
Sub part (a):
Effects of higher interest rate on households and firm behavior.
Sub part (a):
Explanation of Solution
If the Federal Reserve System rises the interest rates, then the borrowing of items become more costly. Therefore, households will reduce the purchase of durable goods such as auto mobiles and houses. So when the rate of interest rises, consumers spending on durable goods reduce.
In the case of firms, when the rate of interest rises, cost of capital becomes higher. Therefore firms will reduce the spending on investment. So when the rate of interest rises, investment will reduce.
Concept introduction:
Rate of interest: The rate of interest: The rate of interest refers to that percentage at which the money is borrowed or is taken as a loan. The amount to be paid as interest is calculated on this given percentage.
Sub part (b):
Effects of higher interest rate on bonds.
Sub part (b):
Explanation of Solution
When the rate of interest rises by the Federal Reserve, it will fall the existing values of fixed rate bonds. Because, in the case of fixed rate bonds, if the holder paying 7% for the next 10 years is become simply worth less if the potential buyers can now earn 8% by buying a new bond. That’s why, the higher interest rate would decrease the value of existing fixed rate bonds held by the public.
Concept introduction:
Bonds: Bond refers to the securities, which are traded in the public to raise the capital when needed. It is an investment with a fixed income, where an investor gives money to an entity or individual for a specified period of time at a fixed rate.
Sub part (c):
Wealth effect of higher interest rate on consumption.
Sub part (c):
Explanation of Solution
Figure 1 illustrates the changes in aggregative
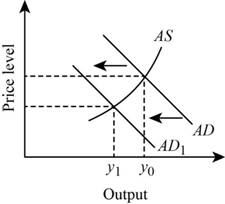
In figure-1, vertical axis shows the output and the horizontal axis shows the
When the rate of interest rises, the cost of borrowing become higher. And also, the investment rate reduces because of the higher rate of capitals. These factors will reduce the wealth of an economy. When wealth reduces, consumers will spend less and they become worse off. In short, higher interest rate will reduce the spending of consumers. Therefore, the aggregative demand curve will shift the left wards. This is higher than the direct effect on investment.
Concept introduction:
Wealth effect: Wealth effect refers to the effect of a change in the price that has on the wealth of the individual.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 30 Solutions
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
- 19. In a paragraph, no bullet, points please answer the question and follow the instructions. Give only the solution: Use the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’re explaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all. How does the Federal Reserve currently get the federal funds rate where they want it to be?arrow_forward18. In a paragraph, no bullet, points please answer the question and follow the instructions. Give only the solution: Use the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’re explaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all. Carefully compare and contrast fiscal policy and monetary policy.arrow_forward15. In a paragraph, no bullet, points please answer the question and follow the instructions. Give only the solution: Use the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’re explaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all. What are the common arguments for and against high levels of federal debt?arrow_forward
- 17. In a paragraph, no bullet, points please answer the question and follow the instructions. Give only the solution: Use the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’re explaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all. Explain the difference between present value and future value. Be sure to use and explain the mathematical formulas for both. How does one interpret these formulas?arrow_forward12. Give the solution: Use the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’re explaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all. Show and carefully explain the Taylor rule and all of its components, used as a monetary policy guide.arrow_forward20. In a paragraph, no bullet, points please answer the question and follow the instructions. Give only the solution: Use the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’re explaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all. What is meant by the Federal Reserve’s new term “ample reserves”? What may be hidden in this new formulation by the Fed?arrow_forward
- 14. In a paragraph, no bullet, points please answer the question and follow the instructions. Give only the solution: Use the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’re explaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all. What is the Keynesian view of fiscal policy and why are some economists skeptical?arrow_forward16. In a paragraph, no bullet, points please answer the question and follow the instructions. Give only the solution: Use the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’re explaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all. Describe a bond or Treasury security. What are its components and what do they mean?arrow_forward13. In a paragraph, no bullet, points please answer the question and follow the instructions. Give only the solution: Use the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’re explaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all. Where does the government get its funds that it spends? What is the difference between federal debt and federal deficit?arrow_forward
- 11. In a paragraph, no bullet, points please answer the question and follow the instructions. Give only the solution: Use the Feynman technique throughout. Assume that you’re explaining the answer to someone who doesn’t know the topic at all. Why is determining the precise interest rate target so difficult for the Fed?arrow_forwardProblem 1 Regression Discontinuity In the beginning of covid, the US government distributed covid stimulus payments. Suppose you are interested in the effect of receiving the full amount of the first stimulus payment on the total spending in dollars by single individuals in the month after receiving the payment. Single individuals with annual income below $75,00 received the full amount of the stimulus payment. You decide to use Regression Discontinuity to answer this question. The graph below shows the RD model. 3150 3100 3050 Total Spending in the month after receiving the stimulus payment 2950 3000 74000 74500 75000 75500 76000 Annual income a. What is the outcome? (5 points) b. What is the treatment? (5 points) C. What is the running variable? (5 points) d. What is the cutoff? (5 points) e. Who is in the treatment group and who is in the control group? (10 points) f. What is the discontinuity in the graph and how do you interpret it? (10 points) g. Explain a scenario which can…arrow_forwardProblem 2 Difference-in-Difference In the beginning of 2005, Minnesota increased the sales tax on alcohol. Suppose you are interested in studying the effect of the increase in sale taxes on alcohol on the number of car accidents due to drinking in Minnesota. Unlike Minnesota, Wisconsin did not change the sales tax on alcohol. You decide to use a Difference-in-difference (DID) Model. The numbers of car accidents in each state at the end of 2004 and 2005 are as follows: Year Number of car accidents in Minnesota Number of car accidents in Wisconsin 2004 2000 2500 2005 2500 3500 a. Which state is the treatment state and which state is the control state? (10 points) b. What is the change in the outcome for the treatment group between 2004 and 2005? (5 points) C. Can we interpret the change in the outcome for the treatment group between 2004 and 2005 as the causal effect of the policy on car accidents? Explain your answer. (10 points) d. What is the change in the outcome for the control…arrow_forward
 Macroeconomics: Private and Public Choice (MindTa...EconomicsISBN:9781305506756Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. MacphersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Macroeconomics: Private and Public Choice (MindTa...EconomicsISBN:9781305506756Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. MacphersonPublisher:Cengage Learning Economics: Private and Public Choice (MindTap Cou...EconomicsISBN:9781305506725Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. MacphersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Economics: Private and Public Choice (MindTap Cou...EconomicsISBN:9781305506725Author:James D. Gwartney, Richard L. Stroup, Russell S. Sobel, David A. MacphersonPublisher:Cengage Learning Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning
Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning







