
Subpart (a):
Long run equilibrium in AD-AS model.
Subpart (a):
Explanation of Solution
The supply depends upon the
The
The equilibrium is a condition where the aggregate demand curve of the economy intersects with the aggregate supply curve of the economy. Then there will be an equilibrium point derived where the economy will be in its equilibrium without any excess demand or supply. The quantity on the X axis will represent the
Concept introduction:
Aggregate demand curve: It is the curve which shows the relationship between the price level in the economy and the quantity of real GDP demanded by the economic agents such as the households, firms as well as the government.
Equilibrium: The equilibrium in the economy is the point where the economy's aggregate demand curve and the aggregate supply curve intersects with each other. There will be no excess demand or
Subpart (b):
Long run equilibrium in AD-AS model.
Subpart (b):
Explanation of Solution
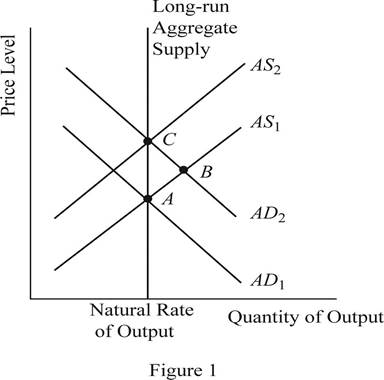
When the money supply of the economy increases with the intervention of the Central Bank of the economy, the money with the public will increase. When the money with the public increases, they will feel wealthier and as a result they will demand more consumer goods and services. As a result, the aggregate demand of the economy increases and it will shift the AD curve towards the right. This can be identified as the change to the equilibrium point B as shown in Figure 1. Thus, in short, the increase in the money supply leads to the increase in the output and price level of the economy.
Concept introduction:
Aggregate demand curve: It is the curve which shows the relationship between the price level in the economy and the quantity of real GDP demanded by the economic agents such as the households, firms as well as the government.
Aggregate supply curve: In the short run, it is a curve which shows the relationship between the price level in the economy and the supply in the economy by the firms. In the long run, it shows the relationship between the price level and the level of quantity supplied by the firms.
Equilibrium: The equilibrium in the economy is the point where the economy's aggregate demand curve and the aggregate supply curve intersects with each other. There will be no excess demand or excess supply in the economy at the equilibrium.
Subpart (c):
Long run equilibrium in AD-AS model.
Subpart (c):
Explanation of Solution
When the AD curve shifts towards the right and increases the output and the price level in the short run, over time, the nominal wages, prices as well as the perceptions and expectations of the economy would adjust to the new equilibrium level. As a result of this gradual adjustment, the cost of production will increase and the result will be a leftward shift in the aggregate supply curve of the economy. Then the economy will return to its natural level of output at a higher price level of the economy. This can be identified as the movement from point B to point C in the graph shown above.
Concept introduction:
Aggregate demand curve: It is the curve which shows the relationship between the price level in the economy and the quantity of real GDP demanded by the economic agents such as the households, firms as well as the government.
Aggregate supply curve: In the short run, it is a curve which shows the relationship between the price level in the economy and the supply in the economy by the firms. In the long run, it shows the relationship between the price level and the level of quantity supplied by the firms.
Equilibrium: The equilibrium in the economy is the point where the economy's aggregate demand curve and the aggregate supply curve intersects with each other. There will be no excess demand or excess supply in the economy at the equilibrium.
Subpart (d):
Long run equilibrium in AD-AS model.
Subpart (d):
Explanation of Solution
The sticky wages theory suggests that when there is inflation in the economy, the wage rate will adjust very slowly to the inflation. More or less the wage rates will be sticky and the main reason will be the long term contracts between the employer and the employees. Thus, in the short run equilibriums such as point A and point B, the wages of the economy would be more or less equal to each other. Whereas the point C represents the long run equilibrium and thus, the wages at the point C will be higher than that in point A and B.
Concept introduction:
Aggregate demand curve: It is the curve which shows the relationship between the price level in the economy and the quantity of real GDP demanded by the economic agents such as the households, firms as well as the government.
Aggregate supply curve: In the short run, it is a curve which shows the relationship between the price level in the economy and the supply in the economy by the firms. In the long run, it shows the relationship between the price level and the level of quantity supplied by the firms.
Equilibrium: The equilibrium in the economy is the point where the economy's aggregate demand curve and the aggregate supply curve intersects with each other. There will be no excess demand or excess supply in the economy at the equilibrium.
Subpart (e):
Long run equilibrium in AD-AS model.
Subpart (e):
Explanation of Solution
The sticky wages theory suggests that when there is inflation in the economy, the wage rate will adjust very slowly to the inflation. More or less, the wage rates will be sticky and the main reason will be the long term contracts between the employer and the employees. So, the nominal wages at equilibrium point A and B will be same. But the increase in the general price level in the economy would reduce the real wages of the workers because, the real wage is the nominal wage divided by the price level. When the denominator increases, it will reduce the value of the real wages in the economy.
Concept introduction:
Aggregate demand curve: It is the curve which shows the relationship between the price level in the economy and the quantity of real GDP demanded by the economic agents such as the households, firms as well as the government.
Aggregate supply curve: In the short run, it is a curve which shows the relationship between the price level in the economy and the supply in the economy by the firms. In the long run, it shows the relationship between the price level and the level of quantity supplied by the firms.
Equilibrium: The equilibrium in the economy is the point where the economy's aggregate demand curve and the aggregate supply curve intersects with each other. There will be no excess demand or excess supply in the economy at the equilibrium.
Sub part (f):
Long run equilibrium in AD-AS model.
Sub part (f):
Explanation of Solution
When the increase in the money supply happens in the economy, it will lead to the increase in the nominal wages as well as the price level in the economy in the long run. As a result of the increase in the nominal wage rate along with the price level in the economy, the real wage rate of the economy would remain unchanged. Thus, the neutrality of money applies in the long run equilibrium.
Concept introduction:
Aggregate demand curve: It is the curve which shows the relationship between the price level in the economy and the quantity of real GDP demanded by the economic agents such as the households, firms as well as the government.
Aggregate supply curve: In the short run, it is a curve which shows the relationship between the price level in the economy and the supply in the economy by the firms. In the long run, it shows the relationship between the price level and the level of quantity supplied by the firms.
Equilibrium: The equilibrium in the economy is the point where the economy's aggregate demand curve and the aggregate supply curve intersects with each other. There will be no excess demand or excess supply in the economy at the equilibrium.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 33 Solutions
Principles of Economics, 7th Edition (MindTap Course List)
- Consider the table on the right, which shows the various revenue concepts for a perfectly competitive firm. Suppose the firm faces a constant market price of $4. Compute first total revenue for each level of output and fill in the TR column of the table. Next, compute marginal revenue for each level of output and fill in the MR column of the table. (Marginal revenue at each level of output is computed using total revenue for two successive levels of output. For example, marginal revenue at 160 uses total revenue for output levels 120 and 160.) Total Marginal Price (p)Quantity (Q) Revenue (TR)Revenue (MR) $4 A EA 120 $4 160 $4 200 $4 240 $4 280 $ EA EA EA 10 S คarrow_forwardThis week we will be discussing measures of economic well-being. Read the following short article from the Office of National Statistics from the U.K. which discusses different measures of economic well-being: https://blog.ons.gov.uk/2017/07/06/beyond-gdp-measuring-the-economic-well-being-of-individuals/ For this assignment, we will narrow down to the economic well-being of the St. Louis region (or another region you choose). As the article indicates there are different measures of well-being. You are interested in creating a Hypothesis Test about the economic well-being of the area. Discuss the following issues: First, think about your research hypothesis and justify it briefly. Remember, a hypothesis is a well-thought and untested proposition. What is the null hypothesis? What is the parameter you are interested in? (i.e., the measure of well-being). Is it going to be a Lower-Tail, Upper-Tail or Two-Tailed test? What is the data that you need and how will you collect the data? What…arrow_forwardJohnny brought $39.50 to the art supply store. He bought a brush, a sketchbook, and a paint set. The brush was 1 6 as much as the sketchbook, and the sketchbook cost 3 4 the cost of the paint set. Johnny had $2.00 left over after buying these items.arrow_forward
- A young woman plans to retire early in 25 years. She believes she can save $10,000 each year starting now. If she plans to begin withdrawing money one year after she makes her last payment into the retirement account (i.e., in the 26th year), what uniform amount could she withdraw each year for 30 years, if the account earns an interest rate of 8% per year? a) Correctly plot the cash flow diagram with its respective vectors, arrowheads, units, and currency values. b) Correct mathematical approach and development, use of compound interest factors.c) Financial logic in the development of the exercise and application of the concept of time value of money. d) Final numerical answer and writing in prose with a minimum of 20 words and a maximum of 50 words of the obtained numerical interpretation.arrow_forwardA hospital charges $200 for a medical procedure, and 1,000 patients use the service. The hospital raises the price to $250, and the number of patients drops to 900. Calculate the price elasticity of demand (PED) and explain your answer. (show all working) Briefly explain how elasticity affects government health policies in the following cases: • Taxes on unhealthy products (cigarettes, alcohol, sugary drinks) • Subsidizing Preventive Care (e.g., vaccines, screenings) Drug Price Controls & Generic Substitutions Co-Payments & Insurance Designarrow_forwardAssume the United States is a large consumer of steel, able to influence the world price. DUS and SUS denote its demand and supply schedules in Figure 1. The overall (United States plus world) supply schedule of steel is denoted by SUS.+W. Figure 1 Import Tariff Levied by a Large Country Answer all questions (a-f) by referring to Figure 1 above. a) Calculate the free trade market equilibrium price, domestic consumption, and volumE Answer all questions (a-f) by referring to Figure 1 above. a) Calculate the free trade market equilibrium price, domestic consumption, and volume of steel imports by the US. [5 marks] b) Suppose the United States imposes a tariff (t) of $100 on each ton of steel imported. With the tariff, calculate the price of steel and the volume of steel imports by the US. [5 marks] c) Of the $100 tariff, how much is passed on to the US consumer via a higher price, and how much is borne by the foreign exporter? [5 marks] d) Calculate the tariff's deadweight welfare loss to…arrow_forward
- 1. A doctor quits his job, which pays $77,000 per annum, to open a non-governmental organization (NGO) to serve the needs of orphans. His annual expenses for the NGO amounts to $62,700 for food and daily supplies, $9,400 for maintenance, and $1,800 for books. What is his opportunity cost of opening the NGO? (Show working) 2. During the COVID-19 pandemic, hospitals worldwide faced severe resource constraints, including: a. Limited ICU beds b. Shortage of ventilators c. Insufficient doctors and nurses d. Lack of vaccines in early 2021 Governments and hospitals had to make critical decisions about who receives treatment first and how to allocate limited resources efficiently. In no more than 150 words and using core economic concepts of scarcity, choice and opportunity cost, how would you help your government make these critical decisions?arrow_forwardWhat is the argument about necessary evil?arrow_forwardWhat are the consequences of declining houses prices?arrow_forward
- Q1 Explain what economic catch 22 is. Q2 What are the consequences of declining houses pricing? Q3 What is the argument about necessary evil? Q4 Explain the idea of irrational exhuberance? Q5 Explain what was the economic paradox?arrow_forward< Files 9:10 Fri Mar 21 Chapter+11-Public+Goods+and+Common+Res... The Economic Catch-22 By Robert J. Samuelson We are now in the "blame phase" of the economic cycle. As the housing slump deepens and financial markets swing erratically, we've embarked on the usual search for culprits. Who got us into this mess? Our investigations will doubtlessly reveal, as they already have, much wishful thinking and miscalculation. They will also find incompetence, predatory behavior and probably some criminality. But let me suggest that, though inevitable and necessary, this exercise is also simplistic and deceptive. -- business It assumes that, absent mistakes and misdeeds, we might remain in a permanent paradise of powerful income and wealth growth. The reality, I think, is that the economy follows its own Catch-22: By taking prosperity for granted, people perversely subvert prosperity. The more we managers, investors, consumers - think that economic growth is guaranteed and that risk and…arrow_forward2.) Using the line drawing tool, plot and label the isocost line. Carefully follow the instructions above, and only draw the required objects. FILL IN BLANK d. Now suppose the price of labour rises to $5 per unit, but the firm still wants to produce 500 tires per day. Explain how a cost-minimizing firm adjusts to this change (with no change in technology). A cost-minimizing firm will be producing on ▼ The samedifferently slopedparallel isocost line. The firm will use ▼ moresameless labour and ▼ less the same amount of more capital and produce on ▼ a higher point on the same a lower point on the same a lower a higher isoquant curve.arrow_forward
 Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337091992Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337091992Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781285165912Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781285165912Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Brief Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Cours...EconomicsISBN:9781337091985Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Brief Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Cours...EconomicsISBN:9781337091985Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Economics, 7th Edition (MindTap Cou...EconomicsISBN:9781285165875Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics, 7th Edition (MindTap Cou...EconomicsISBN:9781285165875Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305971509Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305971509Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning





