
1.
Prepare the T-accounts and enter the beginning balance from the
1.
Explanation of Solution
T-account:
T-account refers to an individual account, where the increasesor decreases in the value of specific asset, liability,
This account is referred to as the T-account, because the alignment of the components of the account resembles the capital letter ‘T’.’ An account consists of the three main components which are as follows:
- (a) The title of the account
- (b) The left or debit side
- (c) The right or credit side
The T-accounts of given item in trial balance are as follows:
| Cash | |||
| $24,600 | |||
| Bal. | $20,000 | ||
| Accounts payable | |||
| $6,700 | |||
| Bal. | $6,700 | ||
| Common stock | |||
| $143,000 | |||
| Bal. | $143,000 | ||
|
Accounts receivables | |||
| $15,400 | |||
| Bal. | $15,400 | ||
| Prepaid Insurance | |||
| $12,000 | |||
| Bal. | $12,000 | ||
| Deferred revenue | |||
| $5,800 | |||
| Bal. | $5,800 | ||
| Land | |||
| 148,000 | |||
| Bal. | 148,000 | ||
| $44,500 | |||
| Bal. | $44,500 | ||
2.
Record the
2.
Explanation of Solution
Journal:
Journal is the method of recording monetary business transactions in chronological order. It records the debit and credit aspects of each transaction to abide by the double-entry system.
Rules of Debit and Credit:
Following rules are followed for debiting and crediting different accounts while they occur in business transactions:
- Debit, all increase in assets, expenses and dividends, all decrease in liabilities, revenues and stockholders’ equities.
- Credit, all increase in liabilities, revenues, and stockholders’ equities, all decrease in assets, expenses.
The journal entries for given transactions of Company Z are as follows:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| 2021 | 52,200 | ||
| January 9 | Cash | 134,100 | |
| Service revenue | 186,300 | ||
| (To record the recognized service revenue on account and cash) | |||
| 2021 | Cash | 51,500 | |
| February, 12 | Accounts receivable | 51,500 | |
| (To record cash collection from customer) | |||
| 2021 | Cash | 12,900 | |
| April 25 | Deferred revenue | 12,900 | |
| (To record the cash received in advance from customers) | |||
| 2021 | Supplies | 9,200 | |
| May 6 | Accounts payable | 9,200 | |
| (To record the purchase of supplies on account) | |||
| 2021 | Property tax expense | 8,500 | |
| July 15 | Cash | 8,500 | |
| (To record the payment of repairs and maintenance expense) | |||
| 2021 | Accounts payable | 11,400 | |
| September 10 | Cash | 11,400 | |
| (To record the payables on account ) | |||
| 2021 | Salaries expense | 123,600 | |
| October 31 | Cash | 123,600 | |
| (To record the payment of salaries for the current year) | |||
| 2021 | Cash | 27,000 | |
| November 20 | Common stock | 27,000 | |
| (To record the payment of issuing shares of common stock) | |||
| 2021 | Dividends | 2,800 | |
| December 30 | Cash | 2,800 | |
| (To record the payment of dividends) | |||
Table (1)
3.
Post the transactions to T-accounts.
3.
Explanation of Solution
T-account:
T-account refers to an individual account, where the increasesor decreases in the value of specific asset, liability, stockholder’s equity, revenue, and expenditure items are recorded.
This account is referred to as the T-account, because the alignment of the components of the account resembles the capital letter ‘T’.’ An account consists of the three main components which are as follows:
- (a) The title of the account
- (b) The left or debit side
- (c) The right or credit side
T-accounts of above transactions are as follows:
| Cash | |||
| $24,600 | $8,500 | ||
| $134,100 | $11,400 | ||
| $51,500 | $123,600 | ||
| $12,900 | $2,800 | ||
| $27,000 | |||
| Bal. | $103,800 | ||
| Supplies | |||
| $0 | |||
| $9,200 | |||
| $9,200 | |||
| Deferred revenue | |||
| $5,800 | |||
| $12,900 | |||
| $18,700 | |||
| Dividends | |||
| $0 | |||
| $2,800 | |||
| $2,800 | |||
|
Salaries expense | |||
| $0 | |||
| $123,600 | |||
| Bal. | $123,600 | ||
| Accounts receivable | ||||
| $15,400 | ||||
| $52,200 | $51,500 | |||
| Bal. | $16,100 | |||
| Land | |||
| $148,000 | |||
| Bal. | $148,000 | ||
| Common stock | ||||||
| $143,000 | ||||||
| $27,000 | ||||||
| Bal. | $170,000 | |||||
| Service revenue | |||
| $0 | |||
| Bal. | $186,300 | ||
| Insurance expense | |||
| $0 | |||
| $0 | |||
| Prepaid Insurance | |||
| $12,000 | |||
| $12,000 | |||
| Accounts payable | |||
| $6,700 | |||
| $11,400 | $9,200 | ||
| $4,500 | |||
| Retained earnings | |||
| 44,500 | |||
| Bal. | $44,500 | ||
| Property Tax Expense | |||
| $0 | |||
| $8,500 | |||
| Supplies expense | |||
| $0 | |||
| $0 | |||
4.
Prepare the unadjusted trial balance of Company Z.
4.
Explanation of Solution
Unadjusted trial balance:
The unadjusted trial balance is the summary of all the ledger accounts before making adjusting journal entries at the end of the period.
| Company Z | ||
| Unadjusted Trial Balance | ||
| December 31, 2021 | ||
| Accounts | Debit | Credit |
| Cash | $103,800 | |
| Accounts Receivable | 16,100 | |
| Prepaid Insurance | 12,000 | |
| Supplies | 9,200 | |
| Land | 148,000 | |
| Accounts Payable | 4,500 | |
| Deferred Revenue | 18,700 | |
| Common stock | 170,000 | |
| Retained earnings | 44,500 | |
| Dividends | 2,800 | |
| Service Revenue | 186,300 | |
| Property Tax expense | 8,500 | |
| Salaries expense | 123,600 | |
| Insurance expense | 0 | |
| Supplies Expense | 0 | |
| Totals | $424,000 | $424,000 |
Table (2)
Therefore, the total of debit, and credit columns of unadjusted trial balance is $424,000 and agree.
5.
Record the given
5.
Explanation of Solution
Adjusting entries:
Adjusting entries refers to the entries that are made at the end of an accounting period in accordance with revenue recognition principle, and expenses recognition principle. The purpose of adjusting entries is to adjust the revenue, and the expenses during the period in which they actually occurs.
Rules of Debit and Credit:
Following rules are followed for debiting and crediting different accounts while they occur in business transactions:
- Debit, all increase in assets, expenses and dividends, all decrease in liabilities, revenues and stockholders’ equities.
- Credit, all increase in liabilities, revenues, and stockholders’ equities, all decrease in assets, expenses.
Adjusting entries of Company R are as follows:
Accrued salaries:
| Date | Accounts title and explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| December 31, 2021 | Deferred Revenue | 11,800 | ||
| Service revenue | 11,800 | |||
| (To record the salaries expense incurred at the end of the accounting year) |
Table (3)
Following is the rule of debit and credit of above transaction:
- Deferred revenue is a liability, and it decreases the value of stockholder’s equity. Therefore, it is debited.
- Service revenue is a component of stockholders’ equity. There is an Increase in stockholders’ equity, therefore it is credited.
Depreciation expense:
| Date | Accounts title and explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| December 31, 2021 | Insurance Expense | 7,000 | ||
| Prepaid Insurance | 7,000 | |||
| (To record the amount of Reduced prepaid insurance due to passage of time) |
Table (4)
Following is the rule of debit and credit of above transaction:
- Insurance expense is an expense, and it decreased the value of stockholder’s equity. Therefore, it is debited.
- Prepaid Insurance is a contra-asset account. There is a decrease in assets, therefore it is credited.
Office supplies expense:
| Date | Accounts title and explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| December 31, 2021 | Suppliesexpense | 6,300 | ||
| Supplies | 6,300 | |||
| (To record the supplies expense incurred at the end of the accounting year) |
Table (5)
Working Note:
Calculate the supplies expense.
Following is the rule of debit and credit of above transaction:
- Supplies expense is an expense, and it decreased the value of stockholder’s equity. Therefore, it is debited.
- Supplies are an asset account. There is a decrease in assets, therefore it is credited.
6.
Post the adjusting entries to appropriate T-accounts.
6.
Explanation of Solution
| Cash | |||
| $24,600 | $8,500 | ||
| $134,100 | $11,400 | ||
| $51,500 | $123,600 | ||
| $12,900 | $2,800 | ||
| $27,000 | |||
| Bal. | $103,800 | ||
| Supplies | |||
| $0 | |||
| $9,200 | $6,300 | ||
| $2,900 | |||
| Deferred revenue | |||
| $5,800 | |||
| 11,800 | $12,900 | ||
| $6,900 | |||
| Dividends | ||||
| $0 | ||||
| $2,800 | ||||
| $2,800 | ||||
| Salaries expense | |||
| $0 | |||
| $123,600 | |||
| $123,600 | |||
| Accounts receivable | |||
| $15,400 | |||
| $52,200 | $51,500 | ||
| Bal. | $16,100 | ||
| Land | |||
| Jan. 1 | $148,000 | ||
| Bal. | $148,000 | ||
| Common stock | |||
| $143,300 | |||
| Bal. | $27,000 | ||
| Total | $170,000 | ||
| Service revenue | |||
| $0 | |||
| Bal. | $186,300 | ||
| $11,800 | |||
| Total | $198,100 | ||
| Insurance expense | |||
| Jan. 1 | $0 | ||
| $7,000 | |||
| Total | $7,000 | ||
| Prepaid Insurance | |||
| $12,000 | |||
| $7,000 | |||
| $5,000 | |||
| Accounts payable | |||
| $6,700 | |||
| $11,400 | $9,200 | ||
| $4,500 | |||
| Retained earnings | |||
| 44,500 | |||
| Bal. | $44,500 | ||
| Property Tax Expense | |||
| $0 | |||
| $8,500 | |||
| Supplies expense | |||
|
$0 $6,300 | |||
| Bal. | $6,300 | ||
7.
Prepare the adjusted trial balance of Company Z.
7.
Explanation of Solution
Adjusted trial balance:
Adjusted trial balance is a summary of all the ledger accounts, and it contains the balances of all the accounts after the adjustment entries are journalized, and posted.
Adjusted trial balance of Company R is as follows:
| Company Z | ||
| Adjusted Trial Balance | ||
| December 31, 2021 | ||
| Accounts | Debit | Credit |
| Cash | 103,800 | |
| Accounts Receivable | 16,100 | |
| Prepaid insurance | 5,000 | |
| Supplies | 2,900 | |
| Land | 148,000 | |
| Accounts payable | 4,500 | |
| Deferred revenue | 6,900 | |
| Common stock | 170,000 | |
| Retained earnings | 44,500 | |
| Dividends | 2,800 | |
| Service revenue | 198,100 | |
| Property tax expense | 8,500 | |
| Salaries expense | 123,600 | |
| Insurance expense | 7,000 | |
| Supplies expense | 6,300 | |
| Totals | $424,000 | $424,000 |
Table (6)
Therefore, the total of debit, and credit columns of adjusted trial balance is $424,000 and agree.
8.
Prepare an income statement for 2021 and classified
8.
Explanation of Solution
Income statement:
This is the financial statement of a company which shows all the revenues earned and expenses incurred by the company over a period of time.
Classified balance sheet:
This is the financial statement of a company which shows the grouping of similar assets and liabilities under subheadings.
Income statement:
Income statement of Company Z is as follows:
| Company Z | ||
| Income statement | ||
| For the year ended December 31, 2021 | ||
| $ | $ | |
| Service revenue (A) | $198,100 | |
| Expenses: | ||
| Property tax | 8,500 | |
| Salaries | 123,600 | |
| Insurance | 7,000 | |
| Supplies | 6,300 | |
| Total expense (B) | 145,400 | |
| Net income | 52,700 | |
Table (7)
Therefore, the net income of Company Z is $52,700.
Classified balance sheet:
Classified balance sheet of Company Z is as follows:
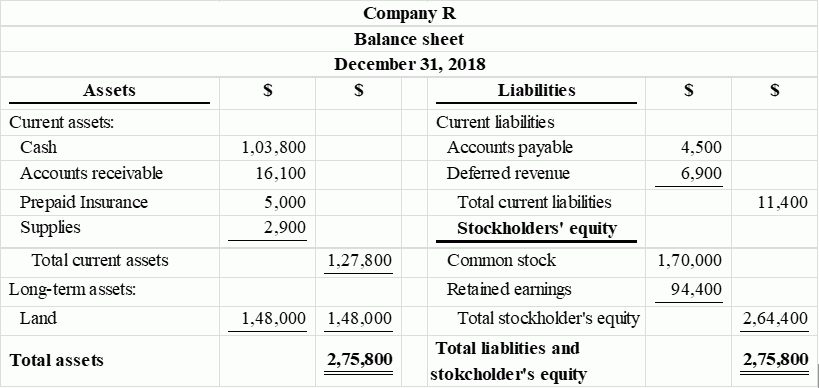
Figure (1)
Therefore, the total assets of Company Z are$275,800, and the total liabilities and stockholders’ equity are $275,800.
Working note:
Calculation of ending balance retained earnings
9.
Record the necessary closing entries of Company R.
9.
Explanation of Solution
Closing entries:
Closing entries are those journal entries, which are passed to transfer the final balances of temporary accounts, (all revenues account, all expenses account and dividend) to the retained earnings. Closing entries produce a zero balance in each temporary account.
Closing entries of Company R is as follows:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation |
Post Ref. |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| 2021 | Service revenue | 198,100 | ||
| December 31 | Retained earnings | 198,100 | ||
| (To close all revenue account) | ||||
| 2021 | Retained earnings | 145,400 | ||
| December 31 | Property tax expense | 8,500 | ||
| Salaries expense | 123,600 | |||
| Insurance expense | 7,000 | |||
| Supplies expense | 6,300 | |||
| (To close all theexpenses account) | ||||
| 2021 | Retained earnings | 2,800 | ||
| December 31 | Dividends | 2,800 | ||
| (To close the dividends account) | ||||
Table (8)
10.
10.
Explanation of Solution
| Cash | |||
| $24,600 | $8,500 | ||
| $134,100 | $11,400 | ||
| $51,500 | $123,600 | ||
| $12,900 | $2,800 | ||
| $27,000 | |||
| Bal. | $103,800 | ||
| Supplies | |||
| $0 | |||
| $9,200 | $6,300 | ||
| $2,900 | |||
| Deferred revenue | |||
| $5,800 | |||
| 11,800 | $12,900 | ||
| $6,900 | |||
| Dividends | |||
| $0 | |||
| $2,800 | $2,800 | ||
| $0 | |||
| Salaries expense | |||
| $0 | |||
| $123,600 | $123,600 | ||
| $0 | |||
| Accounts receivable | |||
| $15,400 | |||
| $52,200 | $51,500 | ||
| Bal. | $16,100 | ||
|
Land | |||
| $148,000 | |||
| Bal. | $148,000 | ||
| Common stock | |||
| $143,300 | |||
| Bal. | $27,000 | ||
| Total | $170,000 | ||
| Service revenue | |||
| $0 | |||
| Bal. | $186,300 | ||
| 198,100 | $11,800 | ||
| Total | $0 | ||
| Insurance expense | |||
| $0 | |||
| $7,000 | $7,000 | ||
| $0 | |||
| Prepaid Insurance | |||
| $12,000 | |||
| $7,000 | |||
| $5,000 | |||
| Accounts payable | |||
| $6,700 | |||
| $11,400 | $9,200 | ||
| $4,500 | |||
| Retained Earnings | |
|
145,400 2,800 |
44,500 198,100 |
| 94,400 | |
| Property Tax Expense | |||
| $0 | |||
| $8,500 | $8,500 | ||
| $0 | |||
| Supplies expense | |||
| $0 | |||
| $6,300 | $6,300 | ||
| $0 | |||
11.
