
Concept explainers
(a)
The magnitude and the direction of the net magnetic field at the mid way between the wires.
(a)
Answer to Problem 20P
The magnitude is
Explanation of Solution
Write the expression to obtain the magnetic field along the conductor.
Here,
The net magnetic field at the mid way between the wires is as shown in the figure below.
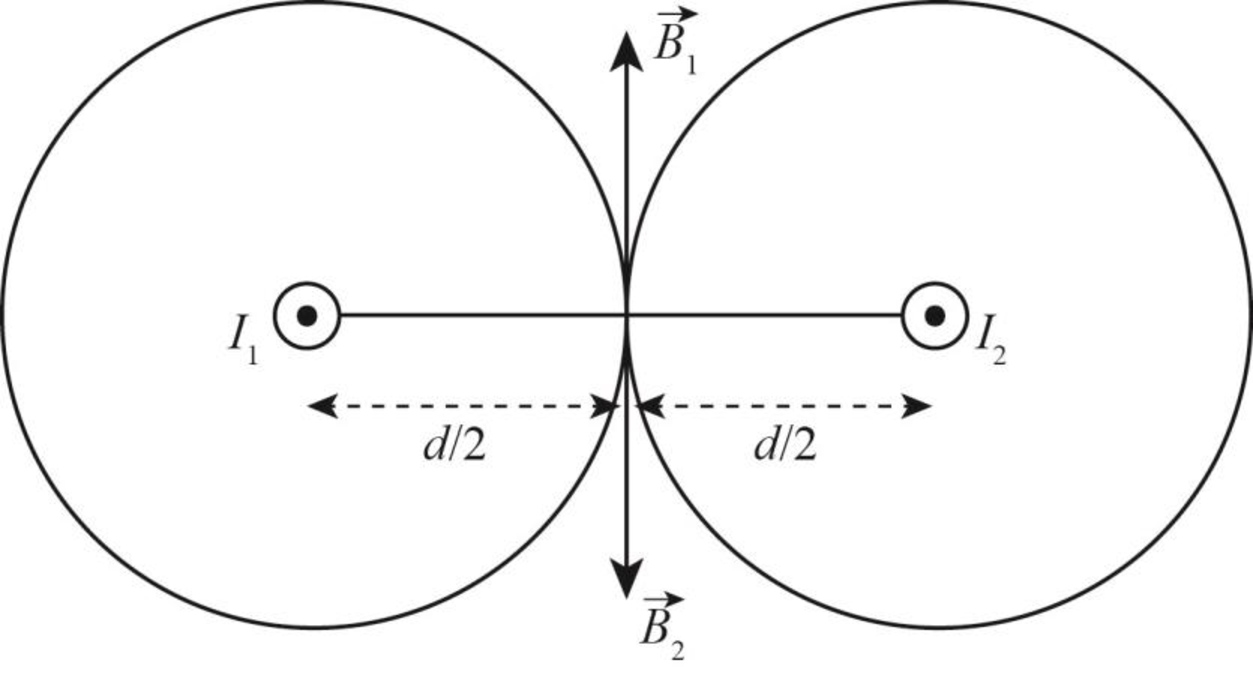
Figure-(1)
Write the expression to obtain the magnetic field due to the wire
Here,
Substitute
Write the expression to obtain the magnetic field due to the wire
Here,
Substitute
Write the expression to obtain the net magnetic field at the mid way between the wires.
Here,
Conclusion:
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Therefore, the magnitude is
(b)
The magnitude and the direction of the net magnetic field at point
(b)
Answer to Problem 20P
The magnitude of net magnetic field at point
Explanation of Solution
The net magnetic field at point
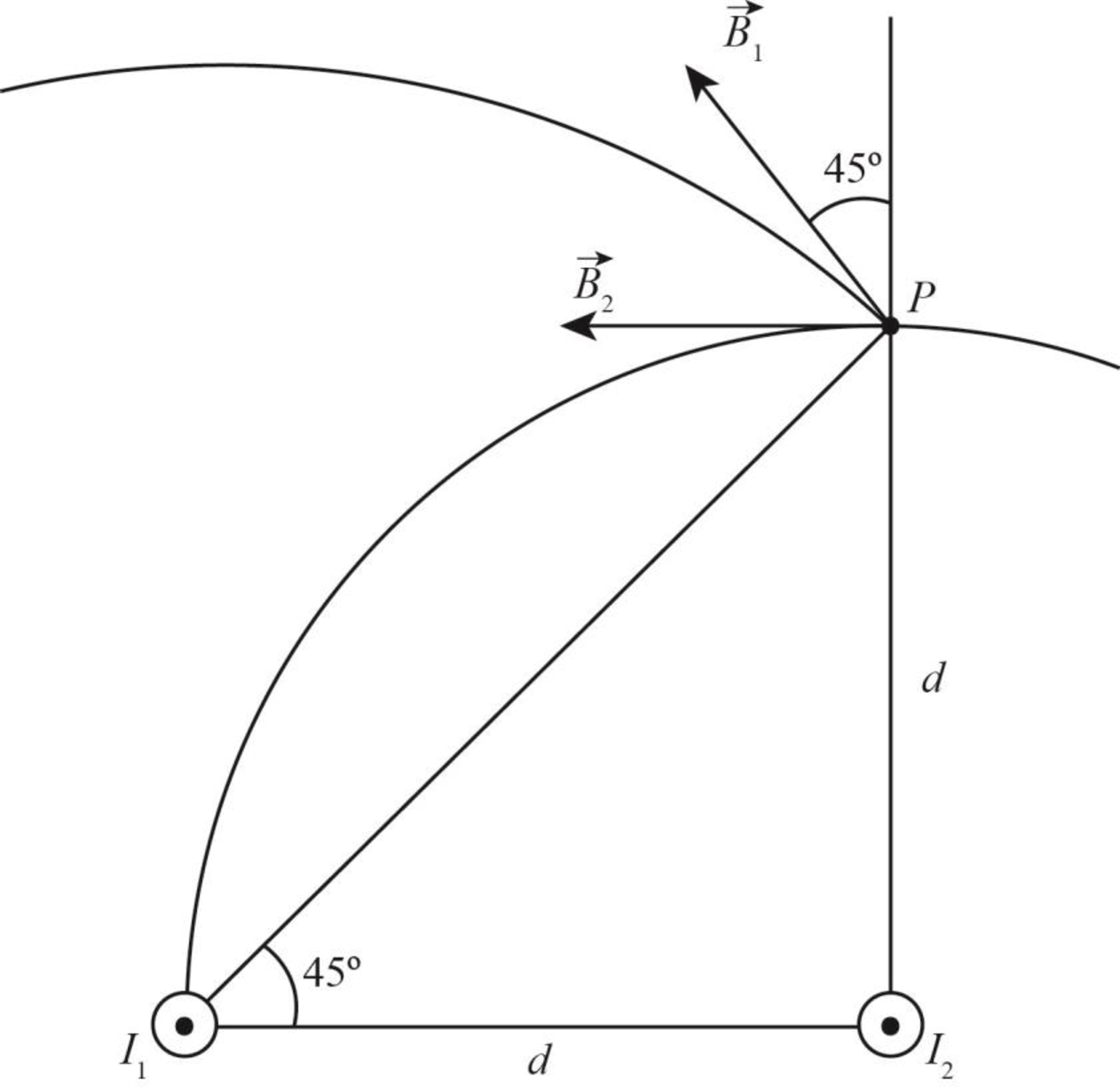
Figure-(2)
Write the expression to obtain the magnetic field due to the wire
Here,
Substitute
Write the expression to obtain the magnetic field due to the wire
Here,
Substitute
Write the expression to obtain the net magnetic field at the distance
Here,
Write the expression to obtain the magnitude of the net magnetic field at the distance
Here,
Write the expression to obtain direction of the net magnetic field at point
Here,
Conclusion:
Substitute
The value of
Substitute
Substitute
The value of
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Therefore, the magnitude of net magnetic field at point
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 30 Solutions
Bundle: Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern Physics, Loose-leaf Version, 9th + WebAssign Printed Access Card, Multi-Term
- (a) For a spherical capacitor with inner radius a and outer radius b, we have the following for the capacitance. ab C = k₂(b- a) 0.0695 m 0.145 m (8.99 × 10º N · m²/c²)( [0.145 m- 0.0695 m × 10-11 F = PF IIarrow_forwardA pendulum bob A (0.5 kg) is given an initialspeed of vA = 4 m/s when the chord ishorizontal. It then hits a stationary block B (1kg) which then slides to a maximum distanced before it stops. Determine the value of d.The coefficient of static friction between theblock and the plane is μk = 0.2. The coefficientof restitution between A and B is e = 0.8.Ans: d=1.0034 marrow_forwardFigure 29-43 Problem 12. ••13 In Fig. 29-44, point P₁ is at distance R = 13.1 cm on the perpendicular bisector of a straight wire of length L = 18.0 cm carrying current i = 58.2 mA. (Note that the wire is not long.) What is the magnitude of the magnetic field at P₁ due to i? P2° R R Larrow_forward
- Checkpoint 1 The figure shows the current i in a single-loop circuit with a battery B and a resistance R (and wires of neg- ligible resistance). (a) Should the emf arrow at B be drawn pointing leftward or rightward? At points a, B C R b, and c, rank (b) the magnitude of the current, (c) the electric potential, and (d) the electric potential energy of the charge carriers, greatest first.arrow_forwardPls help ASAParrow_forwardPls help asaparrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning





