
Concept explainers
You have seen that Earth’s terrestrial biomes reflect regional variations in climate. But what determines these climatic variations? Interpret the following diagrams in reference to how each represents effects on global patterns of temperature, rainfall, and winds.
a. Solar radiation and latitude:
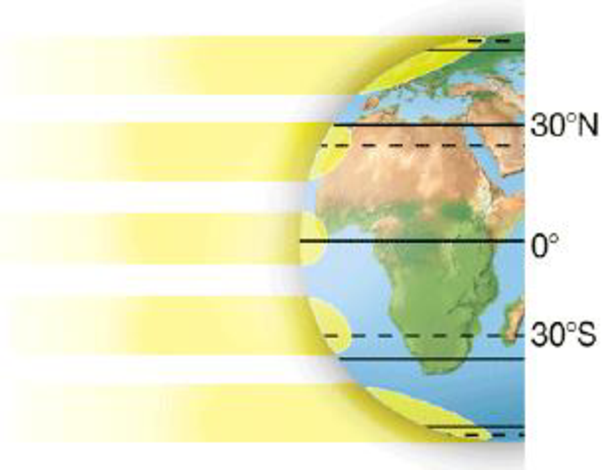
b. Earth’s orbit around the sun:
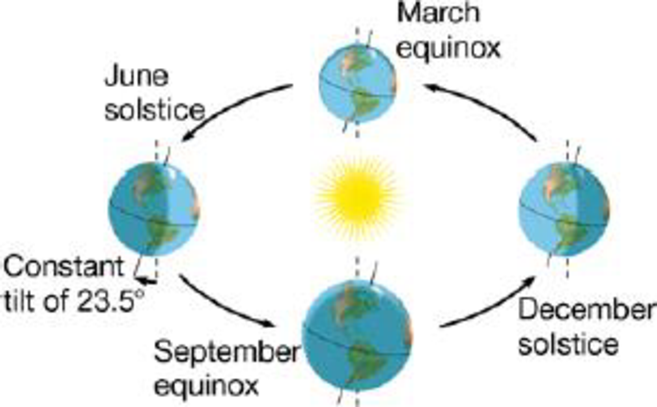
c. Global patterns of air circulation and rainfall:
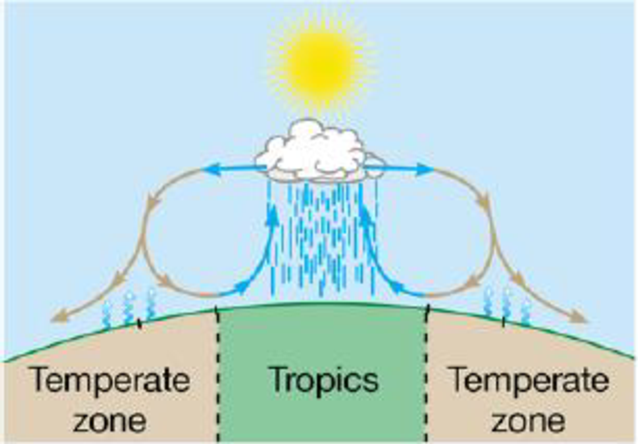
(a)
To determine: Solar radiation and latitude representing the effects on global pattern of temperature, rainfall and wind and also the climatic variations.
Introduction:
Biomes are the regions with similar climate and terrestrial biome distribution is decided by rainfall and temperature. The terrestrial biomes are tundra, rainforest, desert, taiga, temperate forest, alpine and savanna.
Explanation of Solution
The solar radiation amount received by earth is depends upon the location of the biome. The amount of received sunlight will be high if the biome is located at equator, resulting in hot conditions in biome. At the poles, biomes are cold due to the availability of less sunlight.
(b)
To determine: Earth’s orbit around the sun representing the effects on global pattern of temperature, rainfall and wind and also the climatic variations.
Introduction:
Biomes are the regions with similar climate and terrestrial biome distribution is decided by rainfall and temperature. The terrestrial biomes are tundra, rainforest, desert, taiga, temperate forest, alpine and savanna.
Explanation of Solution
Different seasons are the result of earth rotation, because both hemisphere experience opposite season due to tilt of earth on its own axis.
The tilt of the northern hemisphere of earth towards the sun results in summer as the tilt allows entry of more sunlight and summer in the northern hemisphere means winter in the southern hemisphere because it is away from the sun so receives less sunlight.
(c)
To determine: Global pattern of air circulation and rainfall representing the effects on global pattern of temperature, rainfall and wind and also the climatic variations.
Introduction:
Biomes are the regions with similar climate and terrestrial biome distribution is decided by rainfall and temperature. The terrestrial biomes are tundra, rainforest, desert, taiga, temperate forest, alpine and savanna.
Explanation of Solution
Extreme sunlight at equators results in evaporation of water from the land and oceans, which cools and condenses, converting into rain. For example: tropical rainforests.
At 30 degree latitude of south and north, the circulating air warms as it fals causing evaporation of moisture present in the soil, leading to dryness (arid regions in the temperate zones). For example: deserts.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 34 Solutions
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (8th Edition)
- How much ATP will be produced during the following metabolic scenario: Aerobic respiration of a 5mM lipid solution that is made up of one glycerol and an 8-carbon fatty acid and 12-carbon fatty acid. Recall that when glycerol breaks down to Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate it costs one ATP but your get an extra FADH2. Every two carbons of a fatty acid break down to one acetyl-CoA. (pathways will be provided on the exam) Units cannot be entered in this style of question but the units of your answer should be in mM of ATP.arrow_forwardWhen beta-lactamase was isolated from Staphylcoccus aureus and treated with a phosphorylating agent, only the active site, serine was phosphorylated. Additionally, the serine was found to constitute 0.35% (by weight) of this beta-lactamase enzyme. Using this, calculate the molecular weight of this enzyme and estimate the number of amino acids present in the polypeptide.arrow_forwardBased on your results from the Mannitol Salt Agar (MSA) media, which of your bacteria were mannitol fermenters and which were not mannitol fermenters?arrow_forward
- help tutor pleasearrow_forwardQ8. A researcher wants to study the effectiveness of a pill intended to reduce stomach heartburn in pregnant women. The researcher chooses randomly 400 women to participate in this experiment for 9 months of their pregnancy period. They all need to have the same diet. The researcher designs two groups of 200 participants: One group take the real medication intended to reduce heartburn, while the other group take placebo medication. In this study what are: Independent variable: Dependent variable: Control variable: Experimental group: " Control group: If the participants do not know who is consuming the real pills and who is consuming the sugar pills. This study is It happens that 40% of the participants do not find the treatment helpful and drop out after 6 months. The researcher throws out the data from subjects that drop out. What type of bias is there in this study? If the company who makes the medication funds this research, what type of bias might exist in this research work?arrow_forwardHow do I determine the inhertiance pattern from the pedigree diagram?arrow_forward
- 22. Which of the following mutant proteins is expected to have a dominant negative effect when over- expressed in normal cells? a. mutant PI3-kinase that lacks the SH2 domain but retains the kinase function b. mutant Grb2 protein that cannot bind to RTK c. mutant RTK that lacks the extracellular domain d. mutant PDK that has the PH domain but lost the kinase function e. all of the abovearrow_forwardWhat is the label ?arrow_forwardCan you described the image? Can you explain the question as well their answer and how to get to an answer to an problem like this?arrow_forward
 Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax





