
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern Physics
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781337553292
Author: Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 30.3, Problem 30.3QQ
Figure 30.12 (Quick Quiz 30.3)
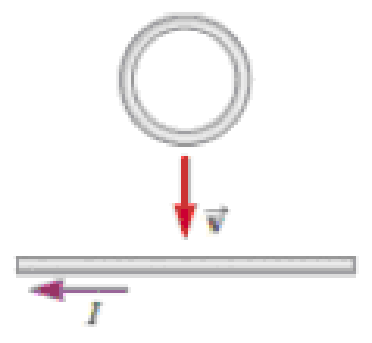
QUICK QUIZ 30.3 Figure 30.12 shows a circular loop of wire falling toward a wire carrying a current to the left. What is the direction of the induced current in the loop of wire? (a) clockwise (b) counterclockwise (c) zero (d) impossible to determine
Expert Solution & Answer
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Students have asked these similar questions
!
Required information
The radius of the Moon is 1.737 Mm and the distance between Earth and the Moon is 384.5 Mm.
The intensity of the moonlight incident on her eye is 0.0220 W/m². What is the intensity incident on her retina if the
diameter of her pupil is 6.54 mm and the diameter of her eye is 1.94 cm?
W/m²
Required information
An object is placed 20.0 cm from a converging lens with focal length 15.0 cm (see the figure, not drawn to scale). A
concave mirror with focal length 10.0 cm is located 76.5 cm to the right of the lens. Light goes through the lens, reflects
from the mirror, and passes through the lens again, forming a final image.
Converging
lens
Object
Concave
mirror
15.0 cm
-20.0 cm-
10.0 cm
d cm
d = 76.5.
What is the location of the final image?
cm to the left of the lens
!
Required information
A man requires reading glasses with +2.15-D refractive power to read a book held 40.0 cm away with a relaxed eye.
Assume the glasses are 1.90 cm from his eyes.
His uncorrected near point is 1.00 m. If one of the lenses is the one for distance vision, what should the refractive power of the other
lens (for close-up vision) in his bifocals be to give him clear vision from 25.0 cm to infinity?
2.98 D
Chapter 30 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern Physics
Ch. 30.1 - A circular loop of wire is held in a uniform...Ch. 30.2 - QUICK QUIZ 30.2 In Figure 30.8a, a given applied...Ch. 30.3 - Figure 30.12 (Quick Quiz 30.3) QUICK QUIZ 30.3...Ch. 30.5 - Prob. 30.4QQCh. 30 - A circular loop of wire of radius 12.0 cm is...Ch. 30 - An instrument based on induced emf has been used...Ch. 30 - Scientific work is currently under way to...Ch. 30 - A long solenoid has n = 400 turns per meter and...Ch. 30 - An aluminum ring of radius r1 = 5.00 cm and...Ch. 30 - Prob. 6P
Ch. 30 - A coil formed by wrapping 50 turns of wire in the...Ch. 30 - Prob. 8PCh. 30 - A toroid having a rectangular cross section (a =...Ch. 30 - A small airplane with a wingspan of 14.0 m is...Ch. 30 - A helicopter (Fig. P30.11) has blades of length...Ch. 30 - A 2.00-m length of wire is held in an eastwest...Ch. 30 - A metal rod of mass m slides without friction...Ch. 30 - Prob. 14PCh. 30 - Prob. 15PCh. 30 - Prob. 16PCh. 30 - You are working for a company that manufactures...Ch. 30 - You are working in a laboratory that uses motional...Ch. 30 - You are working in a factory that produces long...Ch. 30 - Prob. 20PCh. 30 - Within the green dashed circle show in Figure...Ch. 30 - Prob. 22PCh. 30 - Prob. 23PCh. 30 - Figure P30.24 (page 820) is a graph of the induced...Ch. 30 - The rotating loop in an AC generator is a square...Ch. 30 - In Figure P30.26, a semicircular conductor of...Ch. 30 - Prob. 27PCh. 30 - Prob. 28APCh. 30 - Prob. 29APCh. 30 - Prob. 30APCh. 30 - A circular coil enclosing an area of 100 cm2 is...Ch. 30 - Prob. 32APCh. 30 - A guitars steel string vibrates (see Fig. 30.5)....Ch. 30 - Prob. 34APCh. 30 - A conducting rod of length = 35.0 cm is free to...Ch. 30 - Prob. 36APCh. 30 - Prob. 37APCh. 30 - In Figure P30.38, the rolling axle, 1.50 m long,...Ch. 30 - Figure P30.39 shows a stationary conductor whose...Ch. 30 - Prob. 40APCh. 30 - Figure P30.41 shows a compact, circular coil with...Ch. 30 - Review. In Figure P30.42, a uniform magnetic field...Ch. 30 - An N-turn square coil with side and resistance R...Ch. 30 - A conducting rod of length moves with velocity v...Ch. 30 - A long, straight wire carries a current given by I...Ch. 30 - A rectangular loop of dimensions and w moves with...Ch. 30 - A thin wire = 30.0 cm long is held parallel to...Ch. 30 - Prob. 48CPCh. 30 - Prob. 49CPCh. 30 - Prob. 50CPCh. 30 - Review. The bar of mass m in Figure P30.51 is...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- ! Required information Assume that the magnifier is held close to the eye. Use the standard near point of 25.0 cm to find the angular magnification. An insect that is 4.10 mm long is placed 10.3 cm from a simple magnifier with a focal length of 13.0 cm. What is the angular magnification?arrow_forward2arrow_forward3arrow_forward
- Imagine you are out for a stroll on a sunny day when you encounter a lake. Unpolarized light from the sun is reflected off the lake into your eyes. However, you notice when you put on your vertically polarized sunglasses, the light reflected off the lake no longer reaches your eyes. What is the angle between the unpolarized light and the surface of the water, in degrees, measured from the horizontal? You may assume the index of refraction of air is nair=1 and the index of refraction of water is nwater=1.33 . Round your answer to three significant figures. Just enter the number, nothing else.arrow_forwardDeduce what overvoltage is like in reversible electrodes.arrow_forwardpls help on thesearrow_forward
- pls help on thesearrow_forward20. Two small conducting spheres are placed on top of insulating pads. The 3.7 × 10-10 C sphere is fixed whie the 3.0 × 107 C sphere, initially at rest, is free to move. The mass of each sphere is 0.09 kg. If the spheres are initially 0.10 m apart, how fast will the sphere be moving when they are 1.5 m apart?arrow_forwardpls help on allarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781938168000
Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:OpenStax College

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

What is Electromagnetic Induction? | Faraday's Laws and Lenz Law | iKen | iKen Edu | iKen App; Author: Iken Edu;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=3HyORmBip-w;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY