
Concept explainers
Repeat Example 30.1, but use the midpoint method to generate your solution.
To calculate: The solution of the one-dimensional heat conduction equation using midpoint method for a thing rod of length
Answer to Problem 1P
Solution: The desired result is as shown below.
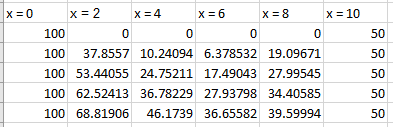
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
The expression of the temperature distribution of long, thin rod is,
Calculation:
Calculate
and
The expression of temperature,
Rewrite the above equation,
Rewrite the above equation,
Substitute the value at t = 0.1 s for the node at x = 2 cm,
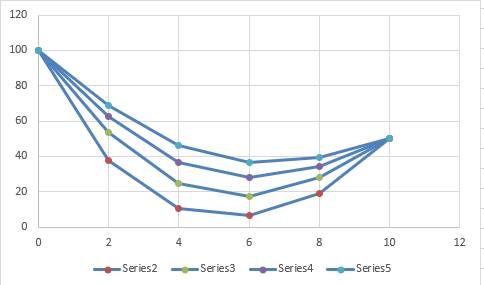
The results at the other interior points are,
Therefore,
Next,
And,
The value at t = 0.2 s; the interior points are four are,
Therefore,
Next,
And,
The Midpoint method in this subpart is,
And,
Use
predictor is calculating as follow:
Slop-midpoint,
Calculate corrector,
Use Excel to create the table as follow,
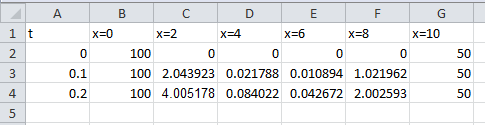
Use excel to solve this problem.
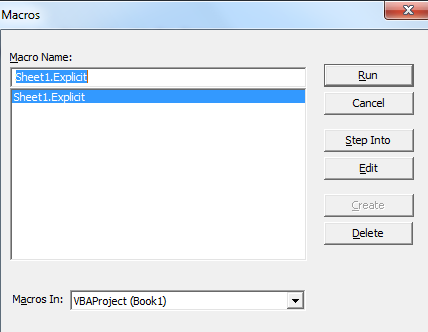
Step 1 Open the excel-spreadsheet and then press Alt+F11.
Step 2 Then there is a window opened in which write the coding to find optimal solution is as below,
Step 3 Now press F5, a new popup window will appear as shown below.
Step 4 Press run after selecting the program name, the desired result will be,
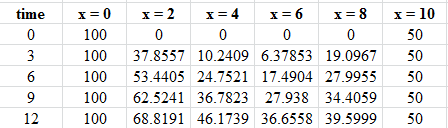
The flotation of the table is,
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 30 Solutions
Numerical Methods for Engineers
- This is an old practice exam. Fce = 110lb and FBCD = 62 lb but whyarrow_forwardQuiz/An eccentrically loaded bracket is welded to the support as shown in Figure below. The load is static. The weld size for weld w1 is h1 = 4mm, for w2 h2 = 6mm, and for w3 is h3 =6.5 mm. Determine the safety factor (S.f) for the welds. F=29 kN. Use an AWS Electrode type (E100xx). 163 mm S 133 mm 140 mm Please solve the question above I solved the question but I'm sure the answer is wrong the link : https://drive.google.com/file/d/1w5UD2EPDiaKSx3W33aj Rv0olChuXtrQx/view?usp=sharingarrow_forwardQ2: (15 Marks) A water-LiBr vapor absorption system incorporates a heat exchanger as shown in the figure. The temperatures of the evaporator, the absorber, the condenser, and the generator are 10°C, 25°C, 40°C, and 100°C respectively. The strong liquid leaving the pump is heated to 50°C in the heat exchanger. The refrigerant flow rate through the condenser is 0.12 kg/s. Calculate (i) the heat rejected in the absorber, and (ii) the COP of the cycle. Yo 8 XE-V lo 9 Pc 7 condenser 5 Qgen PG 100 Qabs Pe evaporator PRV 6 PA 10 3 generator heat exchanger 2 pump 185 absorberarrow_forward
- Q5:(? Design the duct system of the figure below by using the balanced pressure method. The velocity in the duct attached to the AHU must not exceed 5m/s. The pressure loss for each diffuser is equal to 10Pa. 100CFM 100CFM 100CFM ☑ ☑ 40m AHU -16m- 8m- -12m- 57m 250CFM 40m -14m- 26m 36m ☑ 250CFMarrow_forwardA mass of ideal gas in a closed piston-cylinder system expands from 427 °C and 16 bar following the process law, pv1.36 = Constant (p times v to the power of 1.36 equals to a constant). For the gas, initial : final pressure ratio is 4:1 and the initial gas volume is 0.14 m³. The specific heat of the gas at constant pressure, Cp = 0.987 kJ/kg-K and the specific gas constant, R = 0.267 kJ/kg.K. Determine the change in total internal energy in the gas during the expansion. Enter your numerical answer in the answer box below in KILO JOULES (not in Joules) but do not enter the units. (There is no expected number of decimal points or significant figures).arrow_forwardmy ID# 016948724. Please solve this problem step by steparrow_forward
- My ID# 016948724 please find the forces for Fx=0: fy=0: fz=0: please help me to solve this problem step by steparrow_forwardMy ID# 016948724 please solve the proble step by step find the forces fx=o: fy=0; fz=0; and find shear moment and the bending moment diagran please draw the diagram for the shear and bending momentarrow_forwardMy ID#016948724. Please help me to find the moment of inertia lx ly are a please show to solve step by stepsarrow_forward
 Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305387102Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305387102Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Technology (Mi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305578296Author:John Tomczyk, Eugene Silberstein, Bill Whitman, Bill JohnsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Technology (Mi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305578296Author:John Tomczyk, Eugene Silberstein, Bill Whitman, Bill JohnsonPublisher:Cengage Learning Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L Understanding Motor ControlsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337798686Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning
Understanding Motor ControlsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337798686Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning




