
Concept explainers
Price–demand equation. According to economic theory, the demand x for a quantity in a free market decreases as the price p increases (see the figure). Suppose that the number x of DVD players people are willing to buy per week from a retail chain at a price of $p is given by
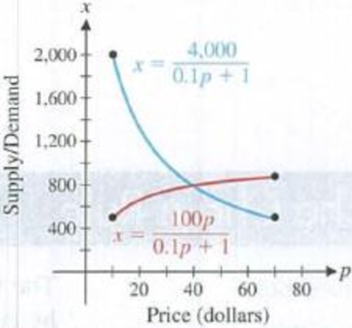
Figure for 95 and 96
- (A) Find dx/dp.
- (B) Find the demand and the instantaneous rate of change of demand with respect to price when the price is $40. Write a brief interpretation of these results.
- (C) Use the results from part (B) to estimate the demand if the price is increased to $41.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 3 Solutions
Calculus for Business, Economics, Life Sciences, and Social Sciences (14th Edition)
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Introductory Statistics
Elementary Statistics (13th Edition)
Pathways To Math Literacy (looseleaf)
College Algebra Essentials (5th Edition)
Probability And Statistical Inference (10th Edition)
College Algebra (Collegiate Math)
- How does the graph of f(x) = (x − 9)4 – 3 compare to the parent function g(x) = x²?arrow_forwardFind the x-intercepts and the y-intercept of the graph of f(x) = (x − 5)(x − 2)(x − 1) without using technology. Show all work.arrow_forwardIn a volatile housing market, the overall value of a home can be modeled by V(x) = 415x² - 4600x + 200000, where V represents the value of the home and x represents each year after 2020. Part A: Find the vertex of V(x). Show all work. Part B: Interpret what the vertex means in terms of the value of the home.arrow_forward
- Show all work to solve 3x² + 5x - 2 = 0.arrow_forwardTwo functions are given below: f(x) and h(x). State the axis of symmetry for each function and explain how to find it. f(x) h(x) 21 5 4+ 3 f(x) = −2(x − 4)² +2 + -5 -4-3-2-1 1 2 3 4 5 -1 -2 -3 5arrow_forwardThe functions f(x) = (x + 1)² - 2 and g(x) = (x-2)² + 1 have been rewritten using the completing-the-square method. Apply your knowledge of functions in vertex form to determine if the vertex for each function is a minimum or a maximum and explain your reasoning.arrow_forward
- Total marks 15 3. (i) Let FRN Rm be a mapping and x = RN is a given point. Which of the following statements are true? Construct counterex- amples for any that are false. (a) If F is continuous at x then F is differentiable at x. (b) If F is differentiable at x then F is continuous at x. If F is differentiable at x then F has all 1st order partial (c) derivatives at x. (d) If all 1st order partial derivatives of F exist and are con- tinuous on RN then F is differentiable at x. [5 Marks] (ii) Let mappings F= (F1, F2) R³ → R² and G=(G1, G2) R² → R² : be defined by F₁ (x1, x2, x3) = x1 + x², G1(1, 2) = 31, F2(x1, x2, x3) = x² + x3, G2(1, 2)=sin(1+ y2). By using the chain rule, calculate the Jacobian matrix of the mapping GoF R3 R², i.e., JGoF(x1, x2, x3). What is JGOF(0, 0, 0)? (iii) [7 Marks] Give reasons why the mapping Go F is differentiable at (0, 0, 0) R³ and determine the derivative matrix D(GF)(0, 0, 0). [3 Marks]arrow_forward5. (i) Let f R2 R be defined by f(x1, x2) = x² - 4x1x2 + 2x3. Find all local minima of f on R². (ii) [10 Marks] Give an example of a function f: R2 R which is not bounded above and has exactly one critical point, which is a minimum. Justify briefly Total marks 15 your answer. [5 Marks]arrow_forwardTotal marks 15 4. : Let f R2 R be defined by f(x1, x2) = 2x²- 8x1x2+4x+2. Find all local minima of f on R². [10 Marks] (ii) Give an example of a function f R2 R which is neither bounded below nor bounded above, and has no critical point. Justify briefly your answer. [5 Marks]arrow_forward
- 4. Let F RNR be a mapping. (i) x ЄRN ? (ii) : What does it mean to say that F is differentiable at a point [1 Mark] In Theorem 5.4 in the Lecture Notes we proved that if F is differentiable at a point x E RN then F is continuous at x. Proof. Let (n) CRN be a sequence such that xn → x ЄERN as n → ∞. We want to show that F(xn) F(x), which means F is continuous at x. Denote hnxn - x, so that ||hn|| 0. Thus we find ||F(xn) − F(x)|| = ||F(x + hn) − F(x)|| * ||DF (x)hn + R(hn) || (**) ||DF(x)hn||+||R(hn)||| → 0, because the linear mapping DF(x) is continuous and for all large nЄ N, (***) ||R(hn) || ||R(hn) || ≤ → 0. ||hn|| (a) Explain in details why ||hn|| → 0. [3 Marks] (b) Explain the steps labelled (*), (**), (***). [6 Marks]arrow_forward4. In Theorem 5.4 in the Lecture Notes we proved that if F: RN → Rm is differentiable at x = RN then F is continuous at x. Proof. Let (xn) CRN be a sequence such that x → x Є RN as n → ∞. We want F(x), which means F is continuous at x. to show that F(xn) Denote hn xnx, so that ||hn||| 0. Thus we find ||F (xn) − F(x) || (*) ||F(x + hn) − F(x)|| = ||DF(x)hn + R(hn)|| (**) ||DF(x)hn|| + ||R(hn) || → 0, because the linear mapping DF(x) is continuous and for all large n = N, |||R(hn) || ≤ (***) ||R(hn)|| ||hn|| → 0. Explain the steps labelled (*), (**), (***) [6 Marks] (ii) Give an example of a function F: RR such that F is contin- Total marks 10 uous at x=0 but F is not differentiable at at x = 0. [4 Marks]arrow_forward3. Let f R2 R be a function. (i) Explain in your own words the relationship between the existence of all partial derivatives of f and differentiability of f at a point x = R². (ii) Consider R2 → R defined by : [5 Marks] f(x1, x2) = |2x1x2|1/2 Show that af af -(0,0) = 0 and -(0, 0) = 0, Jx1 მx2 but f is not differentiable at (0,0). [10 Marks]arrow_forward
- Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage
 Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305071742Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Algebra and Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305071742Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt
Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt 
 Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning





