
a.
Analyze the effects that each of the given transactions will have on the following six components of the company’s financial statements for the month of August.
a.
Explanation of Solution
Income statement:
The financial statement which reports revenues and expenses from business operations and the result of those operations as net income or net loss for a particular time period is referred to as income statement.
This financial statement reports a company’s resources (assets) and claims of creditors (liabilities) and stockholders (stockholders’ equity) over those resources. The resources of the company are assets which include money contributed by stockholders and creditors. Hence, the main elements of the balance sheet are assets, liabilities, and
Analyze the effects that each of the given transactions will have on the following six components of the company’s financial statements for the month of August as follows:
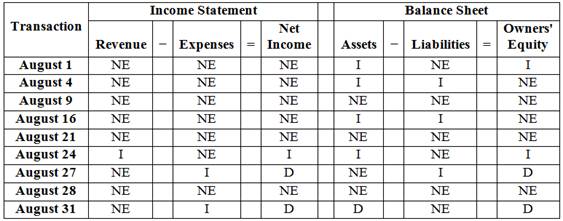
Figure (1)
b.
Prepare journal entries for each transaction.
b.
Explanation of Solution
Journal entry is a set of economic events which can be measured in monetary terms. These are recorded chronologically and systematically.
Prepare journal entries for each transaction as follows:
| Date | Account title and Explanation | Post ref. |
Debit (in $) | Credit (in $) |
| August 1 | Cash | 280,000 | ||
| Capital stock | 280,000 | |||
| (To record the issue of the 1,000 shares of capital stock) | ||||
| August 4 | Land | 60,000 | ||
| Office Building | 340,000 | |||
| Cash | 80,000 | |||
| Notes Payable | 320,000 | |||
| (To record the purchase of land and office building) | ||||
| August 9 | Medical instruments | 75,000 | ||
| Cash | 75,000 | |||
| (To record the purchase of computer systems) | ||||
| August 16 | Office fixtures and equipment | 25,000 | ||
| Cash | 10,000 | |||
| Accounts Payable | 15,000 | |||
| (To record the purchase of office fixtures and equipment) | ||||
| August 21 | Office supplies | 4,200 | ||
| Cash | 4,200 | |||
| (To record the purchase of office supplies purchased on account) | ||||
| August 24 | Cash | 1,000 | ||
| 12,000 | ||||
| Service revenue | 13,000 | |||
| (To record the service revenue earned) | ||||
| August 27 | Advertising expense | 450 | ||
| Accounts payable | 450 | |||
| (To record the advertising expense incurred) | ||||
| August 28 | Cash | 500 | ||
| Accounts receivable | 500 | |||
| (To record the cash collected from accounts receivable) | ||||
| August 31 | Salary expense | 2,200 | ||
| Cash | 2,200 | |||
| (To record the salary expense paid) |
Table (1)
c.
Post each transaction to the appropriate ledger accounts.
c.
Explanation of Solution
T-account:
The condensed form of a ledger is referred to as T-account. The left-hand side of this account is known as debit, and the right hand side is known as credit.
Post each transaction to the appropriate ledger accounts as follows:
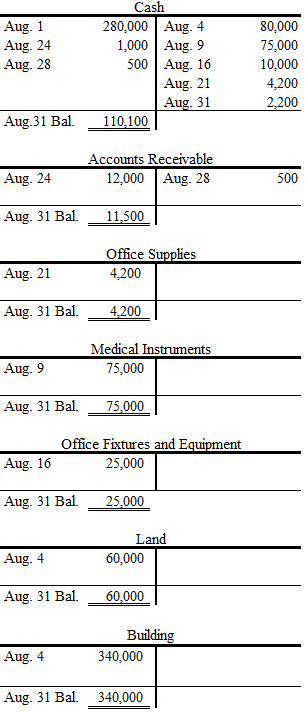
Figure (2)
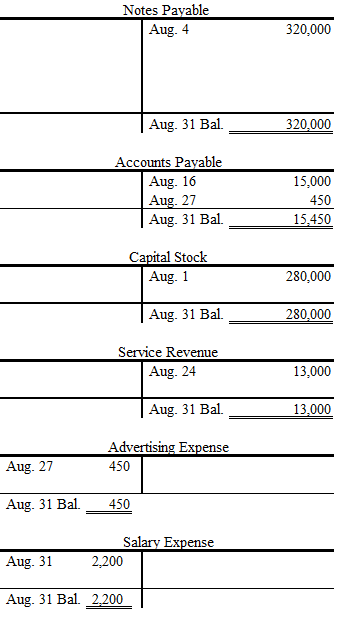
Figure (3)
d.
Prepare a
d.
Explanation of Solution
Trial balance:
Trial balance is a summary of all the ledger accounts balances presented in a tabular form with two column, debit and credit. It checks the mathematical accuracy of the
Prepare a trial balance dated August 31, current year as follows:
| Dental Clinic | ||
| Trial Balance | ||
| August 31, Current Year | ||
| Cash | $110,100 | |
| Accounts receivable | 11,500 | |
| Office supplies | 4,200 | |
| Medical instruments | 75,000 | |
| Office fixtures and equipment | 25,000 | |
| Land | 60,000 | |
| Building | 340,000 | |
| Notes payable | $320,000 | |
| Accounts payable | 15,450 | |
| Capital stock | 280,000 | |
| | 0 | |
| Veterinary service revenue | 13,000 | |
| Advertising expense | 450 | |
| Salary expense | 2,200 | |
| $628,450 | $628,450 | |
Table (2)
e.
Compute total assets, total liabilities, and owners’ equity and identify whether the month August appeared to be a profitable month.
e.
Explanation of Solution
Assets:
These are the resources owned and controlled by business and used to produce benefits for the company. Assets are classified on the balance sheet as current assets, non-current assets, property, plant, and equipment, and intangible assets.
Liabilities:
The claims creditors have over assets or resources of a company are referred to as liabilities. These are the debt obligations owed by company to creditors. Liabilities are classified on the balance sheet as current liabilities and long-term liabilities.
Owners’ equity:
Owner’s equity refers to the right the owner possesses over the resources of the business. Revenues and the expenses are the components of the owner’s equity.
Net income:
The bottom line of income statement which is the result of excess of earnings from operations (revenues) over the costs incurred for earning revenues (expenses) is referred to as net income.
Compute total assets, total liabilities, and owners’ equity as follows:
| Total Assets: | ||
| Cash | $110,100 | |
| Accounts receivable | 11,500 | |
| Office supplies | 4,200 | |
| Medical instruments | 75,000 | |
| Office fixtures and equipment | 25,000 | |
| Land | 60,000 | |
| Building | 340,000 | |
| Total assets | $625,800 | |
| Total Liabilities: | ||
| Notes payable | $320,000 | |
| Accounts payable | 15,450 | |
| Total liabilities | $335,450 | |
| Total Owners' Equity: | ||
| Total assets − Total liabilities | $290,350 |
Table (3)
Identify whether the month August appeared to be a profitable month as follows:
| Amount (In $) | Amount (In $) | |
| Service revenue | 13,000 | |
| Less: Advertising expense | 450 | |
| Salary expense | 2,200 | 2,650 |
| Net income (Profit) | $10,350 |
Table (4)
Hence, the month August appeared to be a profitable month.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Financial Accounting
- Under which method of inventory accounting are the most recent inventory costs matched with current revenues?a) LIFO (Last-In, First-Out)b) FIFO (First-In, First-Out)c) Average Cost Methodd) Specific Identification Methodarrow_forwardWhat is the goal of cost accounting? Explain itarrow_forwardTwo parts of this probarrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





