
Sub part (a):
Impact of different views on inflation on the economy's equilibrium.
Sub part (a):
Explanation of Solution
The supply is dependent upon the
The
When the new chairman is one with the view that the inflation is not a big issue on the economy, the economy would identify the chairman as the silent supporter of the inflation, and they will expect that the chairman will not introduce the active policies to fight against and control the inflation in the economy. As a result, the public will expect that the rise in the inflation and the price level are likely to rise.
Concept introduction:
Aggregate demand curve: It is the curve that shows the relationship between the price level in the economy and the quantity of real GDP demanded by the economic agents such as the households, firms, and the government.
Equilibrium: The equilibrium in the economy is the point where the economy's aggregate demand curve and the aggregate supply curve intersect with each other. There will be no excess demand or
Sub part (b):
Impact of different views on inflation on the economy's equilibrium.
Sub part (b):
Explanation of Solution
When the people expect higher inflation for the next year, they will start to calculate the changes in the price level. According to the expected higher level of inflation over the next year, they will expect higher cost of living for the next year. As a result of this, they will demand higher nominal wage rate for the next year with the employers.
Concept introduction:
Aggregate demand curve: It is the curve that shows the relationship between the price level in the economy and the quantity of real GDP demanded by the economic agents such as the households, firms, and the government.
Aggregate supply curve: In the short run, it is a curve that shows the relationship between the price level in the economy and the supply in the economy by the firms. In the long run, it shows the relationship between the price level and the level of quantity supplied by the firms.
Equilibrium: The equilibrium in the economy is the point where the economy's aggregate demand curve and the aggregate supply curve intersect with each other. There will be no excess demand or excess supply in the economy at the equilibrium.
Sub part (c):
Impact of different views on inflation on the economy's equilibrium.
Sub part (c):
Explanation of Solution
The profit of the firm is the difference between the total cost and the total revenue of the firm's products. When the total cost is higher than the total revenue, the firm faces the loss and if it is vice versa, the firm earns the profit. When the nominal wages increase, it increases the cost of production. So at any given price point, the increase in the labor cost reduces the profitability of the firm because it increases the total cost of production of the firm.
Concept introduction:
Aggregate demand curve: It is the curve that shows the relationship between the price level in the economy and the quantity of real GDP demanded by the economic agents such as the households, firms, and the government.
Aggregate supply curve: In the short run, it is a curve that shows the relationship between the price level in the economy and the supply in the economy by the firms. In the long run, it shows the relationship between the price level and the level of quantity supplied by the firms.
Equilibrium: The equilibrium in the economy is the point where the economy's aggregate demand curve and the aggregate supply curve intersect with each other. There will be no excess demand or excess supply in the economy at the equilibrium.
Sub part (d):
Impact of different views on inflation on the economy's equilibrium.
Sub part (d):
Explanation of Solution
When the profitability of the firm decreases due to the increased nominal wage rate of the labor, the supply will decline in the economy, which will cause the short run aggregate supply curve to shift upward and this can be illustrated on the graph as follows:
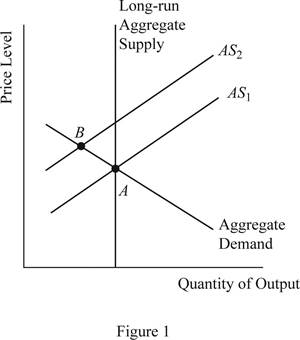
Concept introduction:
Aggregate demand curve: It is the curve that shows the relationship between the price level in the economy and the quantity of real GDP demanded by the economic agents such as the households, firms, and the government.
Aggregate supply curve: In the short run, it is a curve that shows the relationship between the price level in the economy and the supply in the economy by the firms. In the long run, it shows the relationship between the price level and the level of quantity supplied by the firms.
Equilibrium: The equilibrium in the economy is the point where the economy's aggregate demand curve and the aggregate supply curve intersect with each other. There will be no excess demand or excess supply in the economy at the equilibrium.
Sub part (e):
Impact of different views on inflation on the economy's equilibrium.
Sub part (e):
Explanation of Solution
When the aggregate demand is held constant without any change and the aggregate supply shifts to AS2 as given above, it will lead to lower output in the economy along with higher price level in the economy. This is because when the SRAS curve shifts upward, the new equilibrium will be derived at point B, which is lying above and leftward to the initial equilibrium point A.
Concept introduction:
Aggregate demand curve: It is the curve that shows the relationship between the price level in the economy and the quantity of real GDP demanded by the economic agents such as the households, firms, and the government.
Aggregate supply curve: In the short run, it is a curve that shows the relationship between the price level in the economy and the supply in the economy by the firms. In the long run, it shows the relationship between the price level and the level of quantity supplied by the firms.
Equilibrium: The equilibrium in the economy is the point where the economy's aggregate demand curve and the aggregate supply curve intersect with each other. There will be no excess demand or excess supply in the economy at the equilibrium.
Sub part (f):
Impact of different views on inflation on the economy's equilibrium.
Sub part (f):
Explanation of Solution
The situation explained above that the total output of the economy falls, whereas the price level in the economy increases leading to the situation of stagflation and this means that the appointment choice of the new chairman was not a wise choice.
Concept introduction:
Aggregate demand curve: It is the curve that shows the relationship between the price level in the economy and the quantity of real GDP demanded by the economic agents such as the households, firms, and the government.
Aggregate supply curve: In the short run, it is a curve that shows the relationship between the price level in the economy and the supply in the economy by the firms. In the long run, it shows the relationship between the price level and the level of quantity supplied by the firms.
Equilibrium: The equilibrium in the economy is the point where the economy's aggregate demand curve and the aggregate supply curve intersect with each other. There will be no excess demand or excess supply in the economy at the equilibrium.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 33 Solutions
Principles of Economics, 7th Edition (MindTap Course List)
- In a paragraph, no bullet, points please answer the question and follow the instructions. Give only the solution: Use the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’re explaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all. 6.Draw a standard Commercial Bank Balance Sheet and briefly explain each of the main components.arrow_forwardC1 The following model can be used to study whether campaign expenditures affect election outcomes: voteA = 0 + B₁ log(expendA) + ẞ₂ log(expendB) + ẞ3 prtystrA + u, where voteA is the percentage of the vote received by Candidate A, expendA and expend are campaign expenditures by Candidates A and B, and prtystrA is a measure of party strength for Candidate A (the percentage of the most recent presidential vote that went to A's party). == (i) (ii) (iii) (iv) What is the interpretation of B₁? In terms of the parameters, state the null hypothesis that a 1% increase in A's expenditures is offset by a 1% increase in B's expenditures. Estimate the given model using the data in VOTE1.DTA and report the results in usual form. Do A's expenditures affect the outcome? What about B's expenditures? Can you use these results to test the hypothesis in part (ii)? Estimate a model that directly gives the t statistic for testing the hypothesis in part (ii). What do you conclude? (Use a two-sided…arrow_forwardIn a paragraph, no bullet, points please answer the question and follow the instructions. Give only the solution: Use the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’re explaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all. 10. What is Tinbergen’s constraint? Explain its importance in regard to US monetary policy.arrow_forward
- In a paragraph, no bullet, points please answer the question and follow the instructions. Give only the solution: Use the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’re explaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all. 8. How does monetary policy supposedly translate into changes in AD?arrow_forwardIn a paragraph, no bullet, points please answer the question and follow the instructions. Give only the solution: Use the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’re explaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all. 2. Carefully explain either Keynes’ “cookie jar” motive for holding money or the “saw-toothed model’s” motive for holding a safety stock.arrow_forwardIn a paragraph, no bullet, points please answer the question and follow the instructions. Give only the solution: Use the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’re explaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all. 7.Carefully explain the Fisher equation for interest rates. What insight does it provide?arrow_forward
- In a paragraph, no bullet, points please answer the question and follow the instructions. Give only the solution: Use the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’re explaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all. 3. Describe the general architecture of the Federal Reserve System.arrow_forwardIn a paragraph, no bullet, points please answer the question and follow the instructions. Give only the solution: Use the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’re explaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all. 1. Define money. Carefully explain the three functions of money.arrow_forwardIn a paragraph, no bullet, points please answer the question and follow the instructions. Give only the solution: Use the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’re explaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all. 5.Draw the Federal Reserve System’s Balance Sheet and briefly explain each of the main (highlighted in the PowerPoints and text) components.arrow_forward
- In a paragraph, no bullet, points please answer the question and follow the instructions. Give only the solution: Use the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’re explaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all. 9. What are monetary rules? How are they carried out and what is the difference between monetary rules and discretionary behavior?arrow_forwardIn a paragraph, no bullet, points please answer the question and follow the instructions. Give only the solution: Use the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’re explaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all. 4. What is interest payment on reserve balances used for? How does it work?arrow_forwardA linear programming computer package is needed. As part of the settlement for a class action lawsuit, Hoxworth Corporation must provide sufficient cash to make the following annual payments (in thousands of dollars). Year 1 2 3 4 5 6 Payment 170 195 220 265 295 440 The annual payments must be made at the beginning of each year. The judge will approve an amount that, along with earnings on its investment, will cover the annual payments. Investment of the funds will be limited to savings (at 4% annually) and government securities, at prices and rates currently quoted in The Wall Street Journal. Hoxworth wants to develop a plan for making the annual payments by investing in the following securities (par value = $1,000). Funds not invested in these securities will be placed in savings. Security Current Price Rate (%) Years to Maturity 1 $1,055 6.750 3 2 $1,000 5.125 4 Assume that interest is paid annually. The plan will be submitted to the judge and, if approved,…arrow_forward
 Macroeconomics: Private and Public Choice (MindTa...EconomicsISBN:9781305506756Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. MacphersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Macroeconomics: Private and Public Choice (MindTa...EconomicsISBN:9781305506756Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. MacphersonPublisher:Cengage Learning Economics: Private and Public Choice (MindTap Cou...EconomicsISBN:9781305506725Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. MacphersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Economics: Private and Public Choice (MindTap Cou...EconomicsISBN:9781305506725Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. MacphersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Exploring EconomicsEconomicsISBN:9781544336329Author:Robert L. SextonPublisher:SAGE Publications, Inc
Exploring EconomicsEconomicsISBN:9781544336329Author:Robert L. SextonPublisher:SAGE Publications, Inc Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning
Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning





