
Concept explainers
A force
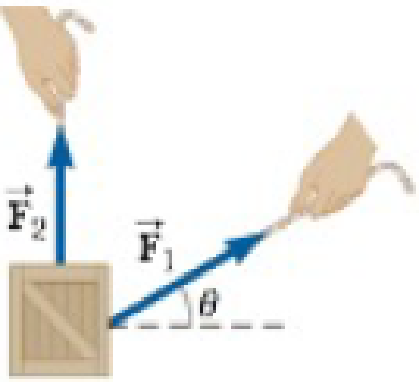
Figure P3.7
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 3 Solutions
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern Physics
- Why can't this be correct: &= 7m?arrow_forwardgive a brief definition of the word "paradigm" as well as an example of a current scientific paradigmarrow_forward7. Are all scientific theories testable in the commonly understood sense? How does this make you feel? How should you proceed as a scientist or engineer with this understanding?arrow_forward
- What is an an example of a hypothesis that sounds scientific but is notarrow_forwardWhat is an example of a scientific hypothesisarrow_forwardMultiverse is called a theory. It has been proposed to account for the apparent and uncanny fine tuning of our own universe. The idea of the multiverse is that there are infinite, distinct universes out there - all with distinct laws of nature and natural constants - and we live in just one of them. Using the accepted definition of the universe being all that there is (matter, space and energy), would you say that multiverse is a scientific theory?arrow_forward
- How is a law usually different than a theoryarrow_forwardA 1.50 mLmL syringe has an inner diameter of 5.00 mmmm, a needle inner diameter of 0.270 mmmm, and a plunger pad diameter (where you place your finger) of 1.2 cmcm. A nurse uses the syringe to inject medicine into a patient whose blood pressure is 140/100. Part A What is the minimum force the nurse needs to apply to the syringe? Express your answer with the appropriate units. View Available Hint(s)for Part A Hint 1for Part A. How to approach the question The force the nurse applies to the syringe can be determined from the fluid pressure and the area of the plunger. The minimum force corresponds to the patient's lowest blood pressure. Use the following equality 760mmofHg=1atm=1.013×10^5Pa760mmofHg=1atm=1.013×10^5Pa.arrow_forwardA 1.50 mLmL syringe has an inner diameter of 5.00 mmmm, a needle inner diameter of 0.270 mmmm, and a plunger pad diameter (where you place your finger) of 1.2 cmcm. A nurse uses the syringe to inject medicine into a patient whose blood pressure is 140/100. Part A What is the minimum force the nurse needs to apply to the syringe? Express your answer with the appropriate units. View Available Hint(s)for Part A Hint 1for Part A. How to approach the question The force the nurse applies to the syringe can be determined from the fluid pressure and the area of the plunger. The minimum force corresponds to the patient's lowest blood pressure. Use the following equality 760mmofHg=1atm=1.013×10^5Pa760mmofHg=1atm=1.013×10^5Pa.arrow_forward
- Is a scientific theory supposed to just be someone's idea about somethingarrow_forwardwhat is the agenda of physicsarrow_forwardWatch the video of Cooper’s play, while conducting and documenting your observation using a chosen observation tool. Case Study 1b - Cooper Carol has asked you to support the babies and toddler’s room educators this week. She has requested that you complete an observation on Cooper, who is a 10-month-old toddler. Carol wants to see how well you conduct an observation and is interested in how you manage to communicate in any observations made, using a strengths-based, non-judgemental, anti-biased approach, as this is a fundamental part of creating a supportive and respectful culture at Little Catalysts ELC. Video: Cooper's play (6:45 min) Resources Module 7 eLearns Template: Learning story observation, Section 1 Template: Running record observation, Section 1 Template: Anecdotal record observation, Section 1 Video: Cooper's play (6:45 min) Complete and upload an observation of Cooper to support educators in future curriculum planning. Choose one (1) of the observation…arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning





