
Concept explainers
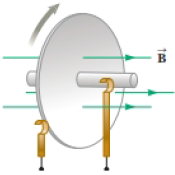
You are working for a company that manufactures motors and generators. At the end of your first day of work, your supervisor explains to you that you will be assigned to a team that is designing a new homopolar generator. You have no idea what that is, but agree wholeheartedly to the assignment. At home that evening, you go online to learn about the homopolar generator and find the following. The homopolar generator, also called the Faraday disk, is a low-voltage, high-current electric generator. It consists of a rotating
Figure P30.17
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 30 Solutions
Physics:f/sci.+engrs.,ap Ed.
- Blocks 1 and 2, with masses M1=0.50 kg and M2=1.5 kg, are connected by an ideal string, which passes over a pulley without slipping (see figure). The magnitudes of the wire voltages applied to blocks 1 and 2 are represented, respectively, by T1 and T2. Consider T2>T1. In this case, the pulley rotates counterclockwise. The pulley has radius R=0.46 m and rotates around an axis perpendicular to its surface passing through its CM. The CM of the pulley coincides with its center. The moment of inertia of the pulley with respect to the axis of rotation is denoted by I and the acceleration of the blocks has magnitude 0.025 m/s2. Use g=10 m/s2. Determine I (in kg⋅m2). Choose an option : a) 3,0 b) 4,0 c) 210 d) 41 e) 64 f) 84 g) 8,0 h) 32arrow_forwardPlease answer each question with all requirements.arrow_forwardA bar magnet is attached solidly to a frictionless surface and its length is aligned with the x axis. To the right of the first magnet a short distance away is a second bar magnet with its center placed on the x axis and its length perpendicular to the x axis. The second magnet is free to move. Once placed in position at rest, which best describes the initial motion of the second magnet? O The magnet will move away from the fixed magnet. The magnet will not move. The magnet will start to rotate. O The magnet will move toward the fixed magnet.arrow_forward
- You may want to review (Page 796). For help with math skills, you may want to review: The Vector Cross Product 1 The Vector Cross Product 2 Figure P 1 of 1 Part A What is the strength of the magnetic field at point P in the figure? (Figure 1) Assume that I = 6.0 A, T1 = 1.1 cm, and r2 = 2.2 cm. Express your answer to two significant figures and include the appropriate units. B = 1 Submit Part B μà Value Request Answer Submil into the screen out of the screen What is the direction of the magnetic field at point P in the figure? Previous Answers Correct Units B ?arrow_forwardA student has curved magnets; paper clips; a battery, and 0.1 m of cuttable, bendable wire. The student builds a simple motor, as shown. N Wire C S Battery Paper clips However, the student does not observe any motion from the simple motor. What should the student do to fix the motor? Explain your reasoning. B I U X² X₂ Ωarrow_forwardThe earth's magnetic field, with a magnetic dipole moment of 8.0 x 1022 A m², is generated by currents within the molten iron of the earth's outer core. Suppose we model the core current as a 3000-km-diameter current loop made from a 1000-km-diameter "wire." The loop diameter is measured from the centers of this very fat wire. m What is the current in the current loop? Express your answer to two significant figures and include the appropriate units. I = Submit Part B Value J = ΜΑ Submit Request Answer What is the current density J in the current loop? Express your answer to two significant figures and include the appropriate units. μÅ Value Units Request Answer ? Units ?arrow_forward
- A 144-Ω light bulb is connected to a conducting wire that is wrapped into the shape of a square with side length of 83.0 cm. This square loop is rotated within a uniform magnetic field of 454 mT. What is the change in magnetic flux through the loop when it rotates from a position where its area vector makes an angle of 30° with the field to a position where the area vector is parallel to the field? The loop rotates from a position where its area vector makes an angle of 30° with the field to a position where the area vector is parallel to the field in 56.3 ms. What is the induced current through the light bulb? This square loop is rotated with a frequency of 60 Hz within a uniform magnetic field of 454 mT. This means the loop makes half a revolution in 8.33 ms. What is the induced current in the light bulb when the loop rotates from a position where its area vector is opposite the magnetic field to a position where its area vector is parallel to the magnetic field?arrow_forwardThe figure shows two closed paths wrapped around two conducting loops carrying currents i = 6.4 A and iz = 3.6 A. What is the value of the integral B ds for (a) path 1 and (b) path 2? D2arrow_forwardThe figure below shows a conducting rod sliding along a pair of conducting rails. The conducting rails have an angle of inclination of θ=30 degrees. There is a resistor at the top of the ramp that connects the two conducting rails R=2.3Ω. The mass of the rod is 0.42 kg. The rod starts from rest at the top of the ramp at time t=0. The rails have negligible resistance and friction, and are separated by a distance L=15.7 m. There is a constant, vertically directed magnetic field of magnitude B=1.5 T. A) Find the emf induced in the rod as a function of its velocity down the rails. What is the emf when the velocity is 5.696E−03 m/s? B) What is the rod's terminal speed? C) When the rod moves at its terminal speed, what is the power dissipated in the resistor?arrow_forward
- 6. Three long, straight wires are mounted on the vertices of an equilateral triangle as shown in the figure. The wires carry currents of I1 = 9.50 A, I2 = 6.50 A, and I3 = 7.00 A. Each side of the triangle has a length of 32.0 cm, and the point (B) is located half way between (I2) and (I3) along one of the sides. Find the magnitude of the magnetic field at point (B). Tarrow_forwardn the Figure, a wire is bent into the shape of a straight wire and a circle, with a circular loop of radius R = 2.8 cm and two long straight sections. The loop center coincides with the origin of the coordinate system as shown. The straight sections are parallel to x-axis. The wire carries a I = 2.8 A current, as shown. Calculate the magnitude and the direction (into or out of the page) of the magnetic field at the origin. (Choose out of the page as the positive z-direction and express the magnetic field by using the sign of the result, which must be in multiples of 10 -5 Teslas and include 2 digit after the decimal point. That means if you get a result of a 9.22 x 10 -5 and the direction of the field is out of the page, just type 9.22 or if you find the direction of the field as into the page, just tpe -9.22 in the answer box. Maximum of 5% of error accepted in your answer. Take vacuum permeability µ 0 = 4π x 10 -7 T /A 2 and π=3.14.)arrow_forwardA uniform magnetic field is going into the plane of the page. Two charged particles move in circles in the plane of the page as shown in the figure. The two particles have the same magnitude of charge, lal, and the same kinetic energy. Which of the following is true about the particles' charges? q2 is positive and q1 is negative q1 and q2 are both negative none of these q1 is positive and q2 is negative there is not enough information to determine O q1 and q2 are both positive O q1 and q2 have opposite signs, but we don't know which is positive and which is negativearrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College





