
Concept explainers
Extensions of the CVP Model—Multiple Products and Taxes
Assume that Painless Dental Clinics, Inc., offers three basic dental services. Here are its prices and costs:
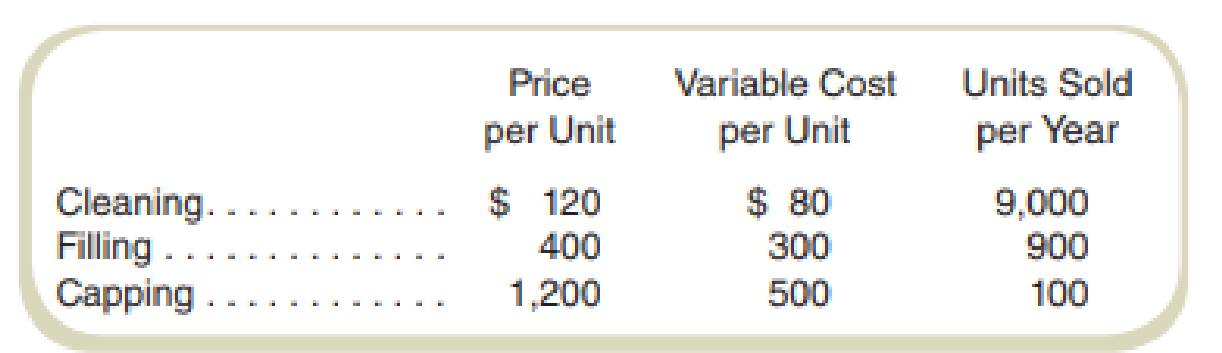
Variable costs include the labor costs of the dental hygienists and dentists. Fixed costs of $400,000 per year include building and equipment costs, marketing costs, and the costs of administration. Painless Dental Clinics is subject to a 30 percent tax rate on income. A cleaning “unit” is a routine teeth cleaning that takes about 45 minutes. A filling “unit” is the work done to fill one or more cavities in one session. A capping “unit” is the work done to put a crown on one tooth. If more than one tooth is crowned in a session, then the clinic counts one unit per tooth (e.g., putting crowns on two teeth counts as two units).
Required
- a. Given the above information, how much will Painless Dental Clinics, Inc., earn each year after taxes?
- b. Assuming the above sales mix is the same at the break-even point, at what sales revenue does Painless Dental Clinics, Inc., break even?
- c. Assuming the above sales mix, at what sales revenue will the company earn $140,000 per year after taxes?
- d. Painless Dental Clinics, Inc., is considering becoming more specialized in cleanings and fillings. What would be the company’s revenues per year if the number of cleanings increased to 12,000 per year, the number of fillings increased to 1,000 per year, while the number of cappings dropped to zero? With this change in product mix, the company would increase its fixed costs to $450,000 per year. What would be the effect of this change in product mix on the clinic’s earnings after taxes per year? If the clinic’s managers seek to maximize the clinic’s after-tax earnings, would this change be a good idea?
a.
Calculate the profit after tax for Company P.
Answer to Problem 69P
Company P earns $84,000 of profit after tax.
Explanation of Solution
Operating profit: The operating profit is the excess of total revenues over total expenses after adjusting for depreciation and taxes.
Contribution margin:
| Particulars | Cleaning | Filling | Capping |
| Sales price (unit) | $120 | $400 | $1,200 |
| Less: variable cost (unit) | $80 | $300 | $500 |
| Contribution margin (unit) | $40 | $100 | $700 |
| Units sold per year | 9,000 | 900 | 100 |
| Fixed cost | $400,000 | ||
| Tax rate | 30% | ||
Table: (1)
Compute the profit after tax of Company P:
| Particulars | Amount |
| Sales revenue | |
| Cleaning | $1,080,000 |
| Filling | $360,000 |
| Capping | $120,000 |
| Total sales revenue (a) | $1,560,000 |
| Less: | |
| Variable cost | |
| Cleaning | $720,000 |
| Filling | $270,000 |
| Capping | $50,000 |
| Total variable cost (b) | $1,040,000 |
| Contribution: | $520,000 |
| Less: | |
| Fixed cost (d) | $400,000 |
| Profit before tax: | $120,000 |
| Tax rate | 30% |
| Tax (f) | $36,000 |
| Profit after tax: | $84,000 |
Table: (2)
Thus, Company P earns $84,000 of profit after tax.
b.
Calculate the sales revenue for cleaning, filling and capping at the break-even point.
Answer to Problem 69P
The sales revenue for cleaning, filling, and capping is $830,760, $276,800 and $91,200 respectively.
Explanation of Solution
Breakeven point (BEP): The breakeven point or BEP is that level of output at which the total revenue is equal to the total cost. The BEP means there are no operating income and no operating losses. The management keeps an eye on the breakeven point in order to avoid the operating losses in order to avoid losses.
Compute the total sales revenue of each product:
| Particulars | Sales mix | Break-even point |
Sales Price (b) |
Total sales revenue |
| Cleaning | 90% | 6,923 | $120 | $830,760 |
| Filling | 9% | 692 | $400 | $276,800 |
| Capping | 1% | 76 | $1,200 | $91,200 |
Table: (3)
Thus, the sales revenue for cleaning, filling, and capping is $830,760, $276,800 and $91,200 respectively.
Working note 1:
Compute the break-even point:
Working note 2:
Compute the total weighted average contribution margin:
| Particulars | Sales price (a) | Variable cost (b) |
Contribution margin | Sales mix (d) |
Weighted average contribution margin |
| Cleaning | $120 | $80 | $40 | 90% | $36 |
| Filling | $400 | $300 | $100 | 9% | $9 |
| Capping | $1,200 | $500 | $700 | 1% | $7 |
| Total weighted average contribution margin | $52 | ||||
Table: (4)
c.
Calculate the dollar sales required to earn the profit after tax of $140,000.
Answer to Problem 69P
To earn the profit after tax of $140,000, Company P must make the sales revenue of $1,246,104, $415,200 and $138,000 for cleaning, filling and capping for respectively.
Explanation of Solution
Breakeven point (BEP): The breakeven point or BEP is that level of output at which the total revenue is equal to the total cost. The BEP means there are no operating income and no operating losses. The management keeps an eye on the breakeven point in order to avoid the operating losses in order to avoid losses.
Compute the dollar sales required to earn the profit after tax of $140,000:
The total target volume is 11,538, so it will be distributed among the products in their sales mix ratio.
| Particulars | Sales mix |
Sales units | Sales price | Sales revenue |
| Cleaning | 90% | 10,384 | $120 | $1,246,104 |
| Filling | 9% | 1,038 | $400 | $415,200 |
| Capping | 1% | 115 | $1,200 | $138,000 |
| Total sales revenue | $1,799,304 | |||
Table: (5)
Thus, to earn the profit after tax of $140,000, Company P must make the sales revenue of $1,246,104, $415,200 and $138,000 for cleaning, filling and capping respectively.
Working note 3:
Compute the volume of sales required to earn the profit after tax of $140,000:
d.
- I. Calculate the revenue of Company P if the number of cleanings increased to 12,000 per year, the number of fillings increased to 1,000 per year, while the number of capping dropped to zero.
- II. Calculate the effect on the profit after tax if the company increases its fixed cost to $450,000 with the given product mix.
- III. Suggest that the given change is a good idea or not.
Answer to Problem 69P
- I. The revenue of Company P would be $1,840,000 if the number of cleanings increased to 12,000 per year, the number of fillings increased to 1,000 per year, while the number of capping dropped to zero.
- II. The profit after tax increases by $7,000 if the company increases its fixed cost to $450,000 with the given product mix.
- III. Yes, the change of sales mix and an increase in fixed cost is a good idea for Company P.
Explanation of Solution
I.
Compute the revenue of Company P if the number of cleanings increased to 12,000 per year, the number of fillings increased to 1,000 per year, while the number of capping dropped to zero:
| Particulars | Amount |
| Sales revenue | |
| Cleaning | $1,440,000 |
| Filling | $400,000 |
| Capping | $0 |
| Total sales revenue (a) | $1,840,000 |
Table: (6)
Thus, the revenue of Company P is $1,840,000 if the number of cleanings increased to 12,000 per year, the number of fillings increased to 1,000 per year, while the number of capping dropped to zero.
II.
Compute the effect on the profit after tax if the company increases its fixed cost to $450,000 with the given product mix:
Thus, the profit after tax increases by $7,000 if the company increases fixed cost to $450,000 with the given product mix.
Working note 4:
Compute the profit after tax of Company P:
| Particulars | Amount |
| Sales revenue | |
| Cleaning | $1,440,000 |
| Filling | $400,000 |
| Capping | $0 |
| Total sales revenue (a) | $1,840,000 |
| Less: | |
| Variable cost | |
| Cleaning | $960,000 |
| Filling | $300,000 |
| Capping | $0 |
| Total variable cost (b) | $1,260,000 |
| Contribution: | $580,000 |
| Less: | |
| Fixed cost (d) | $450,000 |
| Profit before tax: | $130,000 |
| Tax rate | 30% |
| Tax (f) | $39,000 |
| Profit after tax: | $91,000 |
Table: (7)
III.
If the clinic’s managers seek to maximize the clinic’s after-tax earnings, this is a good idea as the profit has increased by 7,000 with the change in sales mix and an increase in fixed cost.
Thus, the change in sales mix and an increase in fixed cost is a good idea for Company P.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Connect Access Card For Fundamentals Of Cost Accounting
- compared to the individual risks of constituting assets. Question 5 (6 marks) The common shares of Almond Beach Inc, have a beta of 0.75, offer a return of 9%, and have an historical standard deviation of return of 17%. Alternatively, the common shares of Palm Beach Inc. have a beta of 1.25, offer a return of 10%, and have an historical standard deviation of return of 13%. Both firms have a marginal tax rate of 37%. The risk-free rate of return is 3% and the expected rate of return on the market portfolio is 9½%. 1. Which company would a well-diversified investor prefer to invest in? Explain why and show all calculations. 2. Which company Would an investor who can invest in the shares of only one firm prefer to invest in? Explain why. RELEASED BY THE CI, MGMT2023, MARCH 2, 2025 5 Use the following template to organize and present your results: Theoretical CAPM Actual offered prediction for expected return (%) return (%) Standard deviation of return (%) Beta Almond Beach Inc. Palm Beach…arrow_forwardprovide correct answerarrow_forwardPlease solve. The screen print is kind of split. Please look carefully.arrow_forward
- Coronado Fire, Inc. manufactures steel cylinders and nozzles for two models of fire extinguishers: (1) a home fire extinguisher and (2) a commercial fire extinguisher. The home model is a high-volume (54,000 units), half-gallon cylinder that holds 2 1/2 pounds of multi- purpose dry chemical at 480 PSI. The commercial model is a low-volume (10,200 units), two-gallon cylinder that holds 10 pounds of multi-purpose dry chemical at 390 PSI. Both products require 1.5 hours of direct labor for completion. Therefore, total annual direct labor hours are 96,300 or [1.5 hours x (54,000+10,200)]. Estimated annual manufacturing overhead is $1,566,090. Thus, the predetermined overhead rate is $16.26 or ($1,566,090 ÷ 96,300) per direct labor hour. The direct materials cost per unit is $18.50 for the home model and $26.50 for the commercial model. The direct labor cost is $19 per unit for both the home and the commercial models. The company's managers identified six activity cost pools and related…arrow_forwardCoronado Fire, Inc. manufactures steel cylinders and nozzles for two models of fire extinguishers: (1) a home fire extinguisher and (2) a commercial fire extinguisher. The home model is a high-volume (54,000 units), half-gallon cylinder that holds 2 1/2 pounds of multi- purpose dry chemical at 480 PSI. The commercial model is a low-volume (10,200 units), two-gallon cylinder that holds 10 pounds of multi-purpose dry chemical at 390 PSI. Both products require 1.5 hours of direct labor for completion. Therefore, total annual direct labor hours are 96,300 or [1.5 hours x (54,000+ 10,200)]. Estimated annual manufacturing overhead is $1,566,090. Thus, the predetermined overhead rate is $16.26 or ($1,566,090 ÷ 96,300) per direct labor hour. The direct materials cost per unit is $18.50 for the home model and $26.50 for the commercial model. The direct labor cost is $19 per unit for both the home and the commercial models. The company's managers identified six activity cost pools and related…arrow_forwardThe completed Payroll Register for the February and March biweekly pay periods is provided, assuming benefits went into effect as anticipated. Required: Using the payroll registers, complete the General Journal entries as follows: February 10 Journalize the employee pay. February 10 Journalize the employer payroll tax for the February 10 pay period. Use 5.4 percent SUTA and 0.6 percent FUTA. No employees will exceed the FUTA or SUTA wage base. February 14 Issue the employee pay. February 24 Journalize the employee pay. February 24 Journalize the employer payroll tax for the February 24 pay period. Use 5.4 percent SUTA and 0.6 percent FUTA. No employee will exceed the FUTA or SUTA wage base. February 28 Issue the employee pay. February 28 Issue payment for the payroll liabilities. March 10 Journalize the employee pay. March 10 Journalize the employer payroll tax for the March 10 pay period. Use 5.4 percent SUTA and 0.6 percent FUTA. No employees will exceed the FUTA or SUTA wage base.…arrow_forward
 Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning



