one is able to do logic," q be one is fit...Ch. 3.6 - Prob. 51ECh. 3.6 - Let p be it is a guinea pig. q be it is hopelessly...Ch. 3.6 - Prob. 53ECh. 3.6 - Prob. 54ECh. 3 - Write a negation for each statement. 63=3Ch. 3 - Write a negation for each statement. All men are...Ch. 3 - Prob. 3TCh. 3 - Write a negation for each statement. If I fall in...Ch. 3 - Write a negation for each statement.
5. She...Ch. 3 - Prob. 6TCh. 3 - Prob. 7TCh. 3 - Prob. 8TCh. 3 - Using the same statements as for Exercises 6-8,...Ch. 3 - Prob. 10TCh. 3 - In each of the following assume that p is true and...Ch. 3 - In each of the following assume that p is true and...Ch. 3 - In each of the following, assume that p is true...Ch. 3 - In each of the following assume that p is true and...Ch. 3 - 15 Explain in your own words why, if p is a...Ch. 3 - State the necessary conditions for each of the...Ch. 3 - Construct a truth table for each of the following....Ch. 3 - Construct a truth table for each of the following....Ch. 3 - Decide whether each statement is true or false....Ch. 3 - Decide whether each statement is true or false.
20...Ch. 3 - Write each conditional statement in if... then...Ch. 3 - Write each conditional statement in if then form....Ch. 3 - Write each conditional statement in if… then...Ch. 3 - Write each conditional statement in if then form....Ch. 3 - For each statement in Exercises 25 and 26, write...Ch. 3 - Prob. 26TCh. 3 - Prob. 27TCh. 3 - 28 Match each argument in parts (a) - (d) in the...Ch. 3 - Use a truth table to determine whether each...Ch. 3 - Use a truth table to determine whether each...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, subject and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Let A = {a, b, c, d}, B = {a,b,c}, and C = {s, t, u,v}. Draw an arrow diagram of a function for each of the following descriptions. If no such function exists, briefly explain why. (a) A function f : AC whose range is the set C. (b) A function g: BC whose range is the set C. (c) A function g: BC that is injective. (d) A function j : A → C that is not bijective.arrow_forwardLet f:R->R be defined by f(x)=x^(3)+5.(a) Determine if f is injective. why?(b) Determine if f is surjective. why?(c) Based upon (a) and (b), is f bijective? why?arrow_forwardLet f:R->R be defined by f(x)=x^(3)+5.(a) Determine if f is injective.(b) Determine if f is surjective. (c) Based upon (a) and (b), is f bijective?arrow_forward
- Please as many detarrow_forward8–23. Sketching vector fields Sketch the following vector fieldsarrow_forward25-30. Normal and tangential components For the vector field F and curve C, complete the following: a. Determine the points (if any) along the curve C at which the vector field F is tangent to C. b. Determine the points (if any) along the curve C at which the vector field F is normal to C. c. Sketch C and a few representative vectors of F on C. 25. F = (2½³, 0); c = {(x, y); y − x² = 1} 26. F = x (23 - 212) ; C = {(x, y); y = x² = 1}) , 2 27. F(x, y); C = {(x, y): x² + y² = 4} 28. F = (y, x); C = {(x, y): x² + y² = 1} 29. F = (x, y); C = 30. F = (y, x); C = {(x, y): x = 1} {(x, y): x² + y² = 1}arrow_forward
- ٣/١ B msl kd 180 Ka, Sin (1) I sin () sin(30) Sin (30) اذا ميريد شرح الكتب بس 0 بالفراغ 3) Cos (30) 0.866 4) Rotating 5) Synchronous speed, 120 x 50 G 5005 1000 s = 1000-950 Copper bosses 5kW Rotor input 5 0.05 : loo kw 6) 1 /0001 ined sove in peaper I need a detailed solution on paper please وه اذا ميريد شرح الكتب فقط ١٥٠ DC 7) rotor a ' (y+xlny + xe*)dx + (xsiny + xlnx + dy = 0. Q1// Find the solution of: ( 357arrow_forward۳/۱ R₂ = X2 2) slots per pole per phase 3/31 B. 180 msl Kas Sin (I) 1sin() sin(30) Sin (30) اذا ميريد شرح الكتب بس 0 بالفراغ 3) Cos (30): 0.866 4) Rotating 5) Synchronous speeds 120×50 looo G 1000-950 1000 Copper losses 5kw Rotor input 5 loo kw 0.05 6) 1 اذا ميريد شرح الكتب فقط look 7) rotor DC ined sove in peaper I need a detailed solution on paper please 0 64 Find the general solution of the following equations: QI//y(4)-16y= 0. Find the general solution of the following equations: Q2ll yll-4y/ +13y=esinx.arrow_forwardR₂ = X2 2) slots per pole per phase = 3/31 B-180 60 msl kd Kas Sin () 2 I sin (6) sin(30) Sin (30) اذا مريد شرح الكتب بس 0 بالفراغ 3 Cos (30) 0.866 4) Rotating ined sove in peaper 5) Synchronous speed s 120×50 6 s = 1000-950 1000 Copper losses 5kw Rotor input 5 0.05 6) 1 loo kw اذا ميريد شرح الكتب فقط Look 7) rotov DC I need a detailed solution on paper please 0 64 Solve the following equations: 0 Q1// Find the solution of: ( y • with y(0) = 1. dx x²+y²arrow_forward
- R₂ = X2 2) slots per pole per phase = 3/3 1 B-180-60 msl Ka Sin (1) Isin () sin(30) Sin (30) اذا ميريد شرح الكتب بس 0 بالفراغ 3) Cos (30) 0.866 4) Rotating 5) Synchronous speed, 120 x 50 s = 1000-950 1000 Copper losses 5kw Rotor input 5 6) 1 0.05 G 50105 loo kw اذا ميريد شرح الكتب فقط look 7) rotov DC ined sove in peaper I need a detailed solution on paper please 064 2- A hot ball (D=15 cm ) is cooled by forced air T.-30°C, the rate of heat transfer from the ball is 460.86 W. Take for the air -0.025 Wim °C and Nu=144.89, find the ball surface temperature a) 300 °C 16 b) 327 °C c) 376 °C d) None か = 750 01arrow_forwardAnswer questions 8.3.3 and 8.3.4 respectively 8.3.4 .WP An article in Medicine and Science in Sports and Exercise [“Electrostimulation Training Effects on the Physical Performance of Ice Hockey Players” (2005, Vol. 37, pp. 455–460)] considered the use of electromyostimulation (EMS) as a method to train healthy skeletal muscle. EMS sessions consisted of 30 contractions (4-second duration, 85 Hz) and were carried out three times per week for 3 weeks on 17 ice hockey players. The 10-meter skating performance test showed a standard deviation of 0.09 seconds. Construct a 95% confidence interval of the standard deviation of the skating performance test.arrow_forward8.6.7 Consider the tire-testing data in Exercise 8.2.3. Compute a 95% tolerance interval on the life of the tires that has confidence level 95%. Compare the length of the tolerance interval with the length of the 95% CI on the population mean. Which interval is shorter? Discuss the difference in interpretation of these two intervals.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage,
Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage, Elements Of Modern AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781285463230Author:Gilbert, Linda, JimmiePublisher:Cengage Learning,
Elements Of Modern AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781285463230Author:Gilbert, Linda, JimmiePublisher:Cengage Learning, Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1AlgebraISBN:9780395977224Author:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. ColePublisher:McDougal Littell
Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1AlgebraISBN:9780395977224Author:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. ColePublisher:McDougal Littell

Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7e
Geometry
ISBN:9781337614085
Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.
Publisher:Cengage,

Elements Of Modern Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:9781285463230
Author:Gilbert, Linda, Jimmie
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1
Algebra
ISBN:9780395977224
Author:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. Cole
Publisher:McDougal Littell
Logical Arguments - Modus Ponens & Modus Tollens; Author: Dr. Trefor Bazett;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=NTSZMdGlo4g;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY