
To analyze:
The limiting factor for the size of the insects, among the tracheal density of the leg or the tracheal density of the entire body by describing the graph shown below.
Introduction:
Insects belong to the phylum Arthropoda. The respiratory system of insects comprises spiracles and trachea. Spiracles are the small openings present on the exoskeleton of the insect. These openings are connected to the network of dense tubes called trachea or windpipe, which acts as the internal respiratory system for all the insects connecting pharynx and larynx to the lungs.
Explanation of Solution
The oxygen diffuses through the spiracles present on the exoskeleton and is further passed to the underlying tracheal tubes. The tracheal tubes branch into tracheoles that deliver oxygen to tissues and cells via diffusion. A study showed that level of oxygen in the atmosphere plays a crucial role in the body size of arthropods.
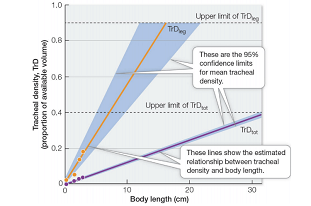
This leads to more tracheal density inside the insect’s body, which differs in legs as compared to the body, because larger the body of an organism, more is the tracheal network and tracheal density required to supply oxygen to all the internal tissues. However, from the graph, it is clear that as the body length of the organism increases, the tracheal density also increases in both body (TrDtot) and legs (TrDleg) but was found to be decreased or absent as both reaches the upper limit. Between both legs and body, density in legs was found to be more as compared to density in the body in small-sized organisms but its levels were found to be absent as the body length of organism increases.
The reason for the above observation is the concentration of oxygen, which is less in the atmosphere (21%). Thus small organisms is more efficient in intake of oxygen due to their small body size and tracheal density is sufficient to supply appropriate amount of oxygen. In large organisms, enhanced tracheal network is required to supply air to each organ of the body. But this does not cope-up with the present available oxygen levels as more oxygen in air (during Paleozoic times) allow minimum
Hence, it can be concluded that tracheal density in the legs is most limiting factor in the size of insects. This is so because large body length and size requires more tracheal network to transport air to all the tissues of body. Absence or less amount of trachea in legs of an organism shows the lack of oxygen supply in legs due to large body length.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
- Molecular Biology Please help with question. Thank you in advance. Discuss, compare and contrast the structure of promoters inprokaryotes and eukaryotes.arrow_forwardMolecular Biology Please help with question. Thank you You are studying the expression of the lac operon. You have isolated mutants as described below. In the absence of glucose, explain/describe what would happen, for each mutant, to the expression of the lac operon when you add lactose AND what would happen when the bacteria has used up all of the lactose (if the mutant is able to use lactose).1. Mutations in the lac repressor gene that would prevent the binding of lactose2. Mutations in the lac repressor gene that would prevent release of lactose once lactose hadbound3. Normally the lac repressor gene is located next to (a few hundred base pairs) and upstreamfrom the lac operon. Mutations in the lac repressor gene that move the lac repressor gene 100,000base pairs downstream.4. Mutations in the lac operator that would prevent binding of lac repressorarrow_forwardYou have returned to college to become a phylogeneticist. One of the first things you wish to do is determine how mammals, birds, and reptiles are related. Like any good scientist, you need to consider all available data objectively and without a preconceived “correct” answer. In pursuit of that, you should produce a phylogenetic tree based only on morphological features that show birds and mammals are more closely related. You will then produce a totally different tree, also using morphological features, that shows birds and reptiles are more closely related. Do not forget to include all three groups in both your trees. Based solely off the trees you produce, which relationship would you consider the more likely and why? Once you have answered that question, provide a brief summary of the “modern” understanding of the relationship between these three groups.arrow_forward
- true or false, the reason geckos can walk on walls is hydrogen bonding between their foot pads and the moisture on the wall.arrow_forwardBiology laboratory problem Please help. thank you You have 20 ul of DNA solution and 6X DNA loading buffer solution. You have to mix your DNA solution and DNA loading buffer before load DNA in an agarose gel. The concentration of the DNA loading buffer must be 1X in the DNA and DNA-loading buffer mixture after you mix them. For that, I will add _____ ul of 6X loading buffer to the 20 ul DNA solution.arrow_forwardBiology lab problem To make 20 ul of 5 mM MgCl2 solution using 50 mM MgCl2 stock solution and distilled water, I will mix ________ ul of 50 mM MgCl2 solution and ________ ul of distilled water. Please help . Thank youarrow_forward
- Biology Please help. Thank you. Biology laboratory question You need 50 ml of 1% (w/v) agarose gel. Agarose is a powder. How would you make it? You can ignore the volume of agarose powder. Don't forget the unit.TBE buffer is used to make an agarose gel, not distilled water. I will add _______ of agarose powder into 50 ml of distilled water (final 50 ml).arrow_forwardAn urgent care center experienced the average patient admissions shown in the Table below during the weeks from the first week of December through the second week of April. Week Average Daily Admissions 1-Dec 11 2-Dec 14 3-Dec 17 4-Dec 15 1-Jan 12 2-Jan 11 3-Jan 9 4-Jan 9 1-Feb 12 2-Feb 8 3-Feb 13 4-Feb 11 1-Mar 15 2-Mar 17 3-Mar 14 4-Mar 19 5-Mar 13 1-Apr 17 2-Apr 13 Forecast admissions for the periods from the first week of December through the second week of April. Compare the forecast admissions to the actual admissions; What do you conclude?arrow_forwardAnalyze the effectiveness of the a drug treatment program based on the needs of 18-65 year olds who are in need of treatment by critically describing 4 things in the program is doing effectively and 4 things the program needs some improvement.arrow_forward
- I have the first half finished... just need the bottom half.arrow_forward13. Practice Calculations: 3 colonies were suspended in the following dilution series and then a viable plate count and microscope count was performed. Calculate IDF's, TDF's and then calculate the CFU/mL in each tube by both methods. Finally calculate the cells in 1 colony by both methods. Show all of your calculations in the space provided on the following pages. 3 colonies 56 cells 10 μL 10 μL 100 μL 500 με m OS A B D 5.0 mL 990 με 990 με 900 με 500 μL EN 2 100 με 100 μL 118 colonies 12 coloniesarrow_forwardDescribe and give a specific example of how successionary stage is related to species diversity?arrow_forward
- Case Studies In Health Information ManagementBiologyISBN:9781337676908Author:SCHNERINGPublisher:Cengage
 Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College
Concepts of BiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168116Author:Samantha Fowler, Rebecca Roush, James WisePublisher:OpenStax College





