
Concept explainers
Problems 74 and 75 are paired.
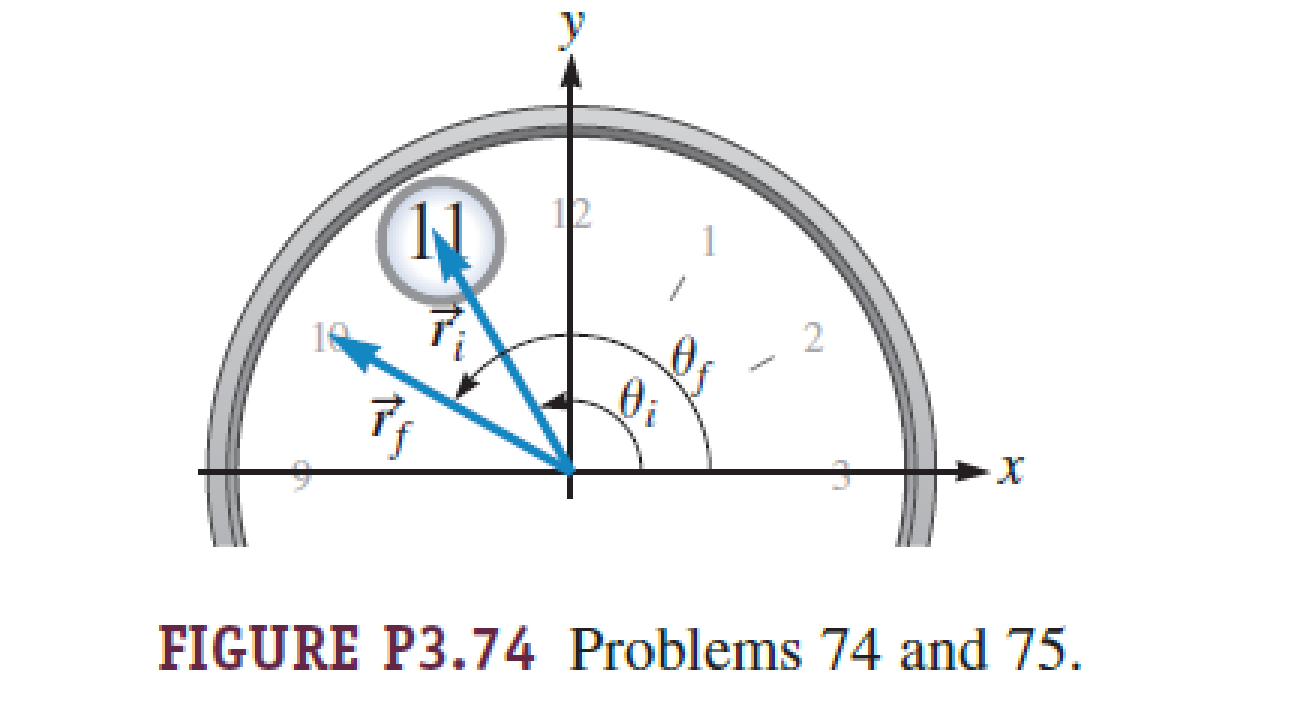
74. N A classroom clock has a small magnifying glass embedded near the end of the minute hand. The magnifying glass may be modeled as a particle. Class begins at 7:55 and ends at 8:50. The length of the minute hand is 0.300 m. a. Find the average velocity of the magnifying glass at the end of the minute hand using the coordinate system shown in Figure P3.74. Give your answer in component form. b. Find the magnitude and direction of the average velocity. c. Find the average speed and in the CHECK and THINK step, compare to the average velocity.
(a)
The average velocity of the magnifying glass at the end of the minute hand using the coordinate system.
Answer to Problem 74PQ
The average velocity of the magnifying glass is
Explanation of Solution
Write the expression for the average velocity.
Here,
The initial position of the minute hand is given by,
The final position of the minute hand is given by,
Conclusion:
It takes
Therefore, the average velocity of the magnifying glass is
(b)
The magnitude and the direction of the average velocity.
Answer to Problem 74PQ
The magnitude and the direction of the average velocity is
Explanation of Solution
The magnitude of the average velocity is given by taking the square root of the sum of the squares of the
The magnitude of the average velocity is,
The direction of the average velocity is given by,
Conclusion:
Substitute
Therefore, the magnitude and the direction of the average velocity is
(c)
The comparison of average speed with the average velocity.
Answer to Problem 74PQ
The speed is about an order of magnitude larger because the distance traveled is much larger than the displacement at that time.
Explanation of Solution
The average speed is the total distance traveled in the time the clock hand moves from the initial to the final position. The distance traveled is 55 out of the 60 of the circumference traced out by the end of the minute hand which can be expressed as,
Write the expression for the displacement.
Here,
Conclusion:
Substitute
Substitute
Comparing the value of displacement and distance the magnitude is larger for the distance so that the magnitude of the speed will be higher than the magnitude of the average velocity.
Therefore, the speed is about an order of magnitude larger because the distance traveled is much larger than the displacement at that time.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Webassign Printed Access Card For Katz's Physics For Scientists And Engineers: Foundations And Connections, 1st Edition, Single-term
- A shot putter releases a shot at 13 m/s at an angle of 42 degrees to the horizontal and from a height of 1.83 m above the ground. (Note: For each question draw a diagram to show the vector/s. Show all the step and provide units in the answers. Provide answer to 2 decimal places unless stated otherwise.) Calculate and answer all parts. Only use equations PROVIDED:arrow_forward"looks" like a particle.) ...32 GO In Fig. 22-55, positive charge q = 7.81 pC is spread uni- formly along a thin nonconducting rod of length L = 14.5 cm. What are the (a) magnitude and (b) direction (relative to the positive direction of the x axis) of the electric field produced at point P, at distance R = 6.00 cm from the rod along its perpendicular bisector? R y Р + + + + + + + + +-× L Figure 22-55 Problem 32.arrow_forward1) A horizontal wire carrying current I in +x direction on the x-axis from x=0 to x=2 2) A vertical wire carrying current I upward at along the x=2 line from y=0 to y=8 3) A diagonal straight wire started at the origin and it ends at y=8 x=2 carrying a current in SE direction ( diagonally downward); y=4x In a regional magnetic field that is given in vector notation by B = ( y i - x j )/(x^2+y^2+25) As components Bx = (y+1)/x^2+y^2+25) By = (1- x )/(x^2+y^2+25) Find the integral expression for the net force for each branch carrying 5 ampere current.arrow_forward
- An electric power station that operates at 30 KV and uses a 15:1 set step-up ideal transformer is producing 400MW (Mega-Watt) of power that is to be sent to a big city with only 2.0% loss. What which is located 270 km away is the resistance of the Two wires that are being used? 52arrow_forwardSlink, from Toy Story, is a slinky dog whose middle section is a giant spring with a spring constant of 10.9 N/m. Woody, who has a mass of 0.412 kg, grabs onto the tail end of Slink and steps off the bed (as shown in figure A) with no initial velocity and reaches the floor right as his velocity hits zero again (as shown in figure C).arrow_forwardThe character Min Min from Arms was a DLC character added to Super Smash Bros. Min Min’s arms are large springs, with a spring constant of 8.53 ⋅ 10^3 N/m, which she uses to punch and fling away her opponents. Min Min pushes her spring arm against Steve, who is not moving, compressing it 1.20 m as shown in figure A. Steve has a mass of 81.6 kg. Assuming she uses only the spring to launch Steve, how fast is Steve moving when the spring is no longer compressed? As Steve goes flying away he goes over the edge of the level, as shown in figure C. What is the magnitude of Steve’s velocity when he is 2.00 m below where he started?arrow_forward
- Calculate the energy needed to melt 50 g of 0°C icearrow_forwardTwo very long line charges are set up along lines that areparallel to the z-axis, so they set up Electric fields strictly in the xy plane. One goes throughthe x-axis at x = −0.40 m and has charge a density λ1 = +12.0 μC/m, the other goesthrough the x-axis at x = +0.40 m has charge density λ2 = −8.0 μC/m.A. Find the Electric field at point A: (0.40, 0.80) (distances in meters). Give answersin unit vector notation and draw a graph of the x-y plane with the E-fields you justfound.B. Find a point on the x-axis at which the total E-field is 0.arrow_forwardIn order to increase the amount of exercise in her daily routine, Tara decides to walk up the four flights of stairs to her car instead of taking the elevator. Each of the steps she takes are 18.0 cm high, and there are 12 steps per flight. (a) If Tara has a mass of 77.0 kg, what is the change in the gravitational potential energy of the Tara-Earth system (in J) when she reaches her car? ] (b) If the human body burns 1.5 Calories (6.28 x 10³ J) for each ten steps climbed, how much energy (in J) has Tara burned during her climb? ] (c) How does the energy she burned compare to the change in the gravitational potential energy of the system? Eburned Δυarrow_forward
- A 4.40 kg steel ball is dropped onto a copper plate from a height of 10.0 m. If the ball leaves a dent 2.75 mm deep, what is the average force exerted by the plate on the ball during the impact? Narrow_forwardA block of mass m = 7.00 kg is released from rest from point and slides on the frictionless track shown in the figure below. (Assume h₂ = 7.80 m.) a m ha 3.20 m 2.00 m i (a) Determine the block's speed at points ® and point B ©. m/s m/s point (b) Determine the net work done by the gravitational force on the block as it moves from point J A to pointarrow_forwardA 1.10 x 10²-g particle is released from rest at point A on the inside of a smooth hemispherical bowl of radius R R B 2R/3 (a) Calculate its gravitational potential energy at A relative to B. ] (b) Calculate its kinetic energy at B. ] (c) Calculate its speed at B. m/s (d) Calculate its potential energy at C relative to B. J (e) Calculate its kinetic energy at C. ] = 26.5 cm (figure below).arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College





