
1.
Journalize the given transactions.
1.
Explanation of Solution
Journalize the given transactions:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
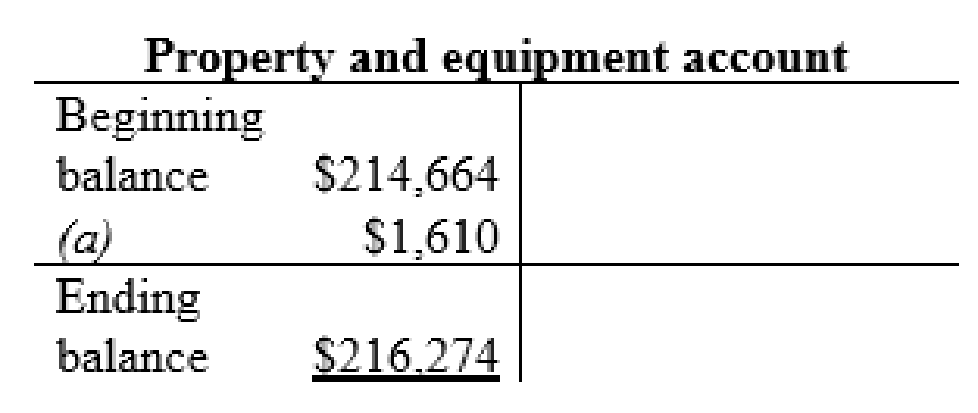
| a | Property and equipment (+A) | $1,610 | |
| Long-term notes payable (+L) | $1,610 | ||
| (To record the long-term notes payable) | |||
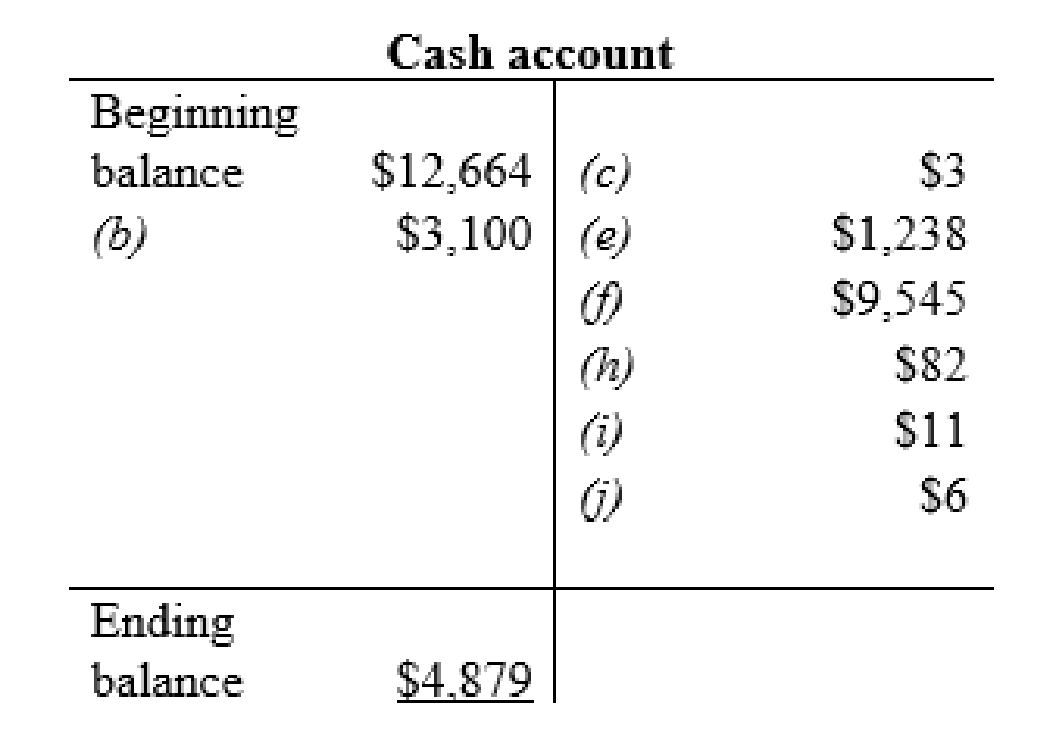
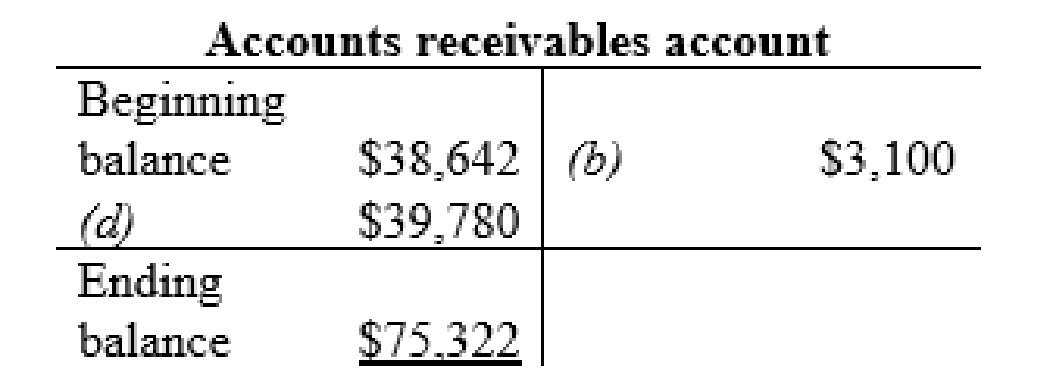
| b | Cash (+A) | $3,100 | |
| $3,100 | |||
| (To record the receivables collected) | |||
| c | Utilities expense (+E) (-SE) | $3 | |
| Cash (-A) | $3 | ||
| (To record the expenses paid) | |||
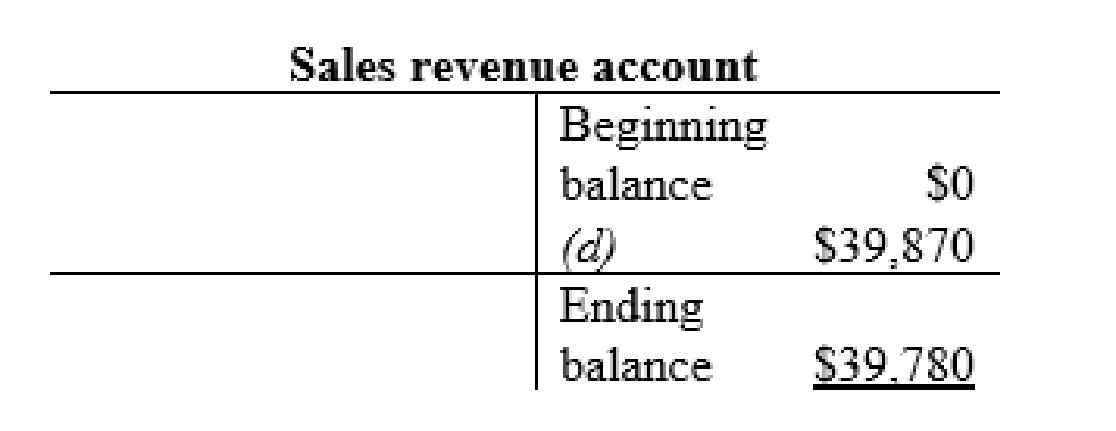
| d | Accounts receivable (+A) | $39,780 | |
| Sales Revenue (+SE, +R) | $39,780 | ||
| (To record the expenses paid) | |||
| Cost of Sales (+E) (-SE) | $5,984 | ||
| Inventory (-A) | $5,984 | ||
| (To record the cost involved in sales) | |||
| e | Wages (+E) (-SE) | $1,238 | |
| Cash (-A) | $1,238 | ||
| (To record the wages paid) | |||
| f | Income tax payable (-L) | $9,545 | |
| Cash (-A) | $9,545 | ||
| (To record the income taxes paid) | |||
| g | Inventory (+A) | $23 | |
| Accounts payable (+L) | $23 | ||
| (To record the inventory purchased on account) | |||
| h | Prepaid expenses (+A) | $82 | |
| Cash (-A) | $82 | ||
| (To record the expenses paid in advance) | |||
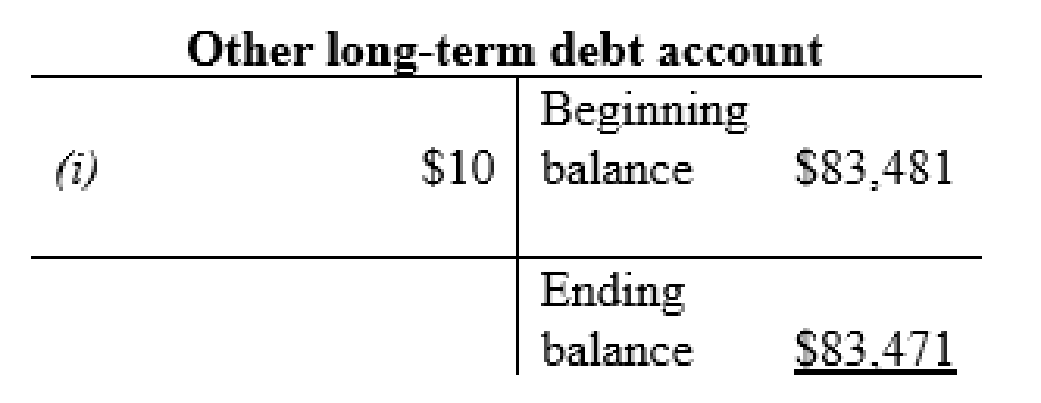
| i | Other long-term debt (-L) | $10 | |
| Interest expense | $1 | ||
| Cash (-A) | $11 | ||
| (To record the debt paid off) | |||
| j | Other assets and intangibles (+A) | $6 | |
| Cash (-A) | $6 | ||
| (To record the purchase of other assets and intangibles) | |||
Table (1)
2
Prepare the T- account and enter the transaction into their respective accounts for calculating the ending balance.
2
Explanation of Solution
Prepare the T-accounts:
Cash account:
Short-term investments account:
Accounts receivables account:
Inventories account:

Prepaid expenses account:
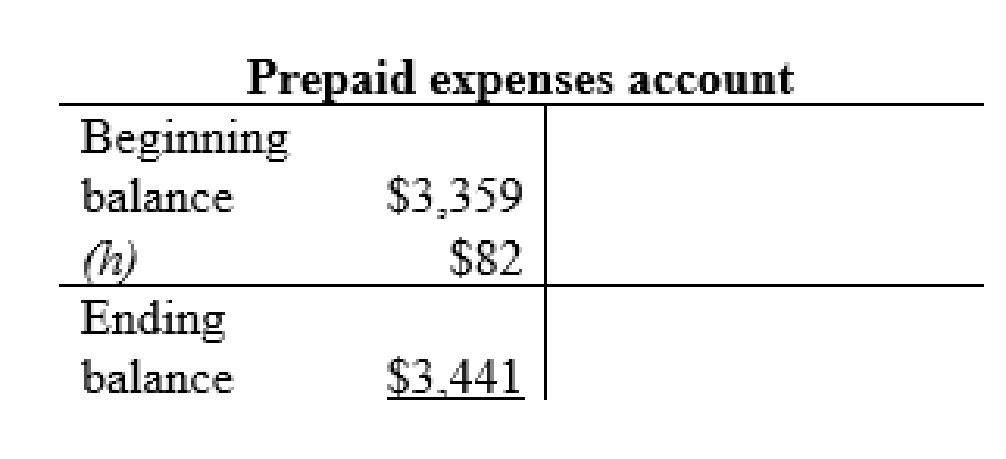
Other current assets account:
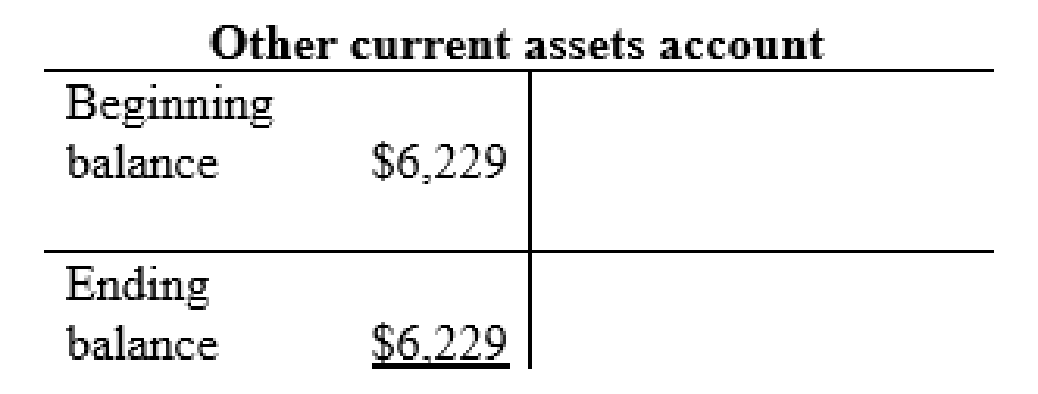
Long-term investments account:
