
Concept explainers
a)
Interpretation:
Mechanism for the given acid-base reaction has to be drawn; the acid, base, conjugate acid, and conjugate base has to be labelled in the reaction.
Concept Introduction:
Bronsted-Lowry Acids and bases: Acid is defined as proton transfer and base is defined as proton acceptor; Bronsted acid and base reaction involves the transfer of Proton.
Conjugate acid: Protonated Base that gets results is called conjugate acid of the given base.
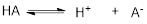
In above reaction, the acid
Conjugate Base: Deprotonated Acid that gets results is called conjugate Base of the given Acid.
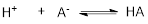
In above reaction, the base
Flow of electron density: Curved arrow notation: In the acid-base reaction, the flow of electron from high electron density to low density using curved arrow.
b)
Interpretation:
Mechanism for the given acid-base reaction has to be drawn; the acid, base, conjugate acid, and conjugate base has to be labelled in the reaction.
Concept Introduction:
Bronsted-Lowry Acids and bases: Acid is defined as proton transfer and base is defined as proton acceptor; Bronsted acid and base reaction involves the transfer of Proton.
Conjugate acid: Protonated Base that gets results is called conjugate acid of the given base.
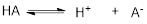
In above reaction, the acid
Conjugate Base: Deprotonated Acid that gets results is called conjugate Base of the given Acid.
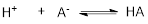
In above reaction, the base
Flow of electron density: Curved arrow notation: In the acid-base reaction, the flow of electron from high electron density to low density using curved arrow.
c)
Interpretation:
Mechanism for the given acid-base reaction has to be drawn; the acid, base, conjugate acid, and conjugate base has to be labelled in the reaction.
Concept Introduction:
Bronsted-Lowry Acids and bases: Acid is defined as proton transfer and base is defined as proton acceptor; Bronsted acid and base reaction involves the transfer of Proton.
Conjugate acid: Protonated Base that gets results is called conjugate acid of the given base.
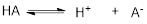
In above reaction, the acid
Conjugate Base: Deprotonated Acid that gets results is called conjugate Base of the given Acid.
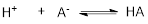
In above reaction, the base
Flow of electron density: Curved arrow notation: In the acid-base reaction, the flow of electron from high electron density to low density using curved arrow.
d)
Interpretation:
Mechanism for the given acid-base reaction has to be drawn; the acid, base, conjugate acid, and conjugate base has to be labelled in the reaction.
Concept Introduction:
Bronsted-Lowry Acids and bases: Acid is defined as proton transfer and base is defined as proton acceptor; Bronsted acid and base reaction involves the transfer of Proton.
Conjugate acid: Protonated Base that gets results is called conjugate acid of the given base.
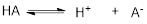
In above reaction, the acid
Conjugate Base: Deprotonated Acid that gets results is called conjugate Base of the given Acid.
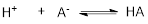
In above reaction, the base
Flow of electron density: Curved arrow notation: In the acid-base reaction, the flow of electron from high electron density to low density using curved arrow.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 3 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Explain the importance of having a sampling plan with respect to food analysis. Explain the importance of having a sampling plan with respect to food analysis. Provide examples.arrow_forwardPlease predict the products for each of the following reactions. Clearly show the regiochemistry (Markovnikov vs anti-Markovnikov) and stereochemistry (syn- vs anti- or both). If a mixture of enantiomers is formed, please draw all the enantiomers. cold KMnO4, NaOH 2. DMS 1. 03 CH3OH Br2 1. 03 2. (CH3)2S H₂ Pd or Pt (catalyst) HBr 18 19 20 1 HBr ROOR (peroxide) H₂O H₂SO4 HCI HI 17 16 6 15 MCPBA 1. BH3 THF 2. H₂O2, NaOH 1. OsO4 2. H₂O₂ 110 CH3CO₂H (peroxyacid) 1. MCPBA 2. H₂O* Br2 H₂O BH3 THF B12 EtOH Pd or Ni (catalyst) D₂ (deuterium) Bra A B C D H OH H OH OH H OH α α α OH H OH OH фон d H "Harrow_forwardBriefly indicate the models that describe the structure of the interface: Helmholtz-Perrin, Gouy-Chapman, Stern and Grahame models.arrow_forward
- Using Benzene as starting materid show how each of the Following molecules Contel Ve syntheswed CHI 9. b -50311 с CHY 503H Ночто d. อ •NOV e 11-0-650 NO2arrow_forwardThe molecule PYRIDINE, 6th electrons and is therefore aromatre and is Assigned the Following structure contering Since aromatk moleculoy undergo electrophilic anomatic substitution, Pyridine shodd undergo The Following reaction + HNO3 12504 a. write all of the possible Mononitration Products that could Result From this reaction 18. Bared upon the reaction mechanison determime which of these producty would be the major Product of the hegetionarrow_forwarda. Explain Why electron withdrawing groups tend to be meta-Directors. Your answer Should lyclude all apropriate. Resonance contributing Structures fo. Explain why -ll is an outho -tura drccton even though chlorine has a very High Electronegativityarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





