
Concept explainers
Reece Financial Services Co., which specializes in appliance repair services, is owned and operated by Joni Reece. Reece Financial Services’ accounting clerk prepared the following unadjusted
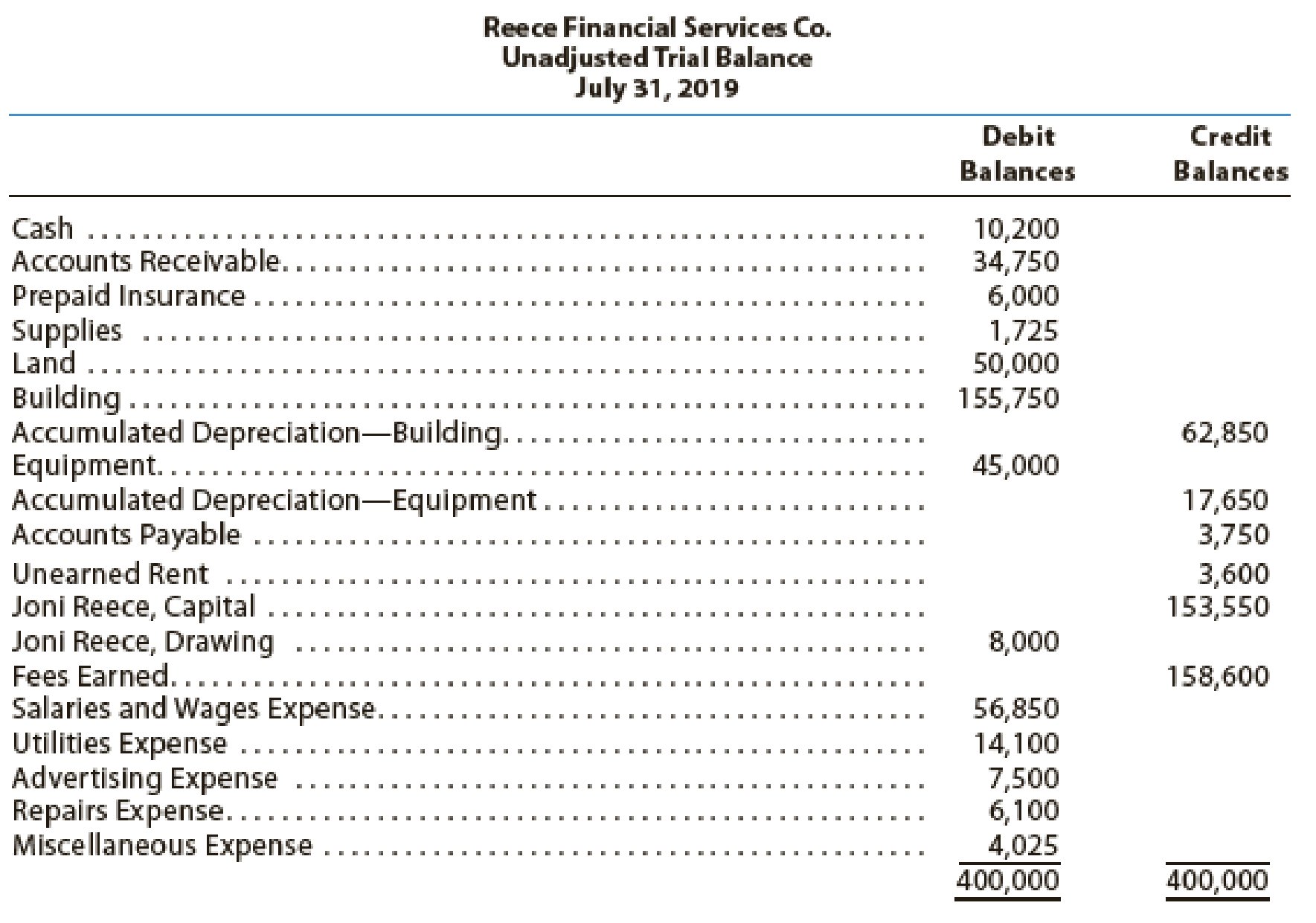
The data needed to determine year-end adjustments are as follows:
- •
Depreciation of building for the year, $6,400. - • Depreciation of equipment for the year, $2,800.
- • Accrued salaries and wages at July 31, $900.
- • Unexpired insurance at July 31, $1,500.
- • Fees earned but unbilled on July 31, $10,200.
- • Supplies on hand at July 31, $615.
- • Rent unearned at July 31, $300.
Instructions
- 1. Journalize the
adjusting entries using the following additional accounts: Salaries and Wages Payable, Rent Revenue, Insurance Expense, Depreciation Expense—Building, Depreciation Expense—Equipment, and Supplies Expense. - 2. Determine the balances of the accounts affected by the adjusting entries and prepare an adjusted trial balance.
(1)
Record the adjusting entries on July 31, 2019 of Company RFS.
Answer to Problem 5PB
The adjusting entry for recording depreciation is as follows:
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| July 31 | Depreciation expense | 6,400 | |
| Accumulated Depreciation- building | 6,400 | ||
| (To record the depreciation on building for the current year.) |
Table (1)
The impact on the accounting equation for the above referred adjusting entry is as follows:
Explanation of Solution
Description of journal entry
- Depreciation expense is component of stockholders’ equity and decreased it, so debit depreciation expense by $6,400.
- Accumulated depreciation is a contra asset account, and it decreases the asset value by $6,400. So credit accumulated depreciation by $6,400.
The adjusting entry for recording depreciation is as follows:
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| July 31 | Depreciation expense | 2,800 | |
| Accumulated Depreciation- equipment | 2,800 | ||
| (To record the depreciation on equipment for the current year.) |
Table (2)
The impact on the accounting equation for the above referred adjusting entry is as follows:
Description of journal entry
- Depreciation expense is component of stockholders’ equity and decreased it, so debit depreciation expense by $2,800.
- Accumulated depreciation is a contra asset account, and it decreases the asset value by $2,800. So credit accumulated depreciation by $2,800.
The following entry shows the adjusting entry for Salary and wages expense on July 31.
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| July 31 | Salary and wages expense | 900 | |
| Wages Payable | 900 | ||
| (To record the salary and wages accrued but not paid at the end of the accounting period.) |
Table (3)
The impact on the accounting equation for the above referred adjusting entry is as follows:
Description of journal entry
- Salary and wages expense is a component of Stockholders ‘equity, and it decreased it by $900. So debit wage expense by $900.
- Salary and wages payable is a liability, and it is increased by $900. So credit Salary and wages payable by $900.
The following entry shows the adjusting entry for unexpired insurance on July 31.
| Date | Description |
Post. Ref |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| July 31 | Insurance expense (1) | 4,500 | ||
| Prepaid insurance | 4,500 | |||
| (To record the insurance expense incurred at the end of the year) |
Table (4)
The impact on the accounting equation for the above referred adjusting entry is as follows:
Working note 1: Calculate the value of insurance expense at the end of the year
Description of journal entry
- Insurance expense is a component of owners’ equity, and decreased it by $4,500 hence debit the insurance expense for $4,500.
- Prepaid insurance is an asset, and it decreases the value of asset by $4,500, hence credit the prepaid insurance for $4,500.
The following entry shows the adjusting entry for accrued fees unearned on July 31.
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| July 31 | Accounts Receivable | 10,200 | |
| Fees earned | 10,200 | ||
| (To record the accounts receivable at the end of the year.) |
Table (1)
The impact on the accounting equation for the above referred adjusting entry is as follows:
Description of journal entry
- Accounts Receivable is an asset, and it is increased by $10,200. So debit Accounts receivable by $10,200.
- Fees earned are component of stockholders’ equity, and it increased it by $10,200. So credit fees earned by $10,200.
The following entry shows the adjusting entry for supplies on July 31.
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| July 31 | Supplies Expense (2) | 1,110 | |
| Supplies | 1,110 | ||
| (To record the supplies expense at the end of the accounting period) |
Table (2)
The impact on the accounting equation for the above referred adjusting entry is as follows:
Description of journal entry
- Supplies expense is a component of stockholders’ equity, and it decreased the stockholders’ equity by $1,110. So debit supplies expense by $1,110.
- Supplies are an asset for the business, and it is decreased by $1,110. So credit supplies by $1,110.
Working Note 2: Calculation of Supplies expense for the accounting period
The following entry shows the adjusting entry for Unearned Rent on July 31.
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| July 31 | Unearned Rent | 3,300 | |
| Rent revenue (3) | 3,300 | ||
| (To record the Rent revenue from services at the end of the accounting period.) |
Table (4)
The impact on the accounting equation for the above referred adjusting entry is as follows:
- Unearned Rent is a liability, and it is decreased by $3,300. So debit unearned rent by $3,300.
- Rent revenue is a component of Stockholders’ equity, and it is increased by $3,300. So credit rent revenue by $3,300.
Working Notes 3: Calculation of Rent Revenue for the accounting period
(2)
Prepare adjusted trial balance of the Company RFS on July 31, 2019
Answer to Problem 5PB
The adjusted trial balance of the Company RFS is as follows:
| Company RFS | ||
| Trial Balance after Adjustments | ||
| July 31, 2019 | ||
| Particulars | Debit $ | Credit $ |
| Cash | 10,200 | |
| Accounts Receivable(5) | 44,950 | |
| Prepaid Insurance | 1,500 | |
| Supplies | 615 | |
| Land | 50,000 | |
| Building | 155,750 | |
| Accumulated Depreciation - Building(1) | 69,250 | |
| Equipment | 45,000 | |
| Accumulated Depreciation - Equipment(2) | 20,450 | |
| Accounts Payable | 3,750 | |
| Unearned Rent | 300 | |
| Salaries and Wages Payable | 900 | |
| Capital | 153,550 | |
| Drawing | 8,000 | |
| Fees earned | 168,800 | |
| Rent Revenue (7) | 3,300 | |
| Salaries and Wages Expense (3) | 57,750 | |
| Utilities Expense | 14,100 | |
| Advertising Expense | 7,500 | |
| Repairs Expense | 6,100 | |
| Depreciation Expense - building | 6,400 | |
| Depreciation Expense - equipment | 2,800 | |
| Insurance Expense (4) | 4,500 | |
| Supplies Expense (6) | 1,110 | |
| Miscellaneous Expense | 4,025 | |
| 420,300 | 420,300 | |
Explanation of Solution
Working Notes:
1. Calculation of accumulated depreciation- building
2. Calculation of accumulated depreciation- equipment
3. Calculation of Salaries and Wages expenses
4. Calculate the value of insurance expense at the end of the year
5. Calculation of accounts receivable
6. Calculation of Supplies expense for the accounting period
7. Calculation of rent revenue
Hence, the total of debit and credit column of the adjusted trial balance matches and they have a total balance of $420,300.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Financial Accounting
- Year Cash Flow 0 -$ 27,000 1 11,000 2 3 14,000 10,000 What is the NPV for the project if the required return is 10 percent? Note: Do not round intermediate calculations and round your answer to 2 decimal places, e.g., 32.16. NPV $ 1,873.28 At a required return of 10 percent, should the firm accept this project? No Yes What is the NPV for the project if the required return is 26 percent?arrow_forwardThe following were selected from among the transactions completed by Babcock Company during November of the current year: Nov. 3 Purchased merchandise on account from Moonlight Co., list price $85,000, trade discount 25%, terms FOB destination, 2/10, n/30. 4 Sold merchandise for cash, $37,680. The cost of the goods sold was $22,600. 5 Purchased merchandise on account from Papoose Creek Co., $47,500, terms FOB shipping point, 2/10, n/30, with prepaid freight of $810 added to the invoice. 6 Returned merchandise with an invoice amount of $13,500 ($18,000 list price less trade discount of 25%) purchased on November 3 from Moonlight Co. 8 Sold merchandise on account to Quinn Co., $15,600 with terms n/15. The cost of the goods sold was $9,400. 13 Paid Moonlight Co. on account for purchase of November 3, less return of November 6. 14 Sold merchandise with a list price of $236,000 to customers who used VISA and who redeemed $8,000 of pointof- sale coupons. The cost…arrow_forwardHello teacher please solve this questionsarrow_forward
 Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning Individual Income TaxesAccountingISBN:9780357109731Author:HoffmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
Individual Income TaxesAccountingISBN:9780357109731Author:HoffmanPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT