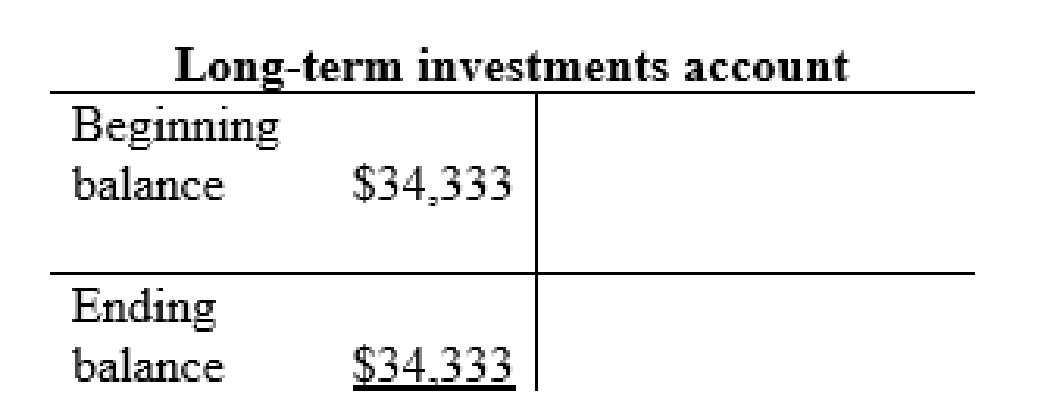
Other assets and intangibles account:
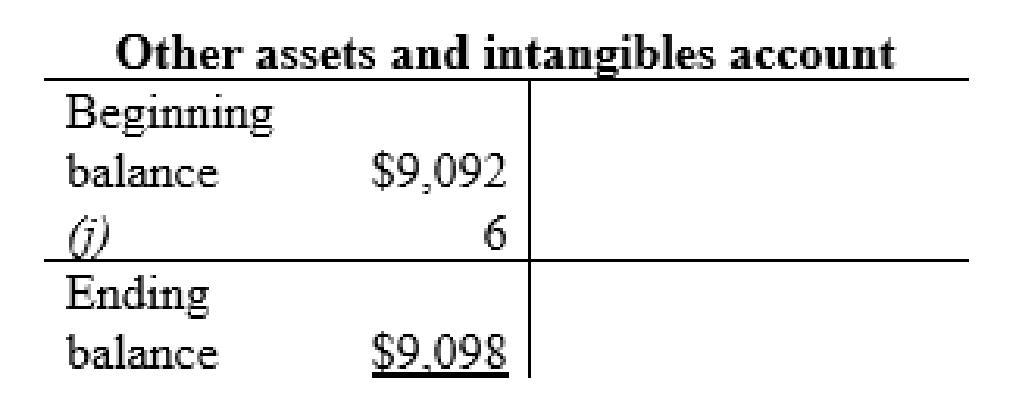
Property and equipment account:
Short-term notes payable account:
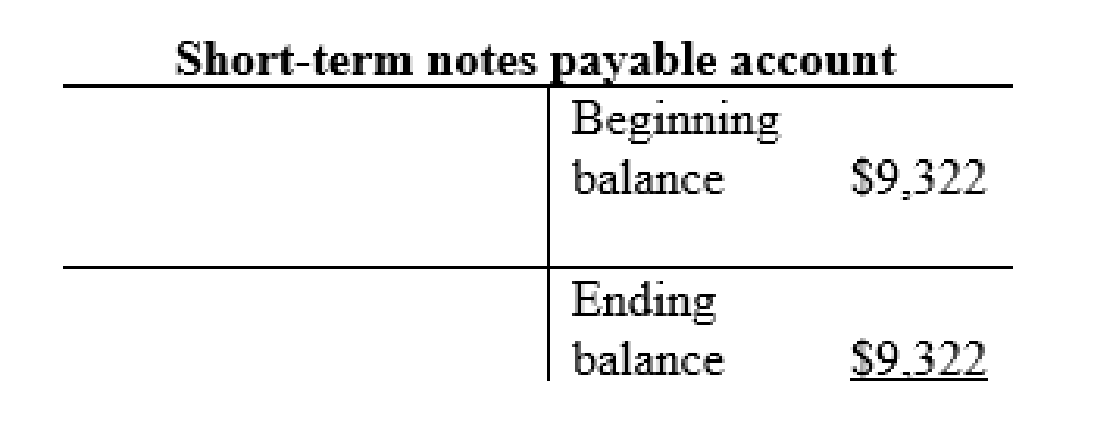
Accounts payable account:
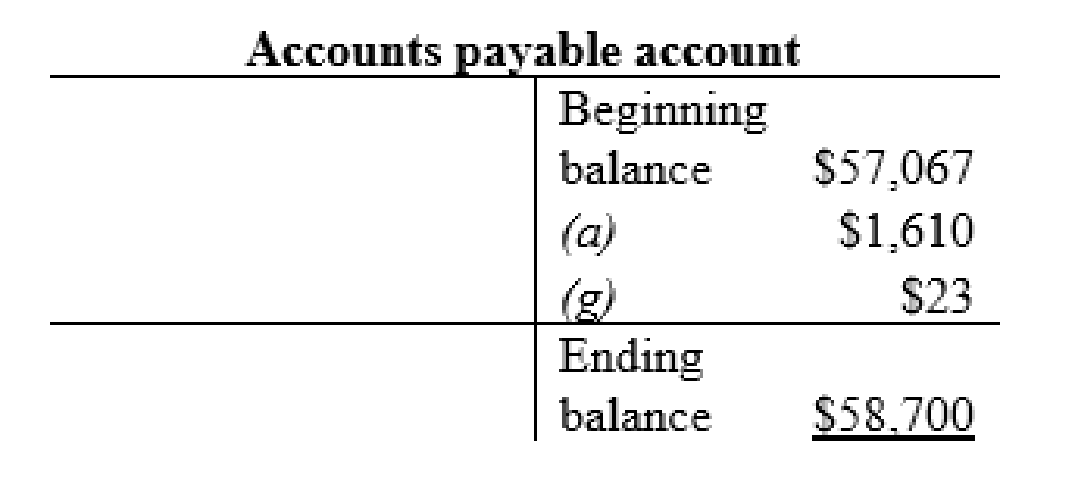
Income taxes payable account:
Long-term note payable account:
Other long-term debt account:
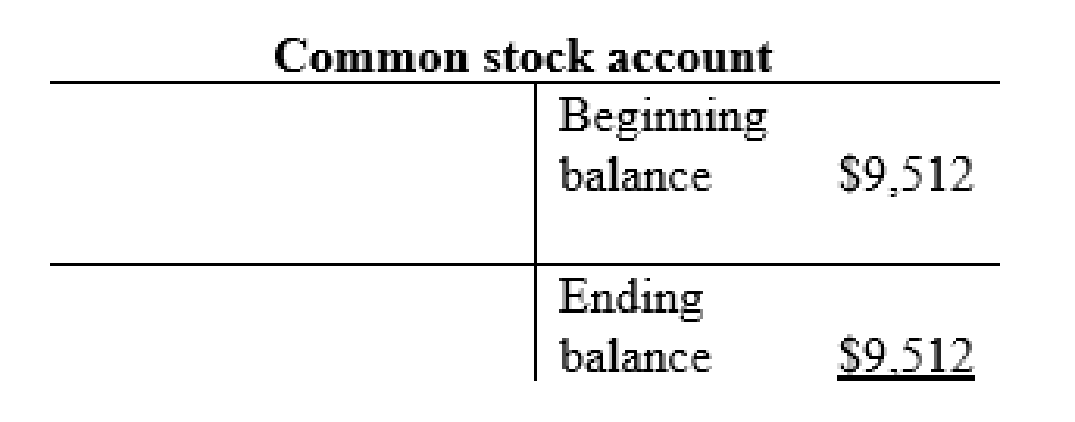
Common stock account:
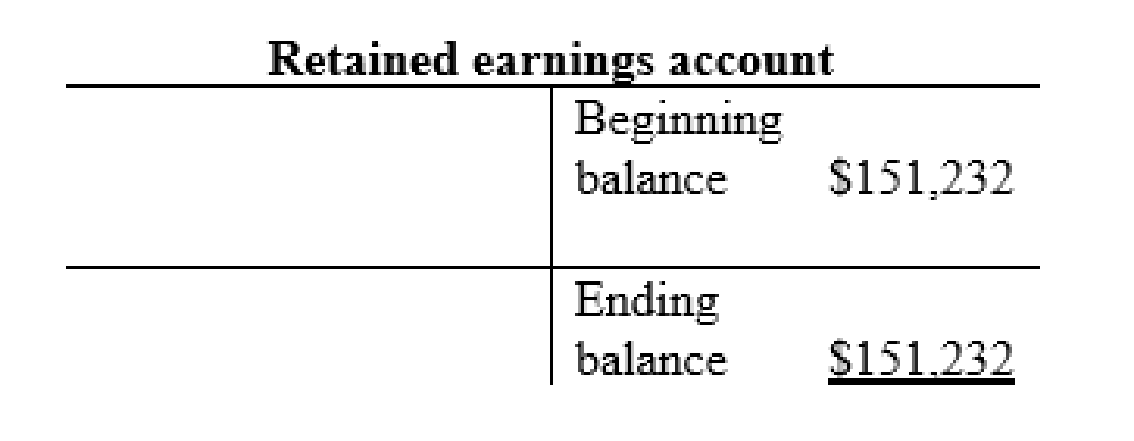
Sales revenue account:
Cost of sales account:
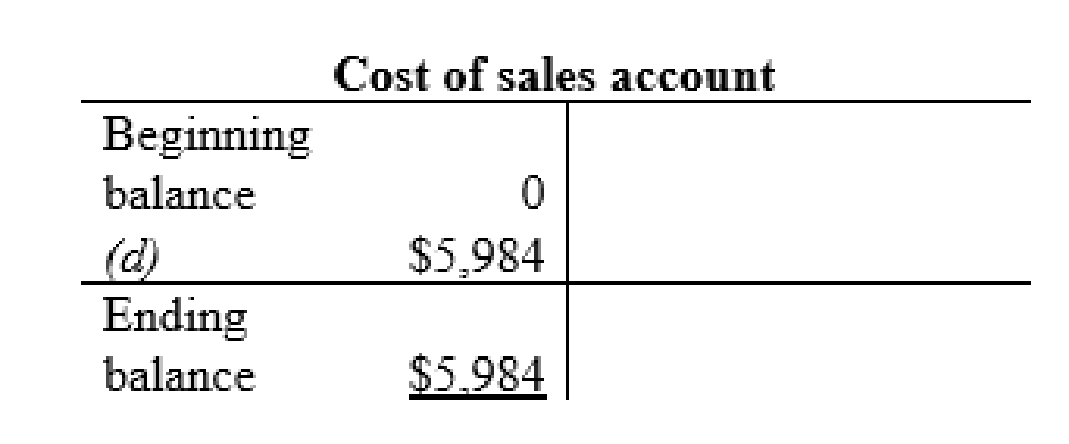
Utilities expense account:
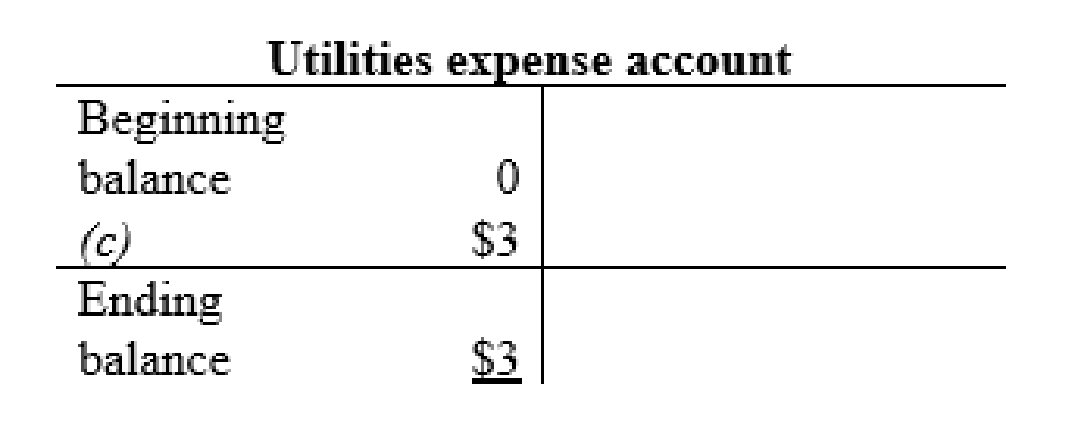
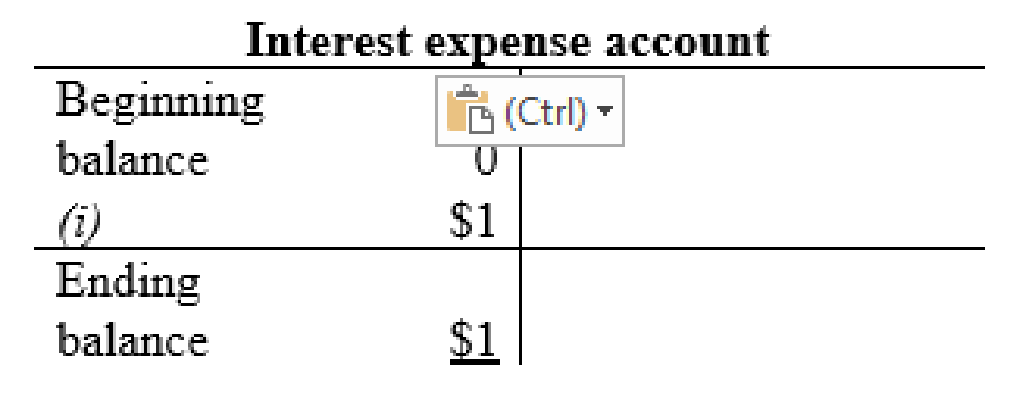
Interest expense account:
Wage expense account:
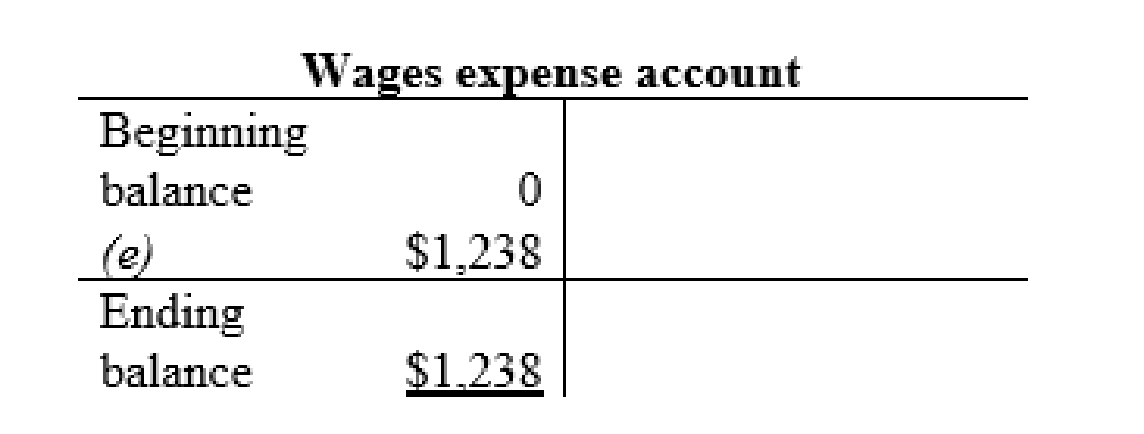
Thus, the t-accounts are prepared and the ending balances are calculated.
3.
Prepare an income statement for the month of January.
3.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare an income statement:
| Corporation EM | ||
| Income statement | ||
| For the month ended 31st January | ||
| Particulars | Amount ($) | Amount ($) |
| Revenues: | ||
| Sales revenue | 39,780 | |
| Expenses: | ||
| Cost of sales | 5,984 | |
| Wage expense | 1,238 | |
| Utilities expense | 3 | |
| Total costs and expenses | 7,225 | |
| Operating income | 32,555 | |
| Less: Other expense | ||
| Interest expense | 1 | |
| Net Income | $32,554 | |
Table (2)
Hence, the net income of Company E is $32,554.
4.
Compute the net profit margin ratio and based on the result give suggestion to the company.
4.
Explanation of Solution
Compute the net profit margin ratio:
Hence, the net profit margin ratio is 0.82.
- By evaluating the net profit margin ratio, the company has earned $0.82 in net income for every $ 1 in the sales revenue.
- To know the better result about the company, net profit margin ratio should be calculated to identify the way in which the management is generating its revenue and controlling the various expenses.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING W/CONNECT PKG
- FILL ALL CELLS. NOTICE THE DROPDOWN OPTIONSarrow_forwardABF's metal spare parts manufacturing company uses the customised production method by attributing the GST to the products it produces with the help of predetermined attribution coefficients. The processing of metal parts is carried out in two production departments: the Cutting and Drilling department, and the Assembly department. The GIS attribution coefficients for the two departments are based on the operating hours of machines and the cost of direct work respectively. At the beginning of the year, the following budgets were implemented: Cutting and Drilling Department Assembly Department Direct Labor Costs (in euros) 1.320.000 2.000.000 G.B.E. (in euros) 4.800.000 2.400.000 Machinery Operating Hours 80.000 5.000 Direct Work Hours 27.000 12.000 Requested: To calculate the coefficient of attribution of the General Secretariat that will be used in each department. (4 units) To determine the production cost per unit for order 158 which…arrow_forwardPLEASE HELP. I HAVE PROVIDED THE DROPDOWN OPTIONSarrow_forward
- The difference between the balance in a company's cash account and its bank statement is documented in the __________ of the bank statement.arrow_forwardLarge corporations should report revenues on their income statements when the __________. Cash Is Received Revenues Are Earnedarrow_forwardPLEASE HELP WITH THIS PROBLEMarrow_forward
- The KLM Medical Clinic has two auxiliary departments: the Building Maintenance Department and the Energy Production Department as well as three main production departments: the Department of Paediatrics, the Department of Internal Medicine and the Department of Surgery. The CLM allocates the cost of the building maintenance department based on the area occupied by the departments in square meters and the cost of the energy department based on the days of hospitalization of patients. No distinction is made between variable and fixed cost elements. The budgeted operating figures for the previous year were as follows: Auxiliary sections Main production departments Building maintenance Energy production Pediatrics Department of Internal Medicine Surgical Estimated cost before allocation 18.000,00 8.000,00 80.000,00 50.000,00 90.000,00 Area (in sq.m) 1.000,00 4.000,00 6.000,00 18.000,00 12.000,00 Patient Hospitalization…arrow_forwardwhat is financial accounting? explain its parts and all things.arrow_forwardSystematic relationship quarrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





