
Concept explainers
A 5.0-kg block rests on a
block and the incline is 0.20. How large a horizontal force must push on the block if
the block is to be on the verge of sliding (a) up the incline and (b) down the incline?
(a)
The minimumhorizontal forcerequired to push the
Answer to Problem 81SP
Solution:
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
The mass of the block is
Coefficient of static friction between the block and incline is
Formula used:
The expression of the coefficient of static friction is
Here,
The expression of the force’s equilibrium is
Here,
Explanation:
Draw the free body diagram of the block representing all the forces and their components as shown in the figure below:
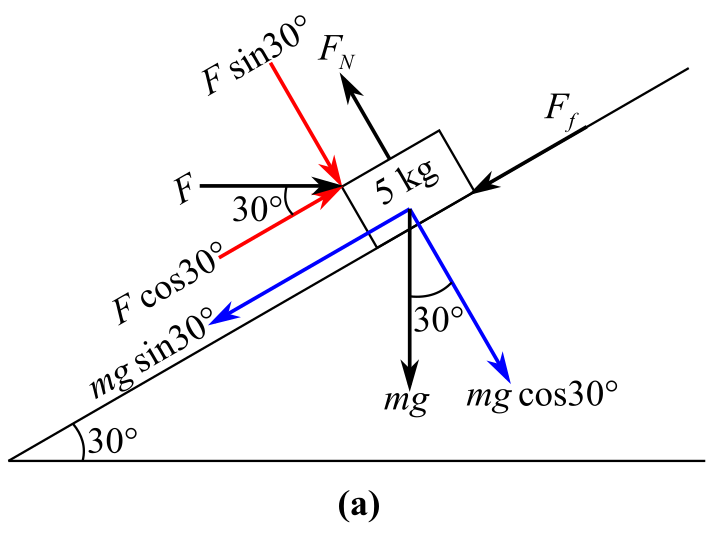
Since the block is considered to be on the verge of sliding, the change in velocity is zero, and therefore, the acceleration of the block is zero.
In the above diagram,
Recall the expression of the force equilibrium along y- direction:
Consider the force normal to the incline in upward direction as positive and the force normal to the incline in the downward direction as negative. Hence,
Recall the expression of
Substitute
Recall the expression of the force equilibrium along x- direction:
Consider the force along the incline in right direction as positive and the force along the incline in the left direction as negative. Hence,
Substitute
Further solving the equation for
Conclusion:
The magnitude of the horizontal force required to push the block up the incline is
(b)
The minimum horizontal force required to push the
Answer to Problem 81SP
Solution:
Explanation of Solution
Given data:
Mass of the block is
Coefficient of static friction between the block and incline is
Formula used:
The expression of the coefficient of static friction is
Here,
The expression of the force’s equilibrium is
Here,
Explanation:
Draw the free body diagram of the block representing all the forces and their components as shown in the figure below:
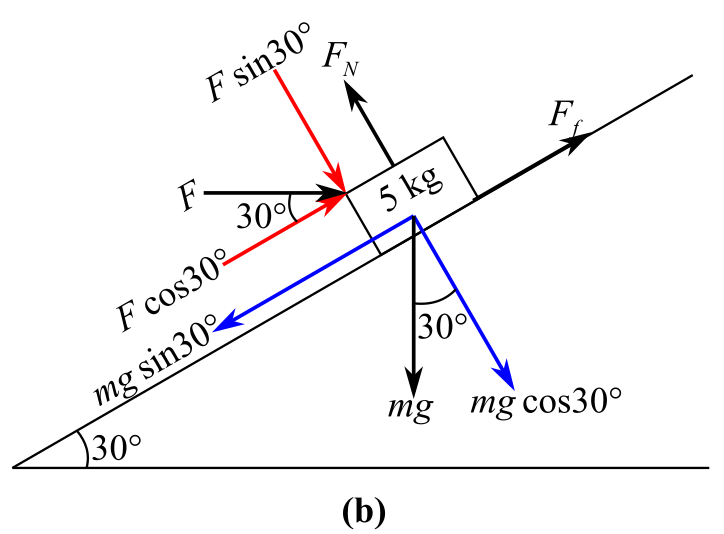
In the above diagram,
Recall the expression of the force equilibrium along x- direction:
Consider the force along the incline in right direction as positive and the force along the incline in the left direction as negative. Hence,
Substitute
Further solving the equation for
Thus,
Conclusion:
The magnitude of the horizontal force required to push the block up the incline is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Schaum's Outline of College Physics, Twelfth Edition (Schaum's Outlines)
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning





