
Review. A fundamental property of a type 1 superconducting material is perfect diamagnetism, or demonstration of the Meissner effect, illustrated in Figure 29.27 in Section 29.6 and described as follows. If a sample of superconducting material is placed into an externally produced magnetic field or is cooled to become superconducting while it is in a magnetic field,
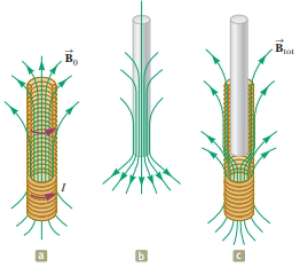
A vertical solenoid with a length of 120 cm and a diameter of 2.50 cm consists of 1 400 turns of copper wire carrying a counterclockwise current (when viewed from above) of 2.00 A as shown in Figure P31.48a. (a) Find the magnetic field in the vacuum inside the solenoid. (b) Find the energy density of the magnetic field. Now a superconducting bar 2.20 cm in diameter is inserted partway into the solenoid. Its upper end is far outside the solenoid, where the magnetic field is negligible. The lower end of the bar is deep inside the solenoid. (c) Explain how you identify the direction required for the current on the curved surface of the bar so that the total magnetic field is zero within the bar. The field created by the supercurrents is sketched in Figure P31.48b, and the total field is sketched in Figure P31.48c. (d) The field of the solenoid exerts a force on the current in the superconductor. Explain how you determine the direction of the force on the bar. (e) Noting that the units J/m3 of energy density are the as the units N/m2 of pressure, calculate the magnitude of the force by multiplying the energy density of the solenoid field times the area of the bottom end of the superconducting bar.
Figure P31.48
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 31 Solutions
PHYSICS:F/SCI.+ENGRS-W/WEBASSIGN
- 3.) The graph shows how current I varies with potential difference V across a component X. 904 80- 70- 60- 50- I/MA 40- 30- 20- 10- 0+ 0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 2.5 3.0 3.5 4.0 4.5 5.0 VIV Component X and a cell of negligible internal resistance are placed in a circuit. A variable resistor R is connected in series with component X. The ammeter reads 20mA. 4.0V 4.0V Component X and the cell are now placed in a potential divider circuit. (a) Outline why component X is considered non-ohmic. [1] (b(i)) Determine the resistance of the variable resistor. [3] (b(ii)) Calculate the power dissipated in the circuit. [1] (c(i)) State the range of current that the ammeter can measure as the slider S of the potential divider is moved from Q to P. [1] (c(ii)) Describe, by reference to your answer for (c)(i), the advantage of the potential divider arrangement over the arrangement in (b).arrow_forward1.) Two long parallel current-carrying wires P and Q are separated by 0.10 m. The current in wire P is 5.0 A. The magnetic force on a length of 0.50 m of wire P due to the current in wire Q is 2.0 × 10-s N. (a) State and explain the magnitude of the force on a length of 0.50 m of wire Q due to the current in P. [2] (b) Calculate the current in wire Q. [2] (c) Another current-carrying wire R is placed parallel to wires P and Q and halfway between them as shown. wire P wire R wire Q 0.05 m 0.05 m The net magnetic force on wire Q is now zero. (c.i) State the direction of the current in R, relative to the current in P.[1] (c.ii) Deduce the current in R. [2]arrow_forward2.) A 50.0 resistor is connected to a cell of emf 3.00 V. The voltmeter and the ammeter in the circuit are ideal. V A 50.00 (a) The current in the ammeter is 59.0 mA. Calculate the internal resistance of the cell. The circuit is changed by connecting another resistor R in parallel to the 50.0 resistor. V A 50.00 R (b) Explain the effect of this change on R is made of a resistive wire of uniform cross-sectional area 3.1 × 10-8 m², resistivity 4.9 × 10-70m and length L. The resistance of R is given by the equation R = KL where k is a constant. (b.i) the reading of the ammeter. [2] (b.ii) the reading of the voltmeter. [2] (c) Calculate k. State an appropriate unit for your answer. [3] [2]arrow_forward
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardA rod 12.0 cm long is uniformly charged and has a total charge of -20.0 μc. Determine the magnitude and direction of the electric field along the axis of the rod at a point 32.0 cm from its center. 361000 ☑ magnitude What is the general expression for the electric field along the axis of a uniform rod? N/C direction toward the rodarrow_forward
- A certain brand of freezer is advertised to use 730 kW h of energy per year. Part A Assuming the freezer operates for 5 hours each day, how much power does it require while operating? Express your answer in watts. ΜΕ ΑΣΦ ? P Submit Request Answer Part B W If the freezer keeps its interior at a temperature of -6.0° C in a 20.0° C room, what is its theoretical maximum performance coefficient? Enter your answer numerically. K = ΜΕ ΑΣΦ Submit Request Answer Part C What is the theoretical maximum amount of ice this freezer could make in an hour, starting with water at 20.0°C? Express your answer in kilograms. m = Ο ΑΣΦ kgarrow_forwardDescribe the development of rational choice theory in sociology. Please includearrow_forwardA-E pleasearrow_forward
- A 11.8 L gas tank containing 3.90 moles of ideal He gas at 26.0°C is placed inside a completely evacuated insulated bell jar of volume 39.0 L .A small hole in the tank allows the He to leak out into the jar until the gas reaches a final equilibrium state with no more leakage. Part A What is the change in entropy of this system due to the leaking of the gas? ■ ΜΕ ΑΣΦ AS = ? J/K Submit Request Answer Part B Is the process reversible or irreversible?arrow_forwardA-E pleasearrow_forwardThree moles of an ideal gas undergo a reversible isothermal compression at 20.0° C. During this compression, 1900 J of work is done on the gas. For related problem-solving tips and strategies, you may want to view a Video Tutor Solution of Entropy change in a free expansion. Part A What is the change of entropy of the gas? ΤΕ ΑΣΦ AS = Submit Request Answer J/Karrow_forward

 Modern PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781111794378Author:Raymond A. Serway, Clement J. Moses, Curt A. MoyerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Modern PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781111794378Author:Raymond A. Serway, Clement J. Moses, Curt A. MoyerPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





