
Concept explainers
1.
Journalize the given transactions.
1.
Explanation of Solution
Journalize the given transactions:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| a | Cash (+A) | $1,390 | |
| Receivables (+A) | $24,704 | ||
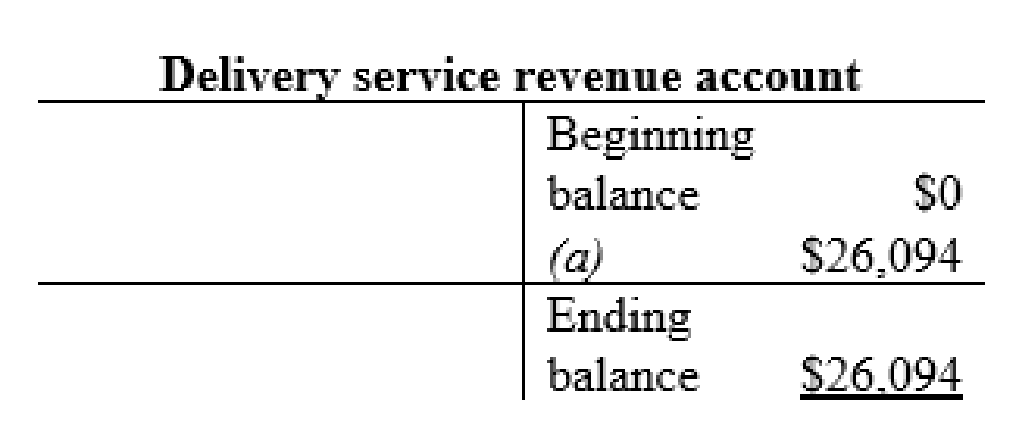
| Delivery Service revenue (+SE, +R) | $26,094 | ||
| (To record the sales) | |||
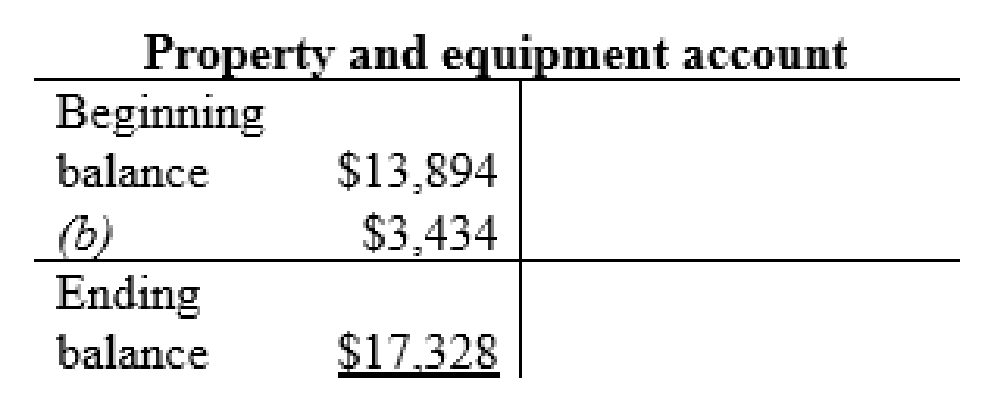
| b | Property and equipment (+A) | $3,434 | |
| Long-term notes payable (+L) | $3,434 | ||
| (To record the long-term notes payable) | |||
| c | Rent expense (+E) (-SE) | $3,136 | |
| Prepaid rent (+A) | $4,728 | ||
| Cash (-A) | $7,864 | ||
| (To record the rent expense and prepaid rent) | |||
| d | Repairs expense (+E) (-SE) | $864 | |
| Cash (-A) | $864 | ||
| (To record the expenses paid) | |||
| e | Cash (+A) | $24,285 | |
| Receivable (-A) | $24,285 | ||
| (To record the receivables collected) | |||
| f | Long-term notes payable (-L) | $150 | |
| Cash (-A) | $150 | ||
| (To record the payment of long-term notes payable) | |||
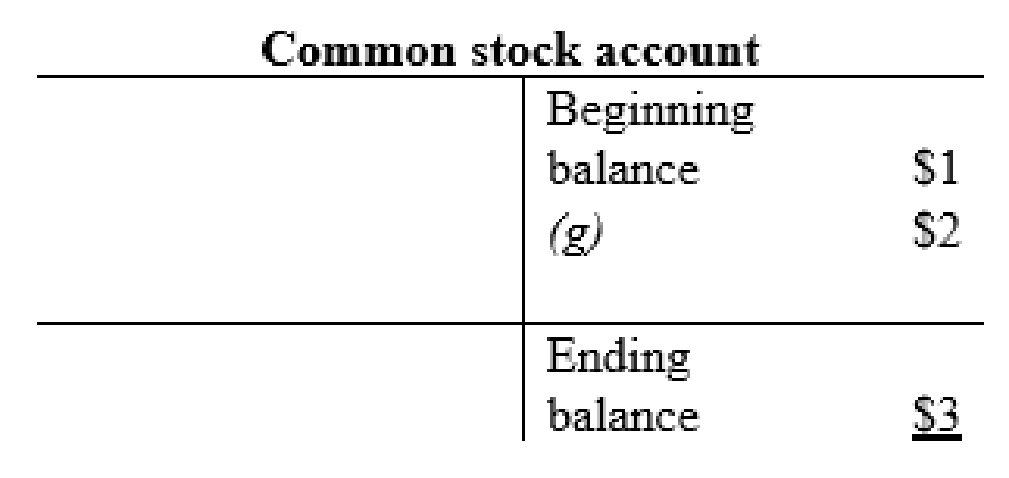
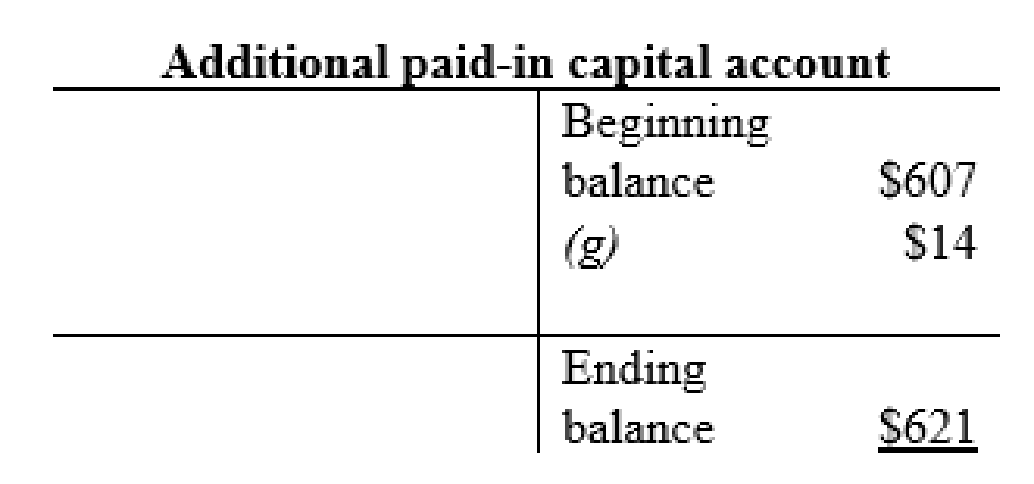
| g | Cash (+A) | $16 | |
| Common Stock (+SE) | $2 | ||
| Additional paid-in-capital (+SE) | $14 | ||
| (To record the receipt of stock) | |||
| h | Wages (+E) (-SE) | $9,276 | |
| Cash (-A) | $9,276 | ||
| (To record the wages paid) | |||
| i | Spare parts, supplies, and fuel (+A) | $6,564 | |
| Cash (-A) | $6,564 | ||
| (To record the sales revenues) | |||
| j | Spare parts, supplies, and fuel expense (+E) (-SE) | $6,450 | |
| Spare parts, supplies, and fuel (-A) | $6,450 | ||
| (To record the sales revenues) | |||
| k | Accounts payable (-L) | $784 | |
| Cash (-A) | $784 | ||
| (To record the sales revenues) | |||
| l | No entry | ||
Table (1)
2
Prepare the T- account and enter the transaction into their respective accounts for calculating the ending balance.
2
Explanation of Solution
Prepare the T-accounts:
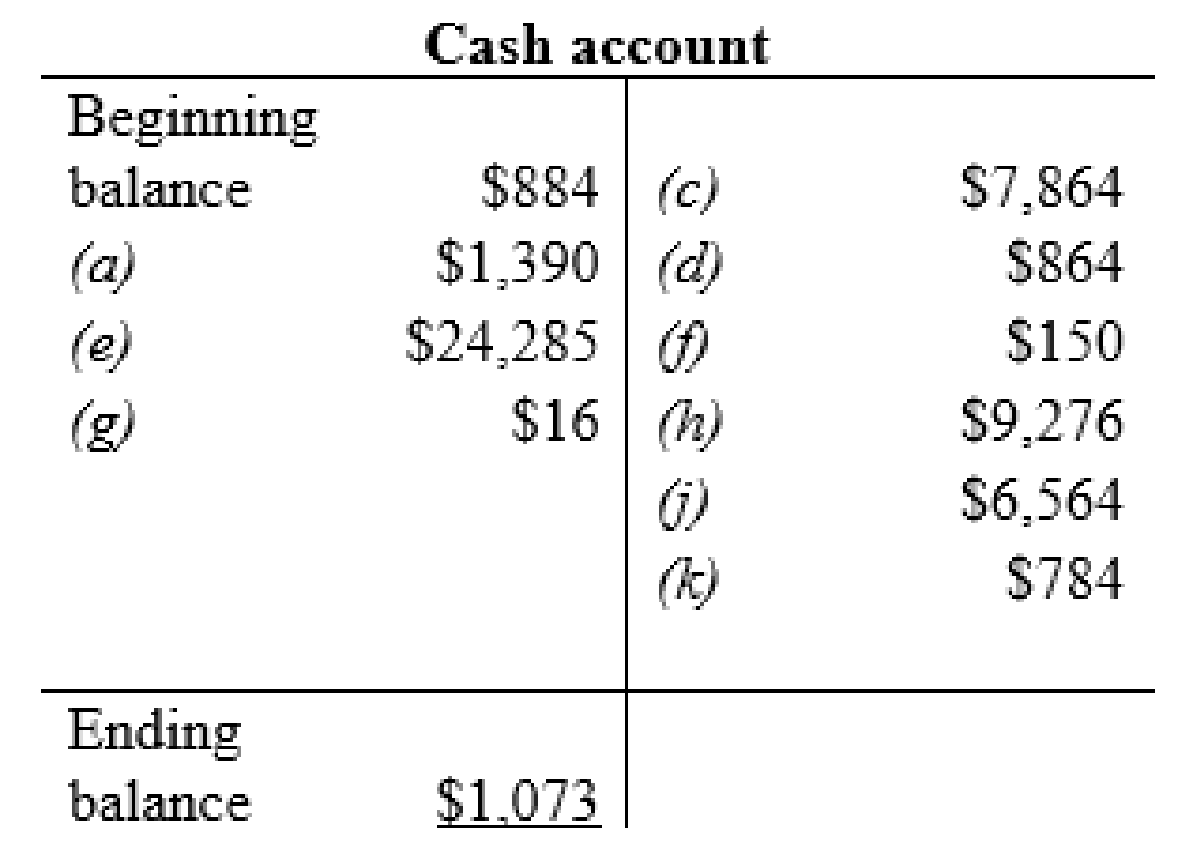
Cash account:
Receivables account:
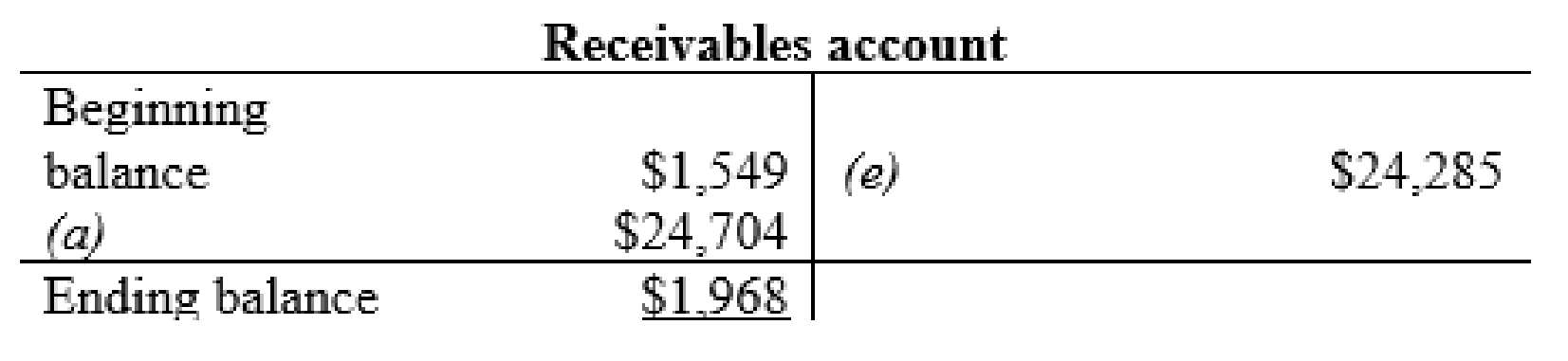
Spare parts, supplies and fuel account:
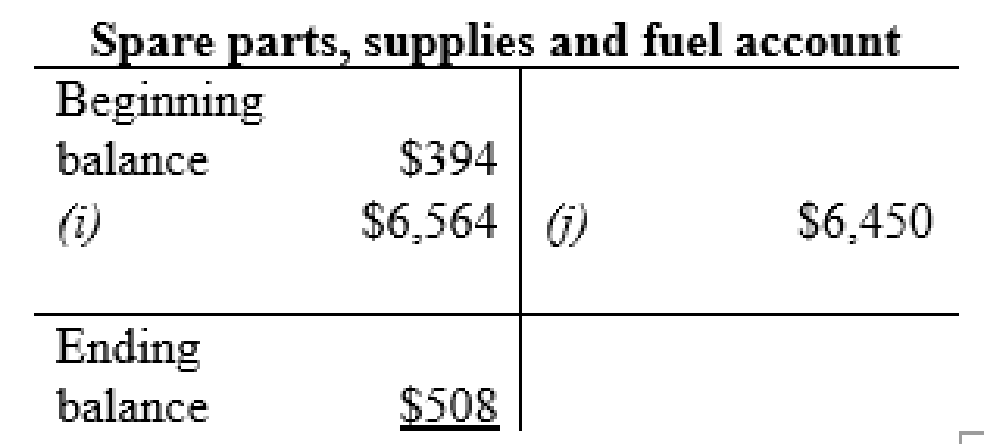
Prepaid expenses account:
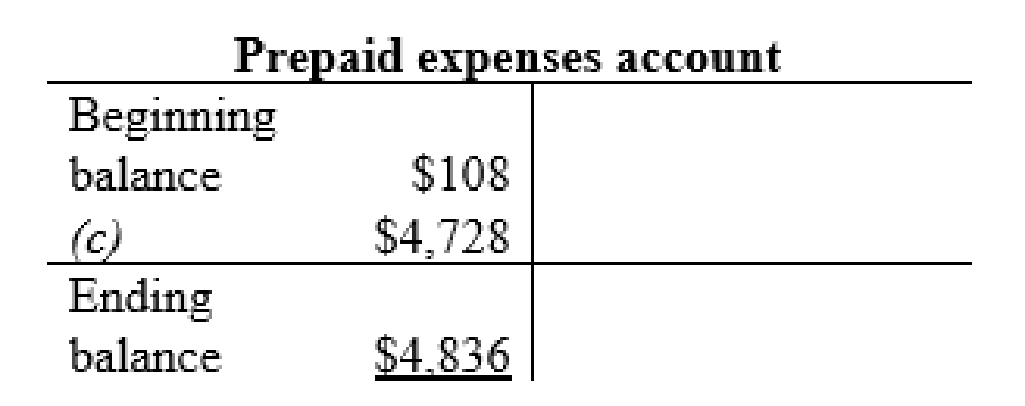
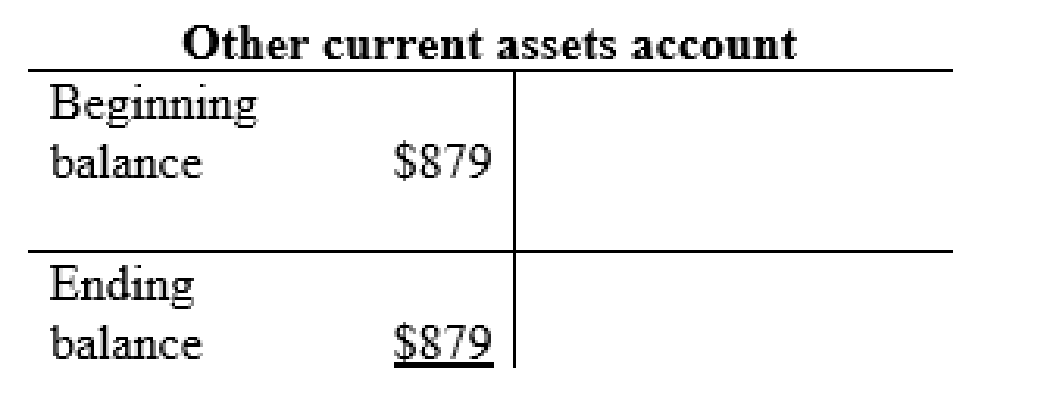
Other current asset account:
Property and equipment account:
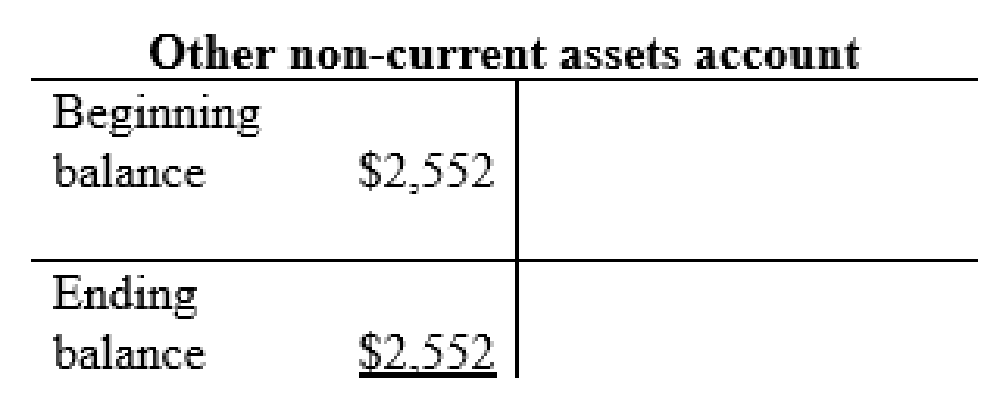
Other non-current asset account:
Accounts payable account:
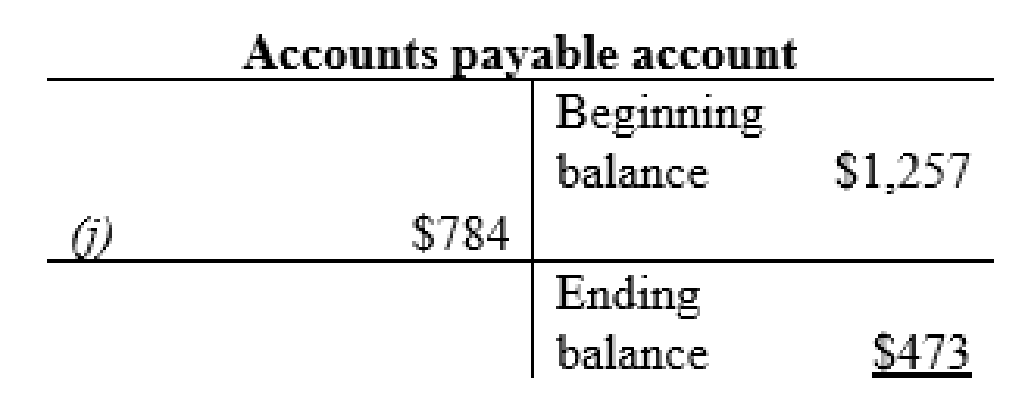
Accrued expenses payable account:
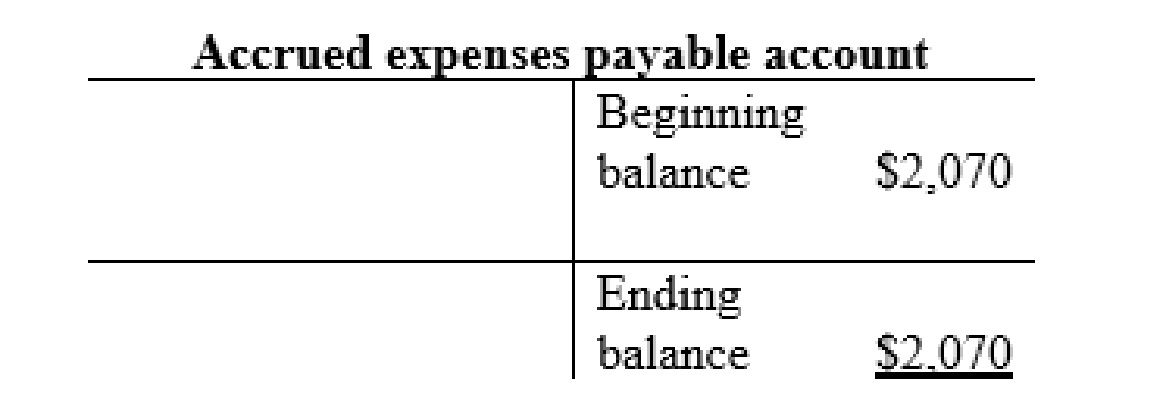
Other current liabilities account:
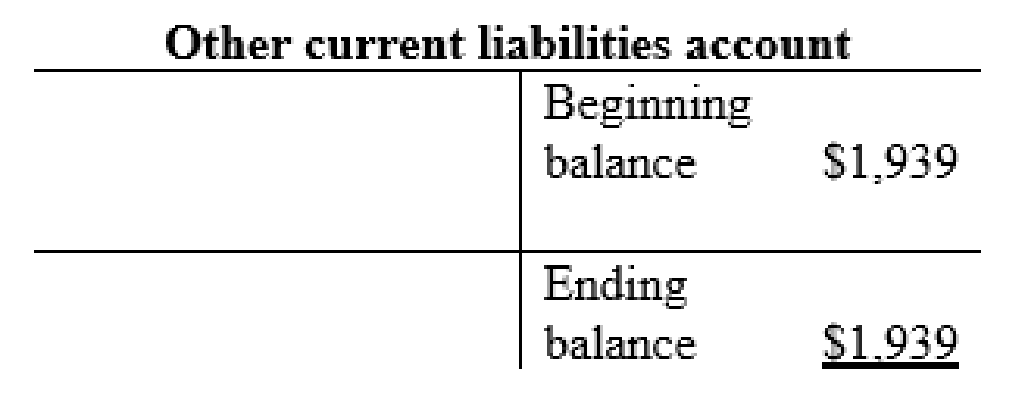
Long-term note payable account:
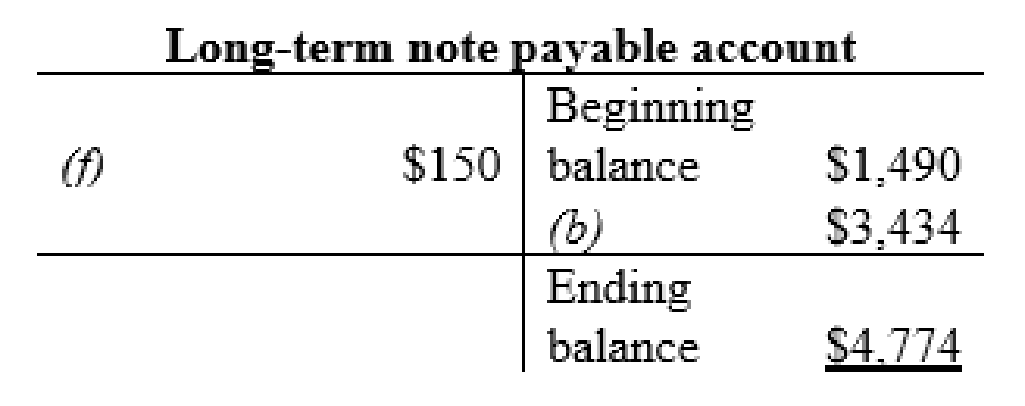
Other non-current liabilities account:
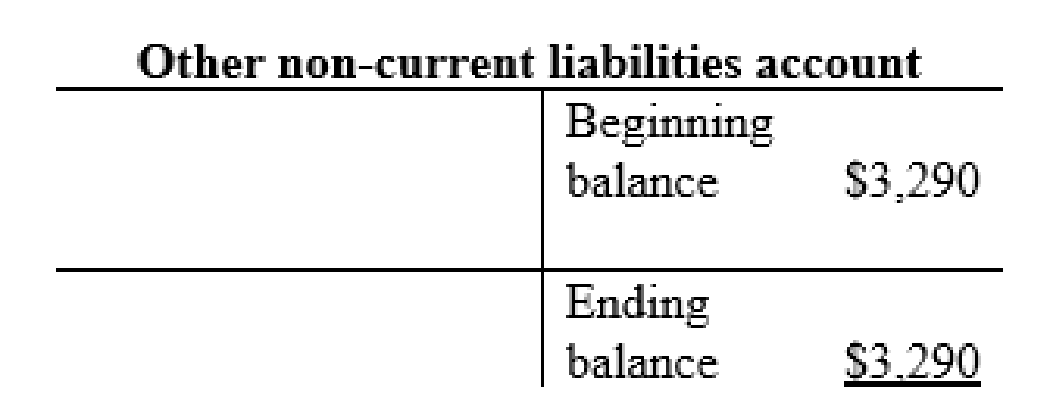
Common stock account:
Additional paid-in capital account:
Delivery service revenue account:
Aircraft rental expense account:
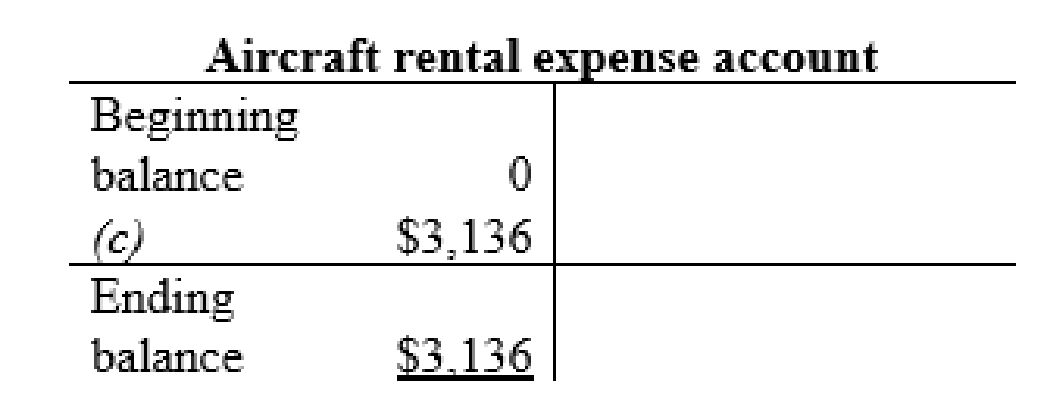
Maintenance and repair expense account:
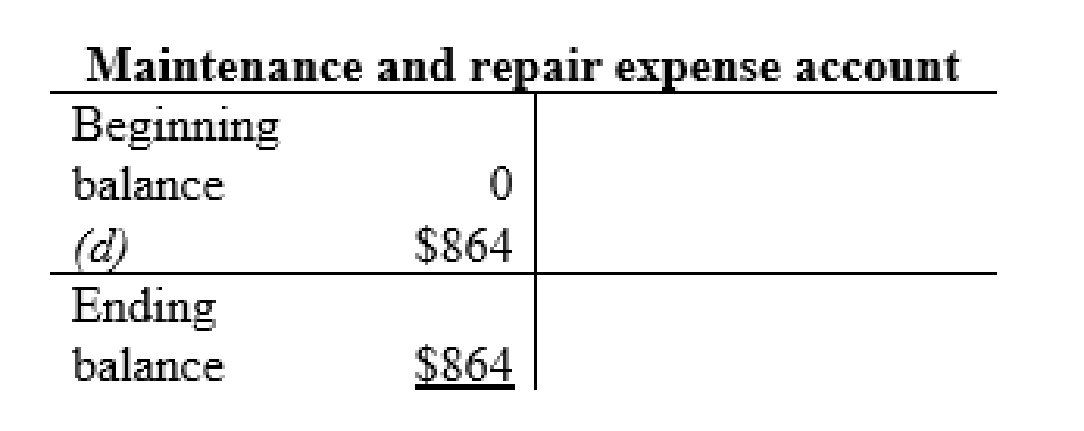
Wage expense account:
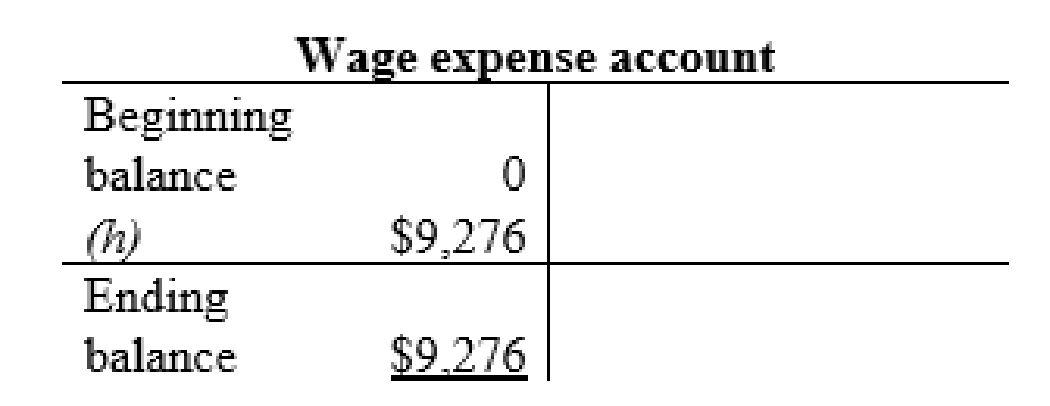
Fuel expense account:
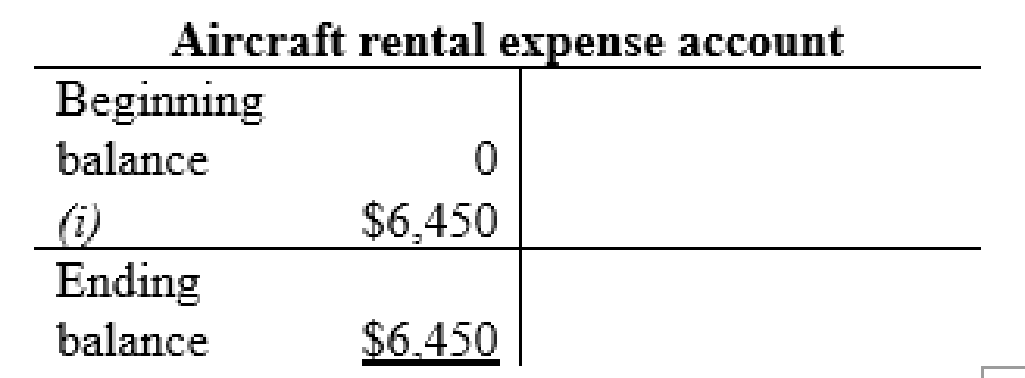
Thus, the t-accounts are prepared and the ending balances are calculated.
3.
Prepare an income statement for the month May.
3.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare an income statement:
| Company F | ||
| Income statement (Unadjusted) | ||
| For the year ended May 31 (in millions) | ||
| Particulars | Amount ($) | Amount ($) |
| Revenues: | ||
| Delivery service revenue | 26,094 | |
| Total revenues (A) | 26,094 | |
| Expenses: | ||
| Rental expense | 3,136 | |
| Fuel expense | 9,276 | |
| Wage expense | 6,450 | |
| Repair expense | 864 | |
| Total expenses (B) | 19,726 | |
| Net Income | $6,368 | |
Table (2)
Hence, the net income of Company F is $6,368 million.
4.
Compute the net profit margin ratio and based on the result give suggestion to the company.
4.
Explanation of Solution
Compute the net profit margin ratio:
Hence, the net profit margin ratio is 0.24.
Suggestion:
- By evaluating the net profit margin ratio, the company has earned $0.24 in net income for every $ 1 in the sales revenue.
- To know the better result about the company, net profit margin ratio should be calculated to identify the way in which the management is generating its revenue and controlling the various expenses.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING (LL)-W/CONNECT
- WW Office Solution simplemented a new supply requisition system. Departments must submit requests by Thursday for next week, maintain minimum 20% buffer stock, and obtain supervisor approval for urgent orders. From 85 total requisitions last month, 65 followed timeline, 72 maintained proper buffer, and 58 met both conditions. What is the compliance rate?arrow_forwardOn January 1, 2013, R Corporation leased equipment to Hela Company. The lease term is 9 years. The first payment of $452,000 was made on January 1, 2013. Remaining payments are made on December 31 each year, beginning with December 31, 2013. The equipment cost R Corporation $2,457,400. The present value of the minimum lease payments is$2,697,400. The lease is appropriately classified as a sales-type lease. Assuming the interest rate for this lease is 12%, what will be the balance reported as a liability by Hela in the December 31, 2014, balance sheet?arrow_forwardPlease help mearrow_forward
- A firm currently has a 40-day cash cycle. Assume that the firm changes its operations such that it decreases its receivables period by 5 days, increases its inventory period by 3 days, and decreases its payables period by 2 days. What will the length of the cash cycle be after these changes?arrow_forwardAnsarrow_forwardMagnus Enterprises has net sales of $1,020,000, net income of $74,500, average current assets of $52,000, average fixed assets of $178,500, and average total assets of $230,500. What is Magnus Enterprises' return on assets?arrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