Prepare a post-closing trial balance of Company Z.
11.
Explanation of Solution
Post-closing trial balance:
The post-closing trial balance is a summary of all ledger accounts, and it shows the debit and the credit balances after the closing entries are journalized and posted. The post-closing trial balance contains only permanent (balance sheet) accounts, and the debit and the credit balances of permanent accounts should agree.
Post-closing trial balance of Company R is as follows:
| Company Z | ||
| Post-closing trial balance | ||
| December 31, 2021 | ||
| Accounts | Debit Amount($) |
Credit Amount($) |
| Cash | $103,800 | |
| Accounts Receivable | 16,100 | |
| Prepaid Insurance | 5,000 | |
| Supplies | 2,900 | |
| Land | 148,000 | |
| Accounts payable | 4,500 | |
| Deferred revenue | 6,900 | |
| Common stock | 170,000 | |
| Retained Earnings | 94,400 | |
| Totals | $275,800 | $275,800 |
Table (9)
Therefore, the total of debit, and credit columns of post-closing trial balance is $275,800 and agree.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Financial Accounting Connect Access Card
- FILL ALL CELLS. NOTICE THE DROPDOWN OPTIONSarrow_forwardABF's metal spare parts manufacturing company uses the customised production method by attributing the GST to the products it produces with the help of predetermined attribution coefficients. The processing of metal parts is carried out in two production departments: the Cutting and Drilling department, and the Assembly department. The GIS attribution coefficients for the two departments are based on the operating hours of machines and the cost of direct work respectively. At the beginning of the year, the following budgets were implemented: Cutting and Drilling Department Assembly Department Direct Labor Costs (in euros) 1.320.000 2.000.000 G.B.E. (in euros) 4.800.000 2.400.000 Machinery Operating Hours 80.000 5.000 Direct Work Hours 27.000 12.000 Requested: To calculate the coefficient of attribution of the General Secretariat that will be used in each department. (4 units) To determine the production cost per unit for order 158 which…arrow_forwardPLEASE HELP. I HAVE PROVIDED THE DROPDOWN OPTIONSarrow_forward
- The difference between the balance in a company's cash account and its bank statement is documented in the __________ of the bank statement.arrow_forwardLarge corporations should report revenues on their income statements when the __________. Cash Is Received Revenues Are Earnedarrow_forwardPLEASE HELP WITH THIS PROBLEMarrow_forward
- The KLM Medical Clinic has two auxiliary departments: the Building Maintenance Department and the Energy Production Department as well as three main production departments: the Department of Paediatrics, the Department of Internal Medicine and the Department of Surgery. The CLM allocates the cost of the building maintenance department based on the area occupied by the departments in square meters and the cost of the energy department based on the days of hospitalization of patients. No distinction is made between variable and fixed cost elements. The budgeted operating figures for the previous year were as follows: Auxiliary sections Main production departments Building maintenance Energy production Pediatrics Department of Internal Medicine Surgical Estimated cost before allocation 18.000,00 8.000,00 80.000,00 50.000,00 90.000,00 Area (in sq.m) 1.000,00 4.000,00 6.000,00 18.000,00 12.000,00 Patient Hospitalization…arrow_forwardwhat is financial accounting? explain its parts and all things.arrow_forwardSystematic relationship quarrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





