
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY W/ALEKS
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781264905430
Author: SMITH
Publisher: MCG CUSTOM
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 3.2, Problem 3P
Classify a carbon atom by the number of carbons to which it is bonded can also be
done in more complex molecules that contain heteroatoms. Classify each
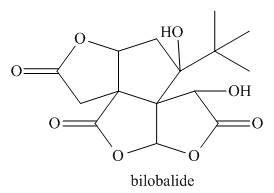
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Draw and describe the hybridization process of PROPENE, CH3CH=CH2. State the type of hybrid of each carbon, label all the bonds involve.
Carbenes (CR2) are neutral compounds with divalent carbon atoms. Propose two different ways that carbenes could exist. Provide the hybridization of each carbene carbon and predict the bond angles based on what you know about hybridization
In benzene, the sideways overlap of p orbitals yields
ΟΔ
π
Ο α
σ
β
molecular orbitals.
Chapter 3 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY W/ALEKS
Ch. 3.1 - Prob. 1PCh. 3.2 - (a) Classify the carbon atoms in each compound as...Ch. 3.2 - Problem 3.3 Classify a carbon atom by the number...Ch. 3.2 - Classify each alkyl halide and alcohol as , or...Ch. 3.2 - Prob. 5PCh. 3.2 - Prob. 6PCh. 3.2 - Draw the structure of a compound of molecular...Ch. 3.2 - Prob. 8PCh. 3.2 - Prob. 9PCh. 3.2 - Draw the structure of a compound fitting each...
Ch. 3.4 - Predict which compound in each pair has the higher...Ch. 3.4 - Prob. 17PCh. 3.4 - a Label the hydrophobic and hydrophilic portions...Ch. 3.5 - Prob. 21PCh. 3 - 3.29
Identify the functional groups in the...Ch. 3 - Prob. 32PCh. 3 - 3.31 For each alkane: (a) classify each carbon...Ch. 3 - 3.32 Identify the functional groups in each...Ch. 3 - 3.33 Identify each functional group located in the...Ch. 3 - 3.34 (a)Identify the functional groups in...Ch. 3 - Draw seven constitutional isomers with molecular...Ch. 3 - Prob. 38PCh. 3 - Prob. 39PCh. 3 - Prob. 40PCh. 3 - Intramolecular force of attraction are often...Ch. 3 - 3.40 (a) Draw four compounds with molecular...Ch. 3 - 3.41 Rank the compounds in each group in order of...Ch. 3 - Explain why CH3CH2NHCH3 has higher boiling point...Ch. 3 - Prob. 45PCh. 3 - 3.44 Rank the following compounds in order of...Ch. 3 - Prob. 47PCh. 3 - 3.50 Predict the solubility of each of the...Ch. 3 - Prob. 52PCh. 3 - Prob. 53PCh. 3 - 3.53 THC is the active component in marijuana, and...Ch. 3 - Prob. 55PCh. 3 - Prob. 56PCh. 3 - 3.60 Quinapril (trade name Accupril) is a drug...Ch. 3 - 3.61 Answer each question about oxycodone, a...Ch. 3 - Prob. 65PCh. 3 - Prob. 66PCh. 3 - 3.64 Explain why A is less water soluble than B,...Ch. 3 - 3.65 Recall from section 1.10B that there is...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- What is the major difference between an antiaromatic and aromatic compound? Antiaromatic compounds have at least one sp³ hybridized atom in the ring. Antiaromatic compounds are not conjugated. Only aromatic compounds have 4n+ 2 pi electrons. The structure must be cyclic for aromatic but not antiaromatic compounds. Aromatic, not Antiaromatic compounds, are planar.arrow_forwardUsing Hydrogenation Data to Determine the Number of Rings and π Bonds in a Molecule How many rings and π bonds are contained in a compound of molecular formula C8H12 that is hydrogenated to a compound of molecular formula C8H14?arrow_forwardSketch the ultraviolet absorption spectrum of 1,3-Butadiene, matching peaks to electronic transitions. show that four isolated p orbital on carbon atoms combine to form pi orbitalarrow_forward
- Draw structural formulas for all linear (not ring) constitutional isomers that have the molecular formula C4H4 and indicate which of the following they possess: 1. sp hybridized carbon atoms 2. sp2 hybridized carbon atoms 3. sp3 hybridized carbon atoms 4. sigma bonds, pi bondsarrow_forward2) Show how the carbon p orbitals overlap to form the lowest energy л molecular orbital of 1,3- butadiene.arrow_forwardCH3+ and CH3– are two highly reactive carbon species. What is the predicted hybridization and geometry around each carbon atom?arrow_forward
- Linoleic acid is an essential fatty acid found in many vegetable oils, such as soy, peanut, and cottonseed. A key structural feature of the molecule is the cis orientation around its two double bonds, where R1 and R2 represent two different groups that form the rest of the molecule. (a) How many different compounds are possible, changing only the cis-trans arrangements around these two double bonds? (b) How many are possible for a similar compound with three double bonds?arrow_forward1. Explain the two ways that methane (CH4) illustrates the need for hybridized molecular bonds. Draw a picture to represent the hybridization of carbon's orbitals and their overlap with hydrogen's. Label each orbital used in bonding with its letters and each bond as sigma or pi.arrow_forwardнн H H а С—Сь H2 H-Ć-Č–H b + a H Many reactions involve a change in hybridization of one or more atoms in the starting material. In this reaction, determine the hybridization of the indicated atoms in the organic starting material, and determine if they have changed hybridization during the reaction. Atom a: Reactant: Product: Atom b: Reactant: Product:arrow_forward
- Draw the Lewis Structures for the following molecules and give the hybridization for each carbon atom. a) 2-methyl-1-butanol, CH3CH2CH2(CH3)CH2OH b) Ethyl propanoate, CH3CH2CO2CH2CH3 c) Methyl cyanide (aka acetonitrile), CH3CN d) Isopropyl phenyl ether, (CH3)2CHOC6H5 e) N,N-dimethylpentamide, CH3CH2CH2CH2CON(CH3)2arrow_forwardCaffeine is an aromatic compound. Using resonance structures, show how the sixmember ring can be drawn in its "benzoid" form. Indicate the hybridization of each nitrogen atom and specify the hybridization of the orbital occupied by each of the lone pairs.Write all possible reasonable resonance structures for the following compounds. Label the major and minor contributors to each resonance hybrid. N : Z— N:arrow_forwardMany reactions involve a change in hybridization of one or more atoms in the starting material. In following reaction, identify the atoms in the organic starting material that change hybridization and indicate the change.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: Principles and Practice
Chemistry
ISBN:9780534420123
Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward Mercer
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning
ENVIRONMENTAL POLLUTION; Author: 7activestudio;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=oxtMFmDTv3Q;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY