
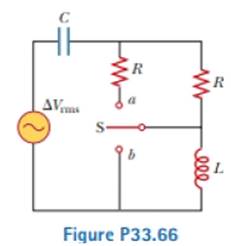
A capacitor, a coil, and two resistors of equal resistance are arranged in an AC circuit as shown in Figure P33.66 (page 1028). An AC source provides an emf of ΔVrms = 20.0 V at a frequency of 60.0 Hz. When the double throw switch S is open as shown in the figure, the rms current is 183 mA. When the switch is closed in position a, the rms current is 298 mA. When the switch is closed in position b, the rms current is 137 mA. Determine the values of (a) R, (b) C, and (c) L. (d) Is more than one set of values possible? Explain.
(a)
The value of resistance.
Answer to Problem 33.66AP
The value of resistance is
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The value of the source emf is
The expression for inductive reactance is,
Here,
The expression for capacitive reactance is,
Here,
The expression for the impedance of the circuit is.
Here,
The expression of the impedance in terms of voltage and current is,
Here,
The figure below depicts the circuit when the switch is in open condition.
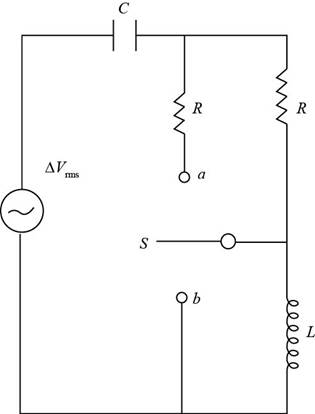
Figure (1)
From figure(1), for the throw switch in open condition:
Substitute
Substitute
For the throw switch at a position:
The two resistances are in parallel.
The expression of the equivalent resistance is.
Substitute
Substitute
Subtract equation (2) from equation (1).
Conclusion:
Therefore, the value of resistance is
(b)
The value of the capacitance.
Answer to Problem 33.66AP
The value of the capacitance is
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The value of the source emf is
The figure below depicts the circuit when switch is at position b.
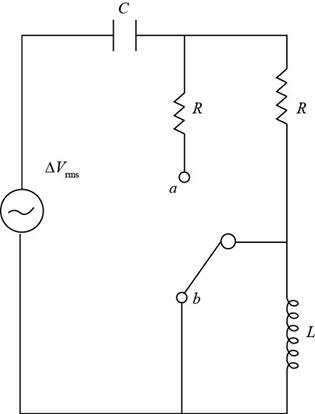
Figure (2)
From figure (2), for the throw switch at b position:
When the switch is at position b the inductor gets short circuited.
Substitute
Rearrange the above expression for value of
Substitute
Substitute
Rearrange the above equation for value of value of
Substitute
Conclusion:
Therefore, the value of the capacitance is
(c)
The value of the inductance.
Answer to Problem 33.66AP
The values of the inductance are
Explanation of Solution
Given info: The value of the source emf is
Substitute
For first value of the inductor,
Substitute
Substitute
Thus, the first value of the inductor is
For second value of the inductor,
Substitute
Substitute 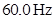 for f in the above expression.
for f in the above expression.
Thus, the second value of the inductor is
Conclusion:
Therefore, the values of the inductance are
(d)
Whether more than one set of value possible.
Answer to Problem 33.66AP
The resistance and capacitance has one set of values, the inductor has in two set of values.
Explanation of Solution
Given info: : The value of the source emf is
From the calculation in part (a),(b) and (c),
The value of resistance is
The value of capacitance is
The values of the inductor are
Hence the resistance and the capacitance has one value while the inductor has two set of value in the circuit.
Conclusion:
Therefore, the resistance and capacitance has one set of values, the inductor has in two set of values.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 33 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers
- 5. Three blocks, each with mass m, are connected by strings and are pulled to the right along the surface of a frictionless table with a constant force of magnitude F. The tensions in the strings connecting the masses are T1 and T2 as shown. m T1 T2 F m m How does the magnitude of tension T₁ compare to F? A) T₁ = F B) T₁ = (1/2)F C) T₁ = (1/3)F D) T₁ = 2F E) T₁ = 3Farrow_forwardUsing Coulombs Law, what is the magnitude of the electrical force between two protons located 1 meter apart from each other in Newtons?arrow_forwardCalculate the magnitude of the gravitational force between 2 protons located 1 meter apart from each other in Newtons using Newton's Law of Universal Gravitation.arrow_forward
- If the metal sphere on the Van de Graff has a charge of 0.14 Coulombs and the person has a mass of 62 kg, how much excess charge would the person need in order to levitate at a distance 25 cm from the center of the charged metal sphere if there is a distance 25 cm from the person to the sphere using Coulomb's Law to calculate the electrical force. Give your answer as the number of Coulombs (with no unit label, as usual).arrow_forwardA balloon is rubbed on a sweater, giving the balloon a negative charge by adding an extra 3.9 x 107 electrons compared to its neutral state. What is the magnitude of the net charge on the balloon, in Coulombs?arrow_forwardA ping pong ball and a tennis ball are dropped and there is a very small gap between them when the tennis ball hits the floor. Indicate the directions of the momentums of the ping pong ball and the tennis ball after the tennis ball collides with the floor, but before the balls collide with each other. (Drawing a diagram may be helpful.)arrow_forward
- Describe how the momentum of a single ball changes as it free falls from a height of approximately 1 m, collides with a hard floor, and rebounds.arrow_forwardIf the answer is 2.8, -2.8 or -8.4, it is not CORRECTarrow_forwardThree blocks, light connecting ropes, and a light frictionless pulley comprise a system, as shown in the figure. An external force of magnitude P is applied downward on block A, causing block A to accelerate downward at a constant 2.5 m/s2. The tension in the rope connecting block B and block C is equal to 60 N. (a) What is the magnitude of the force P? (b) What is the mass of block C?arrow_forward
- Current Attempt in Progress In the figure what is the net electric potential at point P due to the four particles if V = 0 at infinity, q = 2.12 fC, and d = 1.75 cm? d Number MI Units +qarrow_forwardCurrent Attempt in Progress In the figure what is the net electric potential at point P due to the four particles if V = 0 at infinity, q = 2.12 fC, and d = 1.75 cm? d Number MI Units +qarrow_forwardA 0.500 kg sphere moving with a velocity given by (2.00î – 2.60ĵ + 1.00k) m/s strikes another sphere of mass 1.50 kg moving with an initial velocity of (−1.00î + 2.00ĵ – 3.20k) m/s. (a) The velocity of the 0.500 kg sphere after the collision is (-0.90î + 3.00ĵ − 8.00k) m/s. Find the final velocity of the 1.50 kg sphere. R = m/s Identify the kind of collision (elastic, inelastic, or perfectly inelastic). ○ elastic O inelastic O perfectly inelastic (b) Now assume the velocity of the 0.500 kg sphere after the collision is (-0.250 + 0.850ĵ - 2.15k) m/s. Find the final velocity of the 1.50 kg sphere. ✓ = m/s Identify the kind of collision. O elastic O inelastic O perfectly inelastic (c) Take the velocity of the 0.500 kg sphere after the collision as (−1.00ỉ + 3.40] + ak) m/s. Find the value of a and the velocity of the 1.50 kg sphere after an elastic collision. (Two values of a are possible, a positive value and a negative value. Report each with their corresponding final velocities.) a…arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning





