
Student Solutions Manual, Single Variable for Calculus: Early Transcendentals
2nd Edition
ISBN: 9780321954329
Author: William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 3.1, Problem 55E
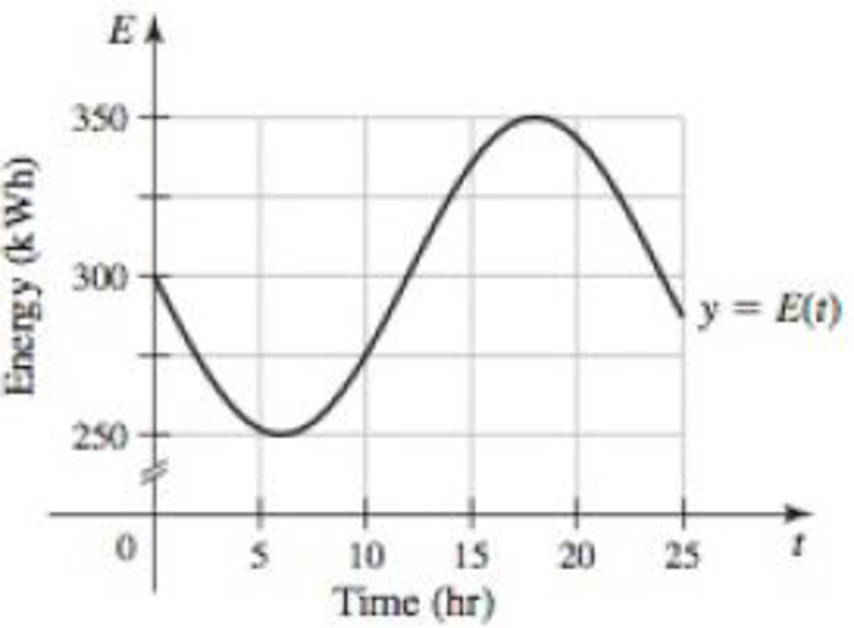
Power and energy Energy is the capacity to do work, and power is the rate at which energy is used or consumed. Therefore, if E(t) is the energy function for a system, then P(t) = E′(t) is the power function. A unit of energy is the kilowatt-hour (1 kWh is the amount of energy needed to light ten 100-W lightbulbs for an hour); the corresponding units for power are kilowatts. The following figure shows the energy consumed by a small community over a 25-hour period.
- a. Estimate the power at t = 10 and t = 20 hr. Be sure to include units in your calculation.
- b. At what times on the interval [0, 25] is the power zero?
- c. At what times on the interval [0, 25] is the power a maximum?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Robbie
Bearing Word Problems
Angles
name:
Jocelyn
date: 1/18
8K
2. A Delta airplane and an SouthWest airplane take off from an airport
at the same time. The bearing from the airport to the Delta plane is
23° and the bearing to the SouthWest plane is 152°. Two hours later
the Delta plane is 1,103 miles from the airport and the SouthWest
plane is 1,156 miles from the airport. What is the distance between the
two planes? What is the bearing from the Delta plane to the SouthWest
plane? What is the bearing to the Delta plane from the SouthWest
plane?
Delta
y
SW
Angles
ThreeFourthsMe MATH
2
Find the derivative of the function.
m(t) = -4t (6t7 - 1)6
Find the derivative of the function.
y= (8x²-6x²+3)4
Chapter 3 Solutions
Student Solutions Manual, Single Variable for Calculus: Early Transcendentals
Ch. 3.1 - Use definition (1) (p. 127) for the slope of a...Ch. 3.1 - Explain why the slope of a secant line can be...Ch. 3.1 - Explain why the slope of the tangent line can be...Ch. 3.1 - Prob. 4ECh. 3.1 - Given a function f and a point a in its domain,...Ch. 3.1 - Explain the relationships among the slope of a...Ch. 3.1 - Prob. 7ECh. 3.1 - Prob. 8ECh. 3.1 - Equations of tangent lines by definition (1) a....Ch. 3.1 - Equations of tangent lines by definition (1) a....
Ch. 3.1 - Equations of tangent lines by definition (1) a....Ch. 3.1 - Prob. 12ECh. 3.1 - Equations of tangent lines by definition (1) a....Ch. 3.1 - Equations of tangent lines by definition (1) a....Ch. 3.1 - Equations of tangent lines by definition (2) a....Ch. 3.1 - Equations of tangent lines by definition (2) a....Ch. 3.1 - Equations of tangent lines by definition (2) a....Ch. 3.1 - Equations of tangent lines by definition (2) a....Ch. 3.1 - Equations of tangent lines by definition (2) a....Ch. 3.1 - Equations of tangent lines by definition (2) a....Ch. 3.1 - Equations of tangent lines by definition (2) a....Ch. 3.1 - Equations of tangent lines by definition (2) a....Ch. 3.1 - Equations of tangent lines by definition (2) a....Ch. 3.1 - Equations of tangent lines by definition (2) a....Ch. 3.1 - Equations of tangent lines by definition (2) a....Ch. 3.1 - Prob. 26ECh. 3.1 - Derivatives and tangent lines a. For the following...Ch. 3.1 - Derivatives and tangent lines a. For the following...Ch. 3.1 - Derivatives and tangent lines a. For the following...Ch. 3.1 - Derivatives and tangent lines a. For the following...Ch. 3.1 - Derivatives and tangent lines a. For the following...Ch. 3.1 - Derivatives and tangent lines a. For the following...Ch. 3.1 - Derivatives and tangent lines a. For the following...Ch. 3.1 - Derivatives and tangent lines a. For the following...Ch. 3.1 - Derivatives and tangent lines a. For the following...Ch. 3.1 - Derivatives and tangent lines a. For the following...Ch. 3.1 - Prob. 37ECh. 3.1 - Prob. 38ECh. 3.1 - Prob. 39ECh. 3.1 - Prob. 40ECh. 3.1 - A derivative formula a. Use the definition of the...Ch. 3.1 - A derivative formula a. Use the definition of the...Ch. 3.1 - Prob. 43ECh. 3.1 - Prob. 44ECh. 3.1 - Prob. 45ECh. 3.1 - Prob. 46ECh. 3.1 - Explain why or why not Determine whether the...Ch. 3.1 - Slope of a line Consider the line f(x) = mx + b,...Ch. 3.1 - Calculating derivatives a. For the following...Ch. 3.1 - Calculating derivatives a. For the following...Ch. 3.1 - Calculating derivatives a. For the following...Ch. 3.1 - Calculating derivatives a. For the following...Ch. 3.1 - Analyzing slopes Use the points A, B, C, D, and E...Ch. 3.1 - Analyzing slopes Use the points A, B, C, D, and E...Ch. 3.1 - Power and energy Energy is the capacity to do...Ch. 3.1 - Population of Las Vegas Let p(t) represent the...Ch. 3.1 - Find the function The following limits represent...Ch. 3.1 - Find the function The following limits represent...Ch. 3.1 - Find the function The following limits represent...Ch. 3.1 - Find the function The following limits represent...Ch. 3.1 - Prob. 61ECh. 3.1 - Looking ahead: Derivative of xn Use the definition...Ch. 3.1 - Prob. 63ECh. 3.1 - Approximating derivatives Assuming the limit...Ch. 3.1 - Approximating derivatives Assuming the limit...Ch. 3.1 - Prob. 66ECh. 3.1 - Approximating derivatives Assuming the limit...Ch. 3.2 - Explain why f(x) could be positive or negative at...Ch. 3.2 - Prob. 2ECh. 3.2 - If f is differentiable at a, must f be continuous...Ch. 3.2 - If f is continuous at a, must f be differentiable...Ch. 3.2 - Derivatives from graphs Use the graph of f to...Ch. 3.2 - Derivatives from graphs Use the graph of f to...Ch. 3.2 - Matching functions with derivatives Match graphs...Ch. 3.2 - Matching derivatives with functions Match graphs...Ch. 3.2 - Matching functions with derivatives Match the...Ch. 3.2 - Sketching derivatives Reproduce the graph of f and...Ch. 3.2 - Sketching derivatives Reproduce the graph of f and...Ch. 3.2 - Sketching derivatives Reproduce the graph of f and...Ch. 3.2 - Graphing the derivative with asymptotes Sketch a...Ch. 3.2 - Graphing the derivative with asymptotes Sketch a...Ch. 3.2 - Where is the function continuous? Differentiable?...Ch. 3.2 - Where is the function continuous? Differentiable?...Ch. 3.2 - Explain why or why not Determine whether the...Ch. 3.2 - Prob. 18ECh. 3.2 - Finding f from f Sketch the graph of f(x) = x....Ch. 3.2 - Prob. 20ECh. 3.2 - Normal lines A line perpendicular to another line...Ch. 3.2 - Normal lines A line perpendicular to another line...Ch. 3.2 - Normal lines A line perpendicular to another line...Ch. 3.2 - Prob. 24ECh. 3.2 - Aiming a tangent line Given the function f and the...Ch. 3.2 - Aiming a tangent line Given the function f and the...Ch. 3.2 - Prob. 27ECh. 3.2 - Prob. 28ECh. 3.2 - Voltage on a capacitor A capacitor is a device in...Ch. 3.2 - Logistic growth A common model for population...Ch. 3.2 - One-sided derivatives The right-sided and...Ch. 3.2 - One-sided derivatives The right-sided and...Ch. 3.2 - Prob. 33ECh. 3.2 - Prob. 34ECh. 3.2 - Prob. 35ECh. 3.2 - Vertical tangent lines If a function f is...Ch. 3.2 - Continuity is necessary for differentiability a....Ch. 3.3 - Assume the derivatives of f and g exist in...Ch. 3.3 - Assume the derivatives of f and g exist in...Ch. 3.3 - Assume the derivatives of f and g exist in...Ch. 3.3 - Prob. 4ECh. 3.3 - Assume the derivatives of f and g exist in...Ch. 3.3 - Prob. 6ECh. 3.3 - Prob. 7ECh. 3.3 - Derivatives of power and constant functions Find...Ch. 3.3 - Prob. 9ECh. 3.3 - Derivatives of power and constant functions Find...Ch. 3.3 - Derivatives of power and constant functions Find...Ch. 3.3 - Prob. 12ECh. 3.3 - Derivatives of constant multiples of functions...Ch. 3.3 - Prob. 14ECh. 3.3 - Prob. 15ECh. 3.3 - Derivatives of constant multiples of functions...Ch. 3.3 - Prob. 17ECh. 3.3 - Prob. 18ECh. 3.3 - Derivatives of the sum of functions Find the...Ch. 3.3 - Prob. 20ECh. 3.3 - Prob. 21ECh. 3.3 - Prob. 22ECh. 3.3 - Prob. 23ECh. 3.3 - Prob. 24ECh. 3.3 - Derivatives of products Find the derivative of the...Ch. 3.3 - Derivatives of products Find the derivative of the...Ch. 3.3 - Prob. 27ECh. 3.3 - Prob. 28ECh. 3.3 - Derivatives of products Find the derivative of the...Ch. 3.3 - Derivatives of products Find the derivative of the...Ch. 3.3 - Derivatives of products Find the derivative of the...Ch. 3.3 - Derivatives of products Find the derivative of the...Ch. 3.3 - Derivatives of products Find the derivative of the...Ch. 3.3 - Derivatives of products Find the derivative of the...Ch. 3.3 - Equations of tangent lines a. Find an equation of...Ch. 3.3 - Equations of tangent lines a. Find an equation of...Ch. 3.3 - Equations of tangent lines a. Find an equation of...Ch. 3.3 - Equations of tangent lines a. Find an equation of...Ch. 3.3 - Finding slope locations Let f(x) = x3 6x + 5. a....Ch. 3.3 - Finding slope locations Let f(t) = t3 27t + 5. a....Ch. 3.3 - Finding slope locations Let f(x) = 2x3 3x2 12x +...Ch. 3.3 - Finding slope locations Let f(x) = 2ex 6x. a....Ch. 3.3 - Finding slope locations Let f(x)=4xx. a. Find all...Ch. 3.3 - Higher-order derivatives Find f(x), f(x), and f(x)...Ch. 3.3 - Higher-order derivatives Find f(x), f(x), and f(x)...Ch. 3.3 - Higher-order derivatives Find f(x), f(x), and f(x)...Ch. 3.3 - Higher-order derivatives Find f(x), f(x), and f(x)...Ch. 3.3 - Higher-order derivatives Find f(x), f(x), and f(x)...Ch. 3.3 - Explain why or why not Determine whether the...Ch. 3.3 - Tangent lines Suppose f(3) = 1 and f(3) = 4. Let...Ch. 3.3 - Derivatives from tangent lines Suppose the line...Ch. 3.3 - Tangent line Find the equation of the line tangent...Ch. 3.3 - Tangent line given Determine the constants b and c...Ch. 3.3 - Derivatives from a graph Let F = f + g and G = 3f ...Ch. 3.3 - Derivatives from a graph Let F = f + g and G = 3f ...Ch. 3.3 - Derivatives from a graph Let F = f + g and G = 3f ...Ch. 3.3 - Derivatives from a graph Let F = f + g and G = 3f ...Ch. 3.3 - Derivatives from a table Use the table to find the...Ch. 3.3 - Derivatives from a table Use the table to find the...Ch. 3.3 - Derivatives from a table Use the table to find the...Ch. 3.3 - Derivatives from limits The following limits...Ch. 3.3 - Derivatives from limits The following limits...Ch. 3.3 - Derivatives from limits The following limits...Ch. 3.3 - Prob. 64ECh. 3.3 - Prob. 65ECh. 3.3 - Calculator limits Use a calculator to approximate...Ch. 3.3 - Prob. 67ECh. 3.3 - Prob. 68ECh. 3.3 - Prob. 69ECh. 3.3 - Projectile trajectory The position of a small...Ch. 3.3 - Prob. 71ECh. 3.3 - Cell growth When observations begin at t = 0, a...Ch. 3.3 - City urbanization City planners model the size of...Ch. 3.3 - Constant Rule proof For the constant function f(x)...Ch. 3.3 - Prob. 75ECh. 3.3 - Looking ahead: Power Rule for negative integers...Ch. 3.3 - Prob. 77ECh. 3.3 - Computing the derivative of f(x) = ex a. Use the...Ch. 3.3 - Prob. 79ECh. 3.3 - Computing the derivative of f(x) = x2ex a. Use the...Ch. 3.4 - How do you find the derivative of the product of...Ch. 3.4 - How do you find the derivative of the quotient of...Ch. 3.4 - Prob. 3ECh. 3.4 - Show two ways to differentiate f(x) = 1/x10.Ch. 3.4 - Prob. 5ECh. 3.4 - Prob. 6ECh. 3.4 - Derivatives of products Find the derivative of the...Ch. 3.4 - Derivatives of products Find the derivative of the...Ch. 3.4 - Derivatives of products Find the derivative of the...Ch. 3.4 - Derivatives of products Find the derivative of the...Ch. 3.4 - Derivatives of products Find the derivative of the...Ch. 3.4 - Derivatives of products Find the derivative of the...Ch. 3.4 - Derivatives of products Find the derivative of the...Ch. 3.4 - Prob. 14ECh. 3.4 - Prob. 15ECh. 3.4 - Prob. 16ECh. 3.4 - Derivatives by two different methods a. Use the...Ch. 3.4 - Derivatives by two different methods a. Use the...Ch. 3.4 - Derivatives of quotients Find the derivative of...Ch. 3.4 - Derivatives of quotients Find the derivative of...Ch. 3.4 - Derivatives of quotients Find the derivative of...Ch. 3.4 - Derivatives of quotients Find the derivative of...Ch. 3.4 - Derivatives of quotients Find the derivative of...Ch. 3.4 - Prob. 24ECh. 3.4 - Derivatives of quotients Find the derivative of...Ch. 3.4 - Derivatives of quotients Find the derivative of...Ch. 3.4 - Derivatives of quotients Find the derivative of...Ch. 3.4 - Derivatives of quotients Find the derivative of...Ch. 3.4 - Derivatives by two different methods a. Use the...Ch. 3.4 - Prob. 30ECh. 3.4 - Derivatives by two different methods a. Use the...Ch. 3.4 - Derivatives by two different methods a. Use the...Ch. 3.4 - Equations of tangent lines a. Find an equation of...Ch. 3.4 - Equations of tangent lines a. Find an equation of...Ch. 3.4 - Equations of tangent lines a. Find an equation of...Ch. 3.4 - Equations of tangent lines a. Find an equation of...Ch. 3.4 - Extended Power Rule Find the derivative of the...Ch. 3.4 - Extended Power Rule Find the derivative of the...Ch. 3.4 - Extended Power Rule Find the derivative of the...Ch. 3.4 - Extended Power Rule Find the derivative of the...Ch. 3.4 - Extended Power Rule Find the derivative of the...Ch. 3.4 - Extended Power Rule Find the derivative of the...Ch. 3.4 - Prob. 43ECh. 3.4 - Prob. 44ECh. 3.4 - Prob. 45ECh. 3.4 - Prob. 46ECh. 3.4 - Prob. 47ECh. 3.4 - Prob. 48ECh. 3.4 - Prob. 49ECh. 3.4 - Prob. 50ECh. 3.4 - Population growth Consider the following...Ch. 3.4 - Prob. 52ECh. 3.4 - Antibiotic decay The half-life of an antibiotic in...Ch. 3.4 - Bank account A 200 investment in a savings account...Ch. 3.4 - Finding slope locations Let f(x) = xe2x. a. Find...Ch. 3.4 - Prob. 56ECh. 3.4 - Combining rules Compute the derivative of the...Ch. 3.4 - Combining rules Compute the derivative of the...Ch. 3.4 - Combining rules Compute the derivative of the...Ch. 3.4 - Combining rules Compute the derivative of the...Ch. 3.4 - Prob. 61ECh. 3.4 - Higher-order derivatives Find f(x), f(x), and...Ch. 3.4 - Prob. 63ECh. 3.4 - First and second derivatives Find f(x) and f(x)....Ch. 3.4 - First and second derivatives Find f(x) and f(x)....Ch. 3.4 - Choose your method Use any method to evaluate the...Ch. 3.4 - Choose your method Use any method to evaluate the...Ch. 3.4 - Prob. 68ECh. 3.4 - Choose your method Use any method to evaluate the...Ch. 3.4 - Choose your method Use any method to evaluate the...Ch. 3.4 - Choose your method Use any method to evaluate the...Ch. 3.4 - Tangent lines Suppose f(2) = 2 and f(2) = 3. Let...Ch. 3.4 - The Witch of Agnesi The graph of y=a3x2+a2, where...Ch. 3.4 - Derivatives from a table Use the following table...Ch. 3.4 - Derivatives from a table Use the following table...Ch. 3.4 - Derivatives from a table Use the following table...Ch. 3.4 - Derivatives from a table Use the following table...Ch. 3.4 - Derivatives from a table Use the following table...Ch. 3.4 - Derivatives from a table Use the following table...Ch. 3.4 - Derivatives from tangent lines Suppose the line...Ch. 3.4 - Electrostatic force The magnitude of the...Ch. 3.4 - Gravitational force The magnitude of the...Ch. 3.4 - Prob. 83ECh. 3.4 - Prob. 84ECh. 3.4 - Prob. 85ECh. 3.4 - Proof of the Quotient Rule Let F = f/g be the...Ch. 3.4 - Product Rule for the second derivative Assuming...Ch. 3.4 - Prob. 88ECh. 3.4 - Derivative of ekx for negative integers k Use the...Ch. 3.4 - Prob. 90ECh. 3.4 - Product Rule for three functions Assume that f, g,...Ch. 3.4 - One of the Leibniz Rules One of several Leibniz...Ch. 3.5 - Why is it not possible to evaluate limx0sinxx by...Ch. 3.5 - How is limx0sinxx used in this section?Ch. 3.5 - Explain why the Quotient Rule is used to determine...Ch. 3.5 - How can you use the derivatives ddx(sinx)=cosx,...Ch. 3.5 - Let f(x) = sin x. What is the value of f()?Ch. 3.5 - Where does the graph of sin x have a horizontal...Ch. 3.5 - Trigonometric limits Use Theorem 3.11 to evaluate...Ch. 3.5 - Trigonometric limits Use Theorem 3.11 to evaluate...Ch. 3.5 - Trigonometric limits Use Theorem 3.11 to evaluate...Ch. 3.5 - Trigonometric limits Use Theorem 3.11 to evaluate...Ch. 3.5 - Trigonometric limits Use Theorem 3.11 to evaluate...Ch. 3.5 - Trigonometric limits Use Theorem 3.11 to evaluate...Ch. 3.5 - Trigonometric limits Use Theorem 3.11 to evaluate...Ch. 3.5 - Trigonometric limits Use Theorem 3.11 to evaluate...Ch. 3.5 - Trigonometric limits Use Theorem 3.11 to evaluate...Ch. 3.5 - Trigonometric limits Use Theorem 3.11 to evaluate...Ch. 3.5 - Calculating derivatives Find dy/dx for the...Ch. 3.5 - Calculating derivatives Find dy/dx for the...Ch. 3.5 - Calculating derivatives Find dy/dx for the...Ch. 3.5 - Calculating derivatives Find dy/dx for the...Ch. 3.5 - Calculating derivatives Find dy/dx for the...Ch. 3.5 - Prob. 22ECh. 3.5 - Calculating derivatives Find dy/dx for the...Ch. 3.5 - Calculating derivatives Find dy/dx for the...Ch. 3.5 - Calculating derivatives Find dy/dx for the...Ch. 3.5 - Prob. 26ECh. 3.5 - Calculating derivatives Find dy/dx for the...Ch. 3.5 - Calculating derivatives Find dy/dx for the...Ch. 3.5 - Derivatives of other trigonometric functions...Ch. 3.5 - Derivatives of other trigonometric functions...Ch. 3.5 - Derivatives of other trigonometric functions...Ch. 3.5 - Derivatives involving other trigonometric...Ch. 3.5 - Derivatives involving other trigonometric...Ch. 3.5 - Derivatives involving other trigonometric...Ch. 3.5 - Derivatives involving other trigonometric...Ch. 3.5 - Derivatives involving other trigonometric...Ch. 3.5 - Derivatives involving other trigonometric...Ch. 3.5 - Derivatives involving other trigonometric...Ch. 3.5 - Derivatives involving other trigonometric...Ch. 3.5 - Derivatives involving other trigonometric...Ch. 3.5 - Second-order derivatives Find y for the following...Ch. 3.5 - Prob. 42ECh. 3.5 - Second-order derivatives Find y for the following...Ch. 3.5 - Second-order derivatives Find y for the following...Ch. 3.5 - Second-order derivatives Find y for the following...Ch. 3.5 - Second-order derivatives Find y for the following...Ch. 3.5 - Second-order derivatives Find y for the following...Ch. 3.5 - Second-order derivatives Find y for the following...Ch. 3.5 - Explain why or why not Determine whether the...Ch. 3.5 - Trigonometric limits Evaluate the following limits...Ch. 3.5 - Trigonometric limits Evaluate the following limits...Ch. 3.5 - Trigonometric limits Evaluate the following limits...Ch. 3.5 - Prob. 53ECh. 3.5 - Prob. 54ECh. 3.5 - Prob. 55ECh. 3.5 - Calculating derivatives Find dy/dx for the...Ch. 3.5 - Calculating derivatives Find dy/dx for the...Ch. 3.5 - Calculating derivatives Find dy/dx for the...Ch. 3.5 - Prob. 59ECh. 3.5 - Prob. 60ECh. 3.5 - Calculating derivatives Find dy/dx for the...Ch. 3.5 - Equations of tangent lines a. Find an equation of...Ch. 3.5 - Equations of tangent lines a. Find an equation of...Ch. 3.5 - Equations of tangent lines a. Find an equation of...Ch. 3.5 - Equations of tangent lines a. Find an equation of...Ch. 3.5 - Locations of tangent lines a. For what values of x...Ch. 3.5 - Locations of horizontal tangent lines For what...Ch. 3.5 - Matching Match the graphs of the functions in ad...Ch. 3.5 - Velocity of an oscillator An object oscillates...Ch. 3.5 - Prob. 70ECh. 3.5 - A differential equation A differential equation is...Ch. 3.5 - Using identities Use the identity sin 2x = 2 sin x...Ch. 3.5 - Prob. 73ECh. 3.5 - Prob. 74ECh. 3.5 - Proof of ddx(cosx)=sinx Use the definition of the...Ch. 3.5 - Continuity of a piecewise function Let...Ch. 3.5 - Continuity of a piecewise function Let...Ch. 3.5 - Prob. 78ECh. 3.5 - Prob. 79ECh. 3.5 - Prob. 80ECh. 3.5 - Prob. 81ECh. 3.5 - Prob. 82ECh. 3.5 - Prob. 83ECh. 3.5 - Prob. 84ECh. 3.5 - Prob. 85ECh. 3.5 - Prob. 86ECh. 3.6 - Explain the difference between the average rate of...Ch. 3.6 - Complete the following statement. If dydx is...Ch. 3.6 - Complete the following statement: If dydx is...Ch. 3.6 - What is the difference between the velocity and...Ch. 3.6 - Define the acceleration of an object moving in a...Ch. 3.6 - An object moving along a line has a constant...Ch. 3.6 - Prob. 7ECh. 3.6 - Explain why a decreasing demand function has a...Ch. 3.6 - Highway travel A state patrol station is located...Ch. 3.6 - Airline travel The following figure shows the...Ch. 3.6 - Position, velocity, and acceleration Suppose the...Ch. 3.6 - Position, velocity, and acceleration Suppose the...Ch. 3.6 - Position, velocity, and acceleration Suppose the...Ch. 3.6 - Position, velocity, and acceleration Suppose the...Ch. 3.6 - Position, velocity, and acceleration Suppose the...Ch. 3.6 - Position, velocity, and acceleration Suppose the...Ch. 3.6 - A stone thrown vertically on Mars Suppose a stone...Ch. 3.6 - Prob. 18ECh. 3.6 - Population growth in Georgia The population of the...Ch. 3.6 - Consumer price index The U.S. consumer price index...Ch. 3.6 - Average and marginal cost Consider the following...Ch. 3.6 - Average and marginal cost Consider the following...Ch. 3.6 - Average and marginal cost Consider the following...Ch. 3.6 - Average and marginal cost Consider the following...Ch. 3.6 - Demand and elasticity Based on sales data over the...Ch. 3.6 - Demand and elasticity The economic advisor of a...Ch. 3.6 - Prob. 27ECh. 3.6 - Prob. 28ECh. 3.6 - Explain why or why not Determine whether the...Ch. 3.6 - A feather dropped on the moon On the moon, a...Ch. 3.6 - Comparing velocities A stone is thrown vertically...Ch. 3.6 - Comparing velocities Two stones are thrown...Ch. 3.6 - Matching heights A stone is thrown from the edge...Ch. 3.6 - Velocity of a car The graph shows the position s =...Ch. 3.6 - Velocity from position The graph of s = f(t)...Ch. 3.6 - Fish length Assume the length L (in cm) of a...Ch. 3.6 - Average and marginal profit Let C(x) represent the...Ch. 3.6 - Average and marginal profit Let C(x) represent the...Ch. 3.6 - Average and marginal profit Let C(x) represent the...Ch. 3.6 - Average and marginal profit Let C(x) represent the...Ch. 3.6 - Prob. 41ECh. 3.6 - Average and marginal production Economists use...Ch. 3.6 - Velocity of a marble The position (in meters) of a...Ch. 3.6 - Tree growth Let b represent the base diameter of a...Ch. 3.6 - Prob. 45ECh. 3.6 - Diminishing returns A cost function of the form...Ch. 3.6 - Revenue function A store manager estimates that...Ch. 3.6 - Fuel economy Suppose you own a fuel-efficient...Ch. 3.6 - Spring oscillations A spring hangs from the...Ch. 3.6 - Pressure and altitude Earths atmospheric pressure...Ch. 3.6 - A race Jean and Juan run a one-lap race on a...Ch. 3.6 - Power and energy Power and energy are often used...Ch. 3.6 - Flow from a tank A cylindrical tank is full at...Ch. 3.6 - Prob. 54ECh. 3.6 - Bungee jumper A woman attached to a bungee cord...Ch. 3.6 - Spring runoff The flow of a small stream is...Ch. 3.6 - Temperature distribution A thin copper rod, 4...Ch. 3.7 - Two equivalent forms of the Chain Rule for...Ch. 3.7 - Let h(x) = f(g(x)), where f and g are...Ch. 3.7 - Fill in the blanks. The derivative of f(g(x))...Ch. 3.7 - Prob. 4ECh. 3.7 - Identify the inner and outer functions in the...Ch. 3.7 - Express Q(x) = cos4 (x2 + 1) as the composition of...Ch. 3.7 - Version 1 of the Chain Rule Use Version 1 of the...Ch. 3.7 - Version 1 of the Chain Rule Use Version 1 of the...Ch. 3.7 - Version 1 of the Chain Rule Use Version 1 of the...Ch. 3.7 - Prob. 10ECh. 3.7 - Version 1 of the Chain Rule Use Version 1 of the...Ch. 3.7 - Version 1 of the Chain Rule Use Version 1 of the...Ch. 3.7 - Version 1 of the Chain Rule Use Version 1 of the...Ch. 3.7 - Version 1 of the Chain Rule Use Version 1 of the...Ch. 3.7 - Version 1 of the Chain Rule Use Version 1 of the...Ch. 3.7 - Version 1 of the Chain Rule Use Version 1 of the...Ch. 3.7 - Version 1 of the Chain Rule Use Version 1 of the...Ch. 3.7 - Prob. 18ECh. 3.7 - Version 2 of the Chain Rule Use Version 2 of the...Ch. 3.7 - Version 2 of the Chain Rule Use Version 2 of the...Ch. 3.7 - Version 2 of the Chain Rule Use Version 2 of the...Ch. 3.7 - Prob. 22ECh. 3.7 - Version 2 of the Chain Rule Use Version 2 of the...Ch. 3.7 - Version 2 of the Chain Rule Use Version 2 of the...Ch. 3.7 - Version 2 of the Chain Rule Use Version 2 of the...Ch. 3.7 - Version 2 of the Chain Rule Use Version 2 of the...Ch. 3.7 - Version 2 of the Chain Rule Use Version 2 of the...Ch. 3.7 - Version 2 of the Chain Rule Use Version 2 of the...Ch. 3.7 - Version 2 of the Chain Rule Use Version 2 of the...Ch. 3.7 - Version 2 of the Chain Rule Use Version 2 of the...Ch. 3.7 - Prob. 31ECh. 3.7 - Version 2 of the Chain Rule Use Version 2 of the...Ch. 3.7 - Version 2 of the Chain Rule Use Version 2 of the...Ch. 3.7 - Version 2 of the Chain Rule Use Version 2 of the...Ch. 3.7 - Prob. 35ECh. 3.7 - Prob. 36ECh. 3.7 - Chain Rule using a table Let h(x)= f(g(x)) and...Ch. 3.7 - Prob. 38ECh. 3.7 - Applying the Chain Rule Use the data in Tables 3.4...Ch. 3.7 - Chain Rule for powers Use the Chain Rule to find...Ch. 3.7 - Chain Rule for powers Use the Chain Rule to find...Ch. 3.7 - Prob. 43ECh. 3.7 - Chain Rule for powers Use the Chain Rule to find...Ch. 3.7 - Repeated use of the Chain Rule Calculate the...Ch. 3.7 - Prob. 46ECh. 3.7 - Repeated use of the Chain Rule Calculate the...Ch. 3.7 - Repeated use of the Chain Rule Calculate the...Ch. 3.7 - Repeated use of the Chain Rule Calculate the...Ch. 3.7 - Prob. 50ECh. 3.7 - Prob. 51ECh. 3.7 - Repeated use of the Chain Rule Calculate the...Ch. 3.7 - Repeated use of the Chain Rule Calculate the...Ch. 3.7 - Repeated use of the Chain Rule Calculate the...Ch. 3.7 - Repeated use of the Chain Rule Calculate the...Ch. 3.7 - Repeated use of the Chain Rule Calculate the...Ch. 3.7 - Combining rules Use the Chain Rule combined with...Ch. 3.7 - Combining rules Use the Chain Rule combined with...Ch. 3.7 - Combining rules Use the Chain Rule combined with...Ch. 3.7 - Combining rules Use the Chain Rule combined with...Ch. 3.7 - Combining rules Use the Chain Rule combined with...Ch. 3.7 - Combining rules Use the Chain Rule combined with...Ch. 3.7 - Combining rules Use the Chain Rule combined with...Ch. 3.7 - Combining rules Use the Chain Rule combined with...Ch. 3.7 - Prob. 65ECh. 3.7 - Combining rules Use the Chain Rule combined with...Ch. 3.7 - Prob. 67ECh. 3.7 - Prob. 68ECh. 3.7 - Explain why or why not Determine whether the...Ch. 3.7 - Second derivatives Find d2ydx2 for the following...Ch. 3.7 - Second derivatives Find d2ydx2 for the following...Ch. 3.7 - Second derivatives Find d2ydx2 for the following...Ch. 3.7 - Second derivatives Find d2ydx2 for the following...Ch. 3.7 - Prob. 74ECh. 3.7 - Square root derivatives Find the derivative of the...Ch. 3.7 - Prob. 76ECh. 3.7 - Prob. 77ECh. 3.7 - Tangent lines Determine equations of the lines...Ch. 3.7 - Tangent lines Assume f and g are differentiable on...Ch. 3.7 - Prob. 80ECh. 3.7 - Tangent lines Find the equation of the line...Ch. 3.7 - Prob. 82ECh. 3.7 - Composition containing sin x Suppose f is...Ch. 3.7 - Prob. 84ECh. 3.7 - Prob. 85ECh. 3.7 - Prob. 86ECh. 3.7 - A damped oscillator The displacement of a mass on...Ch. 3.7 - Oscillator equation A mechanical oscillator (such...Ch. 3.7 - Prob. 89ECh. 3.7 - Prob. 90ECh. 3.7 - Prob. 91ECh. 3.7 - Deriving trigonometric identities a. Differentiate...Ch. 3.7 - Prob. 93ECh. 3.7 - Prob. 94ECh. 3.7 - Prob. 95ECh. 3.7 - Prob. 96ECh. 3.7 - Prob. 97ECh. 3.7 - Prob. 98ECh. 3.7 - Prob. 99ECh. 3.7 - Prob. 100ECh. 3.7 - Prob. 101ECh. 3.7 - Prob. 102ECh. 3.7 - Prob. 103ECh. 3.8 - For some equations, such as x2 + y2 = l or x y2 =...Ch. 3.8 - Explain the differences between computing the...Ch. 3.8 - Why are both the x-coordinate and the y-coordinate...Ch. 3.8 - In this section, for what values of n did we prove...Ch. 3.8 - Implicit differentiation Carry out the following...Ch. 3.8 - Implicit differentiation Carry out the following...Ch. 3.8 - Implicit differentiation Carry out the following...Ch. 3.8 - Implicit differentiation Carry out the following...Ch. 3.8 - Implicit differentiation Carry out the following...Ch. 3.8 - Implicit differentiation Carry out the following...Ch. 3.8 - Implicit differentiation Carry out the following...Ch. 3.8 - Implicit differentiation Carry out the following...Ch. 3.8 - Implicit differentiation Use implicit...Ch. 3.8 - Implicit differentiation Use implicit...Ch. 3.8 - Implicit differentiation Use implicit...Ch. 3.8 - Implicit differentiation Use implicit...Ch. 3.8 - Implicit differentiation Use implicit...Ch. 3.8 - Implicit differentiation Use implicit...Ch. 3.8 - Implicit differentiation Use implicit...Ch. 3.8 - Implicit differentiation Use implicit...Ch. 3.8 - Implicit differentiation Use implicit...Ch. 3.8 - Implicit differentiation Use implicit...Ch. 3.8 - Implicit differentiation Use implicit...Ch. 3.8 - Implicit differentiation Use implicit...Ch. 3.8 - Tangent lines Carry out the following steps. a....Ch. 3.8 - Tangent lines Carry out the following steps. a....Ch. 3.8 - Prob. 27ECh. 3.8 - Tangent lines Carry out the following steps. a....Ch. 3.8 - Tangent lines Carry out the following steps. a....Ch. 3.8 - Tangent lines Carry out the following steps. a....Ch. 3.8 - Second derivatives Find d2ydx2. 31. x + y2 = 1Ch. 3.8 - Second derivatives Find d2ydx2. 32. 2x2 + y2 = 4Ch. 3.8 - Second derivatives Find d2ydx2. 33. x + y = sin yCh. 3.8 - Second derivatives Find d2ydx2. 34. x4 + y4 = 64Ch. 3.8 - Second derivatives Find d2ydx2. 35. e2y + x = yCh. 3.8 - Second derivatives Find d2ydx2 36. sin x + x2y =...Ch. 3.8 - Prob. 37ECh. 3.8 - Prob. 38ECh. 3.8 - Prob. 39ECh. 3.8 - Prob. 40ECh. 3.8 - Prob. 41ECh. 3.8 - Prob. 42ECh. 3.8 - Prob. 43ECh. 3.8 - Prob. 44ECh. 3.8 - Prob. 45ECh. 3.8 - Prob. 46ECh. 3.8 - Prob. 47ECh. 3.8 - Prob. 48ECh. 3.8 - Prob. 49ECh. 3.8 - Prob. 50ECh. 3.8 - Explain why or why not Determine whether the...Ch. 3.8 - Multiple tangent lines Complete the following...Ch. 3.8 - Multiple tangent lines Complete the following...Ch. 3.8 - Multiple tangent lines Complete the following...Ch. 3.8 - Witch of Agnesi Let y(x2 + 4) = 8 (see figure). a....Ch. 3.8 - Vertical tangent lines a. Determine the points at...Ch. 3.8 - Vertical tangent lines a. Determine the points...Ch. 3.8 - Tangent lines for ellipses Find the equations of...Ch. 3.8 - Tangent lines for ellipses Find the equations of...Ch. 3.8 - Prob. 60ECh. 3.8 - Identifying functions from an equation The...Ch. 3.8 - Prob. 62ECh. 3.8 - Prob. 63ECh. 3.8 - Prob. 64ECh. 3.8 - Normal lines A normal line at a point P on a curve...Ch. 3.8 - Normal lines A normal line at a point P on a curve...Ch. 3.8 - Prob. 67ECh. 3.8 - Normal lines A normal line at a point P on a curve...Ch. 3.8 - Prob. 69ECh. 3.8 - Normal lines A normal line at a point P on a curve...Ch. 3.8 - Prob. 71ECh. 3.8 - Visualizing tangent and normal lines a. Determine...Ch. 3.8 - Visualizing tangent and normal lines a. Determine...Ch. 3.8 - Prob. 74ECh. 3.8 - Cobb-Douglas production function The output of an...Ch. 3.8 - Surface area of a cone The lateral surface area of...Ch. 3.8 - Volume of a spherical cap Imagine slicing through...Ch. 3.8 - Volume of a torus The volume of a torus (doughnut...Ch. 3.8 - Orthogonal trajectories Two curves are orthogonal...Ch. 3.8 - Orthogonal trajectories Two curves are orthogonal...Ch. 3.8 - Orthogonal trajectories Two curves are orthogonal...Ch. 3.8 - Finding slope Find the slope of the curve...Ch. 3.8 - A challenging derivative Find dydx, where (x2 +...Ch. 3.8 - Prob. 84ECh. 3.8 - A challenging derivative Find d2ydx2, where...Ch. 3.8 - Work carefully Proceed with caution when using...Ch. 3.8 - Work carefully Proceed with caution when using...Ch. 3.8 - Work carefully Proceed with caution when using...Ch. 3.8 - Work carefully Proceed with caution when using...Ch. 3.9 - Use x = ey to explain why ddx(lnx)=1x, for x 0.Ch. 3.9 - Prob. 2ECh. 3.9 - Show that ddx(lnkx)=ddx(lnx), where x 0 and k is...Ch. 3.9 - State the derivative rule for the exponential...Ch. 3.9 - State the derivative rule for the logarithmic...Ch. 3.9 - Explain why bx = ex ln bCh. 3.9 - Prob. 7ECh. 3.9 - Prob. 8ECh. 3.9 - Derivatives involving ln x Find the following...Ch. 3.9 - Derivatives involving ln x Find the following...Ch. 3.9 - Derivatives involving ln x Find the following...Ch. 3.9 - Derivatives involving ln x Find the following...Ch. 3.9 - Derivatives involving ln x Find the following...Ch. 3.9 - Derivatives involving ln x Find the following...Ch. 3.9 - Derivatives involving ln x Find the following...Ch. 3.9 - Derivatives involving ln x Find the following...Ch. 3.9 - Derivatives involving ln x Find the following...Ch. 3.9 - Derivatives involving ln x Find the following...Ch. 3.9 - Derivatives involving ln x Find the following...Ch. 3.9 - Derivatives involving ln x Find the following...Ch. 3.9 - Derivatives involving ln x Find the following...Ch. 3.9 - Derivatives involving ln x Find the following...Ch. 3.9 - Derivatives of bx Find the derivatives of the...Ch. 3.9 - Derivatives of bx Find the derivatives of the...Ch. 3.9 - Derivatives of bx Find the derivatives of the...Ch. 3.9 - Derivatives of bx Find the derivatives of the...Ch. 3.9 - Derivatives of bx Find the derivatives of the...Ch. 3.9 - Derivatives of bx Find the derivatives of the...Ch. 3.9 - Derivatives of bx Find the derivatives of the...Ch. 3.9 - Prob. 30ECh. 3.9 - Exponential model The following table shows the...Ch. 3.9 - Magnitude of an earthquake The energy (in joules)...Ch. 3.9 - Diagnostic scanning Iodine-123 is a radioactive...Ch. 3.9 - Prob. 34ECh. 3.9 - Prob. 35ECh. 3.9 - Prob. 36ECh. 3.9 - Prob. 37ECh. 3.9 - General Power Rule Use the General Power Rule...Ch. 3.9 - Prob. 39ECh. 3.9 - General Power Rule Use the General Power Rule...Ch. 3.9 - Prob. 41ECh. 3.9 - Prob. 42ECh. 3.9 - General Power Rule Use the General Power Rule...Ch. 3.9 - General Power Rule Use the General Power Rule...Ch. 3.9 - Derivatives of Tower Functions (or gh) Find the...Ch. 3.9 - Derivatives of Tower Functions (or gh) Find the...Ch. 3.9 - Derivatives of Tower Functions (or gh) Find the...Ch. 3.9 - Derivatives of Tower Functions (or gh) Find the...Ch. 3.9 - Derivatives of Tower Functions (or gh) Find the...Ch. 3.9 - Derivatives of Tower Functions (or gh) Find the...Ch. 3.9 - Find an equation of the line tangent to y = xsin x...Ch. 3.9 - Determine whether the graph of y=xx has any...Ch. 3.9 - The graph of y = (x2)x has two horizontal tangent...Ch. 3.9 - The graph of y = xln x has one horizontal tangent...Ch. 3.9 - Derivatives of logarithmic functions Calculate the...Ch. 3.9 - Derivatives of logarithmic functions Calculate the...Ch. 3.9 - Derivatives of logarithmic functions Calculate the...Ch. 3.9 - Derivatives of logarithmic functions Calculate the...Ch. 3.9 - Derivatives of logarithmic functions Calculate the...Ch. 3.9 - Derivatives of logarithmic functions Calculate the...Ch. 3.9 - Logarithmic differentiation Use logarithmic...Ch. 3.9 - Logarithmic differentiation Use logarithmic...Ch. 3.9 - Logarithmic differentiation Use logarithmic...Ch. 3.9 - Logarithmic differentiation Use logarithmic...Ch. 3.9 - Logarithmic differentiation Use logarithmic...Ch. 3.9 - Logarithmic differentiation Use logarithmic...Ch. 3.9 - Logarithmic differentiation Use logarithmic...Ch. 3.9 - Prob. 68ECh. 3.9 - Prob. 69ECh. 3.9 - Prob. 70ECh. 3.9 - Higher-order derivatives Find the following...Ch. 3.9 - Higher-order derivatives Find the following...Ch. 3.9 - Higher-order derivatives Find the following...Ch. 3.9 - Derivatives by different methods Calculate the...Ch. 3.9 - Derivatives by different methods Calculate the...Ch. 3.9 - Prob. 76ECh. 3.9 - Derivatives of logarithmic functions Use the...Ch. 3.9 - Derivatives of logarithmic functions Use the...Ch. 3.9 - Derivatives of logarithmic functions Use the...Ch. 3.9 - Derivatives of logarithmic functions Use the...Ch. 3.9 - Derivatives of logarithmic functions Use the...Ch. 3.9 - Derivatives of logarithmic functions Use the...Ch. 3.9 - Tangent lines Find the equation of the line...Ch. 3.9 - Horizontal tangents The graph of y = cos x ln...Ch. 3.9 - General logarithmic and exponential derivatives...Ch. 3.9 - General logarithmic and exponential derivatives...Ch. 3.9 - Prob. 87ECh. 3.9 - Prob. 88ECh. 3.9 - Prob. 89ECh. 3.9 - General logarithmic and exponential derivatives...Ch. 3.9 - Prob. 91ECh. 3.9 - Prob. 92ECh. 3.9 - Logistic growth Scientists often use the logistic...Ch. 3.9 - Logistic growth Scientists often use the logistic...Ch. 3.9 - Prob. 95ECh. 3.9 - Logistic growth Scientists often use the logistic...Ch. 3.9 - Savings plan Beginning at age 30, a self-employed...Ch. 3.9 - Tangency question It is easily verified that the...Ch. 3.9 - Tangency question It is easily verified that the...Ch. 3.9 - Triple intersection Graph the functions f(x) = x3,...Ch. 3.9 - Calculating limits exactly Use the definition of...Ch. 3.9 - Calculating limits exactly Use the definition of...Ch. 3.9 - Calculating limits exactly Use the definition of...Ch. 3.9 - Calculating limits exactly Use the definition of...Ch. 3.9 - Derivative of u(x)v(x) Use logarithmic...Ch. 3.9 - Tangent lines and exponentials. Assume b is given...Ch. 3.10 - State the derivative formulas for sin1 x, tan1 x,...Ch. 3.10 - What is the slope of the line tangent to the graph...Ch. 3.10 - What is the slope of the line tangent to the graph...Ch. 3.10 - How are the derivatives of sin1 x and cos1 x...Ch. 3.10 - Suppose f is a one-to-one function with f(2) = 8...Ch. 3.10 - Explain how to find (f1)(y0), given that y0 =...Ch. 3.10 - Derivatives of inverse sine Evaluate the...Ch. 3.10 - Derivatives of inverse sine Evaluate the...Ch. 3.10 - Derivatives of inverse sine Evaluate the...Ch. 3.10 - Derivatives of inverse sine Evaluate the...Ch. 3.10 - Derivatives of inverse sine Evaluate the...Ch. 3.10 - Derivatives of inverse sine Evaluate the...Ch. 3.10 - Derivatives Evaluate the derivatives of the...Ch. 3.10 - Prob. 14ECh. 3.10 - Prob. 15ECh. 3.10 - Derivatives Evaluate the derivatives of the...Ch. 3.10 - Derivatives Evaluate the derivatives of the...Ch. 3.10 - Derivatives Evaluate the derivatives of the...Ch. 3.10 - Derivatives Evaluate the derivatives of the...Ch. 3.10 - Prob. 20ECh. 3.10 - Derivatives Evaluate the derivatives of the...Ch. 3.10 - Derivatives Evaluate the derivatives of the...Ch. 3.10 - Derivatives Evaluate the derivatives of the...Ch. 3.10 - Derivatives Evaluate the derivatives of the...Ch. 3.10 - Derivatives Evaluate the derivatives of the...Ch. 3.10 - Derivatives Evaluate the derivatives of the...Ch. 3.10 - Derivatives Evaluate the derivatives of the...Ch. 3.10 - Derivatives Evaluate the derivatives of the...Ch. 3.10 - Derivatives Evaluate the derivatives of the...Ch. 3.10 - Derivatives Evaluate the derivatives of the...Ch. 3.10 - Tangent lines Find an equation of the line tangent...Ch. 3.10 - Tangent lines Find an equation of the line tangent...Ch. 3.10 - Tangent lines Find an equation of the line tangent...Ch. 3.10 - Tangent lines Find an equation of the line tangent...Ch. 3.10 - Angular size A boat sails directly toward a...Ch. 3.10 - Prob. 36ECh. 3.10 - Derivatives of inverse functions at a point Find...Ch. 3.10 - Derivatives of inverse functions at a point Find...Ch. 3.10 - Prob. 39ECh. 3.10 - Derivatives of inverse functions at a point Find...Ch. 3.10 - Derivatives of inverse functions at a point Find...Ch. 3.10 - Derivatives of inverse functions at a point Find...Ch. 3.10 - Prob. 43ECh. 3.10 - Prob. 44ECh. 3.10 - Slopes of tangent lines Given the function f, find...Ch. 3.10 - Prob. 46ECh. 3.10 - Prob. 47ECh. 3.10 - Prob. 48ECh. 3.10 - Prob. 49ECh. 3.10 - Prob. 50ECh. 3.10 - Derivatives of inverse functions from a table Use...Ch. 3.10 - Derivatives of inverse functions from a table Use...Ch. 3.10 - Explain why or why not Determine whether the...Ch. 3.10 - Prob. 54ECh. 3.10 - Graphing f and f a. Graph f with a graphing...Ch. 3.10 - Prob. 56ECh. 3.10 - Prob. 57ECh. 3.10 - Graphing with inverse trigonometric functions a....Ch. 3.10 - Prob. 59ECh. 3.10 - Prob. 60ECh. 3.10 - Prob. 61ECh. 3.10 - Prob. 62ECh. 3.10 - Prob. 63ECh. 3.10 - Prob. 64ECh. 3.10 - Prob. 65ECh. 3.10 - Prob. 66ECh. 3.10 - Towing a boat A boat is towed toward a dock by a...Ch. 3.10 - Tracking a dive A biologist standing at the bottom...Ch. 3.10 - Angle to a particle, part I A particle travels...Ch. 3.10 - Prob. 70ECh. 3.10 - Prob. 71ECh. 3.10 - Prob. 72ECh. 3.10 - Prob. 73ECh. 3.10 - Prob. 74ECh. 3.10 - Identity proofs Prove the following identities and...Ch. 3.10 - Identity proofs Prove the following identities and...Ch. 3.10 - Identity proofs Prove the following identities and...Ch. 3.10 - Prob. 78ECh. 3.10 - Prob. 79ECh. 3.11 - Give an example in which one dimension of a...Ch. 3.11 - Prob. 2ECh. 3.11 - If two opposite sides of a rectangle increase in...Ch. 3.11 - Prob. 4ECh. 3.11 - Prob. 5ECh. 3.11 - Shrinking square The sides of a square decrease in...Ch. 3.11 - Expanding isosceles triangle The legs of an...Ch. 3.11 - Shrinking isosceles triangle The hypotenuse of an...Ch. 3.11 - Expanding circle The area of a circle increases at...Ch. 3.11 - Prob. 10ECh. 3.11 - Shrinking circle A circle has an initial radius of...Ch. 3.11 - Prob. 12ECh. 3.11 - Balloons A spherical balloon is inflated and its...Ch. 3.11 - Piston compression A piston is seated at the top...Ch. 3.11 - Melting snowball A spherical snowball melts at a...Ch. 3.11 - Prob. 16ECh. 3.11 - Prob. 17ECh. 3.11 - Expanding rectangle A rectangle initially has...Ch. 3.11 - Prob. 19ECh. 3.11 - Altitude of a jet A jet ascends at a 10 angle from...Ch. 3.11 - Rate of dive of a submarine A surface ship is...Ch. 3.11 - Prob. 22ECh. 3.11 - Ladder against the wall A 13-foot ladder is...Ch. 3.11 - Ladder against the wall again A 12-foot ladder is...Ch. 3.11 - Moving shadow A 5-foot-tall woman walks at 8 ft/s...Ch. 3.11 - Baseball runners Runners stand at first and second...Ch. 3.11 - Growing sandpile Sand falls from an overhead bin...Ch. 3.11 - Draining a water heater A water heater that has...Ch. 3.11 - Draining a tank An inverted conical water tank...Ch. 3.11 - Drinking a soda At what rate is soda being sucked...Ch. 3.11 - Prob. 31ECh. 3.11 - Filling a hemispherical tank A hemispherical tank...Ch. 3.11 - Prob. 33ECh. 3.11 - Observing a launch An observer stands 300 ft from...Ch. 3.11 - Another balloon story A hot-air balloon is 150 ft...Ch. 3.11 - Prob. 36ECh. 3.11 - Another fishing story An angler hooks a trout and...Ch. 3.11 - Flying a kite Once Kates kite reaches a height of...Ch. 3.11 - Rope on a boat A rope passing through a capstan on...Ch. 3.11 - Parabolic motion An arrow is shot into the air and...Ch. 3.11 - Time-lagged flights An airliner passes over an...Ch. 3.11 - Disappearing triangle An equilateral triangle...Ch. 3.11 - Clock hands The hands of the clock in the tower of...Ch. 3.11 - Filling two pools Two cylindrical swimming pools...Ch. 3.11 - Filming a race A camera is set up at the starting...Ch. 3.11 - Two tanks A conical tank with an upper radius of 4...Ch. 3.11 - Oblique tracking A port and a radar station are 2...Ch. 3.11 - Oblique tracking A ship leaves port traveling...Ch. 3.11 - Watching an elevator An observer is 20 m above the...Ch. 3.11 - A lighthouse problem A lighthouse stands 500 m off...Ch. 3.11 - Prob. 51ECh. 3.11 - Watching a Ferris wheel An observer stands 20 m...Ch. 3.11 - Viewing angle The bottom of a large theater screen...Ch. 3.11 - Searchlightwide beam A revolving searchlight,...Ch. 3.11 - Draining a trough A trough in the shape of a half...Ch. 3.11 - Divergent paths Two boats leave a port at the same...Ch. 3 - Explain why or why not Determine whether the...Ch. 3 - Prob. 2RECh. 3 - Prob. 3RECh. 3 - Prob. 4RECh. 3 - Prob. 5RECh. 3 - Prob. 6RECh. 3 - Prob. 7RECh. 3 - Growth rate of bacteria Suppose the following...Ch. 3 - Velocity of a skydiver Assume the graph represents...Ch. 3 - Prob. 10RECh. 3 - Prob. 11RECh. 3 - Sketching a derivative graph Sketch a graph of f...Ch. 3 - Sketching a derivative graph Sketch a graph of g...Ch. 3 - Matching functions and derivatives Match the...Ch. 3 - Evaluating derivatives Evaluate and simplify the...Ch. 3 - Evaluating derivatives Evaluate and simplify the...Ch. 3 - Evaluating derivatives Evaluate and simplify the...Ch. 3 - Evaluating derivatives Evaluate and simplify the...Ch. 3 - Evaluating derivatives Evaluate and simplify the...Ch. 3 - Evaluating derivatives Evaluate and simplify the...Ch. 3 - Evaluating derivatives Evaluate and simplify the...Ch. 3 - Evaluating derivatives Evaluate and simplify the...Ch. 3 - Evaluating derivatives Evaluate and simplify the...Ch. 3 - Prob. 24RECh. 3 - Prob. 25RECh. 3 - Evaluating derivatives Evaluate and simplify the...Ch. 3 - Evaluating derivatives Evaluate and simplify the...Ch. 3 - Prob. 28RECh. 3 - Evaluating derivatives Evaluate and simplify the...Ch. 3 - Evaluating derivatives Evaluate and simplify the...Ch. 3 - Evaluating derivatives Evaluate and simplify the...Ch. 3 - Prob. 32RECh. 3 - Evaluating derivatives Evaluate and simplify the...Ch. 3 - Evaluating derivatives Evaluate and simplify the...Ch. 3 - Evaluating derivatives Evaluate and simplify the...Ch. 3 - Evaluating derivatives Evaluate and simplify the...Ch. 3 - Implicit differentiation Calculate y(x) for the...Ch. 3 - Implicit differentiation Calculate y(x) for the...Ch. 3 - Implicit differentiation Calculate y(x) for the...Ch. 3 - Quadratic functions a. Show that if (a, f(a)) is...Ch. 3 - Prob. 41RECh. 3 - Prob. 42RECh. 3 - Prob. 43RECh. 3 - Prob. 44RECh. 3 - Prob. 45RECh. 3 - A parabola property Let f(x) = x2. a. Show that...Ch. 3 - Prob. 47RECh. 3 - Prob. 48RECh. 3 - Derivative formulas Evaluate the following...Ch. 3 - Prob. 50RECh. 3 - Derivative formulas Evaluate the following...Ch. 3 - Derivative formulas Evaluate the following...Ch. 3 - Prob. 53RECh. 3 - Limits The following limits represent the...Ch. 3 - Limits The following limits represent the...Ch. 3 - Derivative of the inverse at a point Consider the...Ch. 3 - Derivative of the inverse at a point Consider the...Ch. 3 - Derivative of the inverse Find the derivative of...Ch. 3 - Derivative of the inverse Find the derivative of...Ch. 3 - A function and its inverse function The function...Ch. 3 - Prob. 61RECh. 3 - Derivatives from a graph If possible, evaluate the...Ch. 3 - Derivatives from a graph If possible, evaluate the...Ch. 3 - Velocity of a probe A small probe is launched...Ch. 3 - Prob. 65RECh. 3 - Marginal and average cost Suppose a company...Ch. 3 - Population growth Suppose p(t) = 1.7t3 + 72t2 +...Ch. 3 - Position of a piston The distance between the head...Ch. 3 - Boat rates Two boats leave a dock at the same...Ch. 3 - Rate of inflation of a balloon A spherical balloon...Ch. 3 - Rate of descent of a hot-air balloon A rope is...Ch. 3 - Filling a tank Water flows into a conical tank at...Ch. 3 - Angle of elevation A jet flies horizontally 500 ft...Ch. 3 - Viewing angle A man whose eye level is 6 ft above...
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Violins Professional musicians listened to five violins being played, without seeing the instruments. One violi...
Introductory Statistics
Explore! Exercises 9 and 10 provide two data sets front “Graphs in Statistical Analysis,” by F J. Anscombe, the...
Elementary Statistics (13th Edition)
To simplify polynomial
Pre-Algebra Student Edition
3. For the same sample statistics, which level of confidence would produce the widest confidence interval? Expl...
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th Edition)
1. combination of numbers, variables, and operation symbols is called an algebraic______.
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, calculus and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Find the derivative of the function. k(x) = − 6(5x +4) -arrow_forwardFind all values of x for the given function where the tangent line is horizontal. 3 =√x³-12x² + 45x+5arrow_forwardFind the equation of the tangent line to the graph of the given function at the given value of x. 6 f(x) = x(x² - 4x+5)*; x=2arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
- Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage

 College AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305115545Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
College AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305115545Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem WatsonPublisher:Cengage Learning  Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1AlgebraISBN:9780395977224Author:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. ColePublisher:McDougal Littell
Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1AlgebraISBN:9780395977224Author:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. ColePublisher:McDougal Littell

Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic Geometry
Algebra
ISBN:9781133382119
Author:Swokowski
Publisher:Cengage


College Algebra
Algebra
ISBN:9781305115545
Author:James Stewart, Lothar Redlin, Saleem Watson
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:9781285463247
Author:David Poole
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...
Algebra
ISBN:9781337111348
Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan Noell
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1
Algebra
ISBN:9780395977224
Author:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. Cole
Publisher:McDougal Littell
01 - What Is A Differential Equation in Calculus? Learn to Solve Ordinary Differential Equations.; Author: Math and Science;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=K80YEHQpx9g;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Higher Order Differential Equation with constant coefficient (GATE) (Part 1) l GATE 2018; Author: GATE Lectures by Dishank;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ODxP7BbqAjA;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Solution of Differential Equations and Initial Value Problems; Author: Jefril Amboy;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Q68sk7XS-dc;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY