
Concept explainers
a)
To draw: A process flow diagram for this process.
a)
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
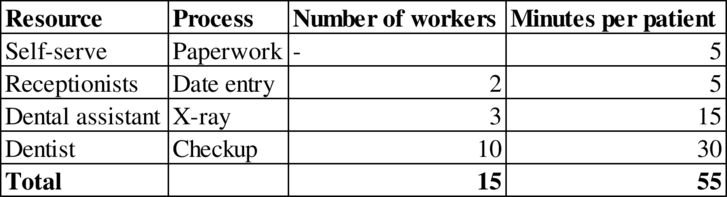
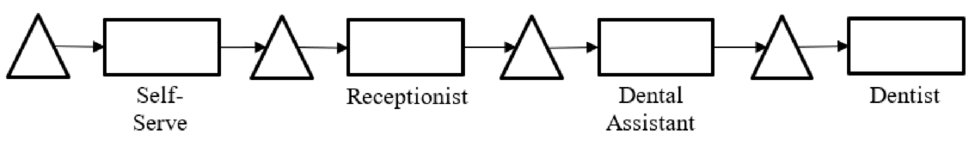
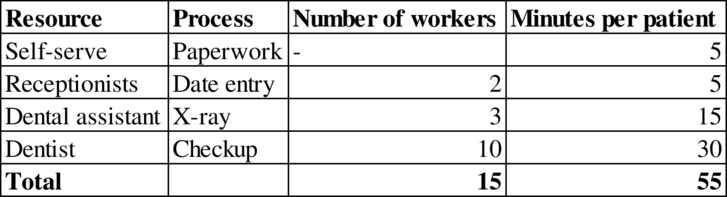
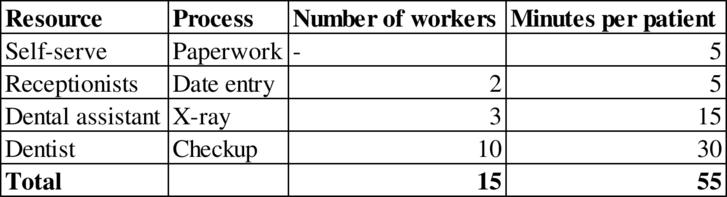
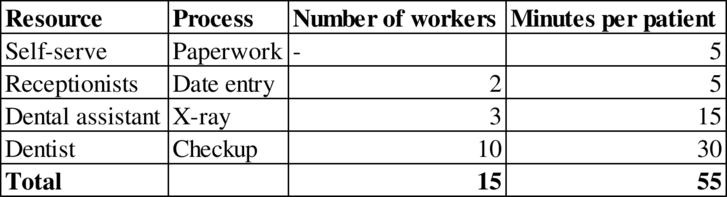
Process flow diagram:
b)
To determine: The capacity at the resource “Dentist”.
b)
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
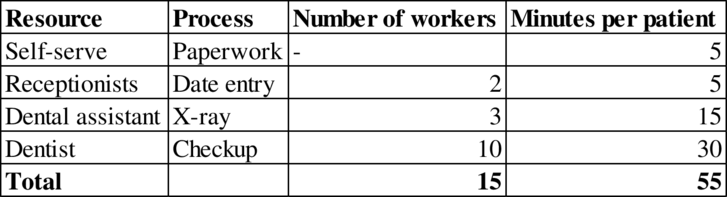
Calculation of capacity:
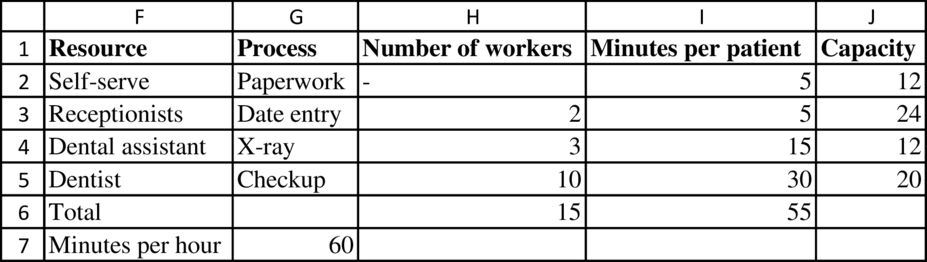
Formula:
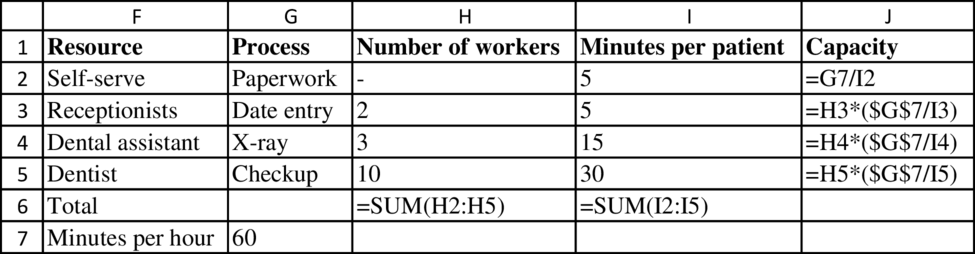
The capacity at “Dentist” is 20 patients.
c)
To determine: The bottleneck in the process.
c)
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
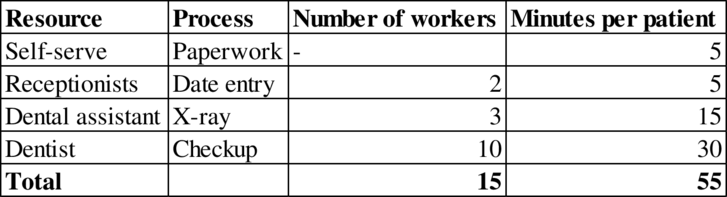
Determination of bottleneck:
The resource with the lowest capacity is the bottleneck. The resource “Dental assistant” has the lowest capacity of 12 patients per hour.
Hence, the bottleneck is Dental assistant.
d)
To determine: The flow rate.
d)
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
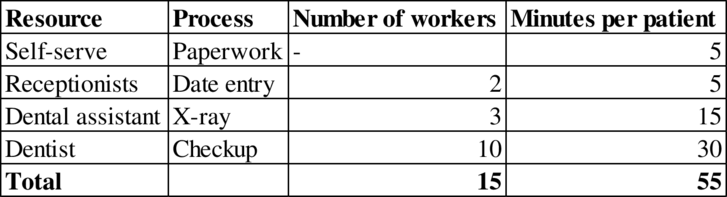
Determination of flow rate:
The bottleneck flow rate determines the flow rate of the process. Therefore, the flow rate of the dentist is:
The flow rate is 12 patients per hour.
e)
To determine: The utilization of resource “Receptionists”.
e)
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
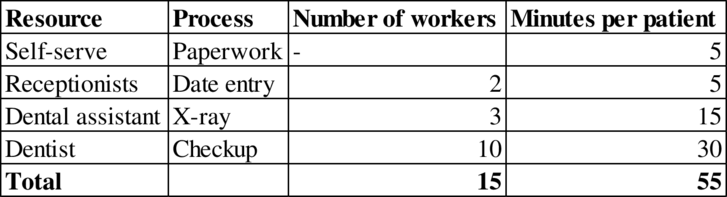
Calculation of utilization:
The utilization is 50%.
f)
To determine: The cycle time of the process.
f)
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Calculation of cycle time:
The demand is constrained and has a flow rate of
The cycle time is 125 minutes.
g)
To determine: The cycle time of the process.
g)
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Calculation of cycle time:
The cycle time is 105 minutes.
h)
To determine: The time taken to serve 20 patients
h)
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Calculation of time taken to serve 20 patients:
There are 3 resources and the cycle time is 5 minutes.
The time taken to serve 20 patients is 110 minutes.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT W/ 360 DAY CONNECT
- The Importance of Food Labeling and Expiration Dates in a nursing home kitchen and how can a nutritionist utilize this in their career? Please not just a short explanation.arrow_forwarda) Huurhun Printing in Ulaanbaatar has four typesetters and four jobs to be completed as given in the table. The $ entries represent the firm’s estimate of what it will cost for each job to be completed by each typesetter. Find the optimal assignment of jobs to typesetters so as to minimize the total costs. Typesetters Jobs A B C D 42HG $7 $3 $4 $8 19DT $5 $4 $6 $5 47ST $6 $7 $9 $6 17VT $8 $6 $7 $4 b) Huurhun Printing in Ulaanbaatar has the following printing jobs waiting to be processed at its work center. The jobs are assigned sequentially upon arrival. All dates are specified as days from today. In what sequence should the firm process the jobs according to the SPT, EDD, and CR scheduling rules? Jobs Due Date Duration (days) 42HG 43 10 19DT 37 12 47ST 34 11 17VT 32 7 LR99 37 15arrow_forward1) Scheduling at Washburn Guitar View the video Scheduling at Washburn Guitar (10.40 minutes, Ctrl+Click on the link); what are your key takeaways (tie to one or more of the topics discussed in Chapters 11 and/or 16) after watching this video. Note: As a rough guideline, please try to keep the written submission to one or two paragraphs. 2) Bosa Limited, a specialist confectionary manufacturer, makes a variety of confectionary products candies in its manufacturing facility at Ulaanbaatar. Its line of confectionary products exhibits a highly seasonal demand pattern. The firm’s costs and quarterly sales forecasts are as follows: Costs: Hiring cost = $200 per worker, Firing cost = $600 per worker, Inventory carrying cost = $0.60 per pound per worker, Production per employee = 1000 pounds per quarter, Beginning workforce = 125 workers. Quarter Sales Forecast/ Demand(pounds) Production Spring 80,000 95,000 Summer 50,000 95,000 Fall 100,000 95,000…arrow_forward
- Note: In chapter 11, section 11.3 of the Stevenson text, level and chase plans are covered with examples (example 1, and example 2); chapter 11 Stevenson lecture power point slides 23 to 32 cover chase and level plans with an example; see lecture video, 12.21 mins to 26.55 mins. 3) a) Huurhun Printing in Ulaanbaatar has four typesetters and four jobs to be completed as given in the table. The $ entries represent the firm’s estimate of what it will cost for each job to be completed by each typesetter. Find the optimal assignment of jobs to typesetters so as to minimize the total costs. Typesetters Jobs A B C D 42HG $7 $3 $4 $8 19DT $5 $4 $6 $5 47ST $6 $7 $9 $6 17VT $8 $6 $7 $4 b) Huurhun Printing in Ulaanbaatar has the following printing jobs waiting to be processed at its work center. The jobs are assigned sequentially upon arrival. All dates are specified as days from today. In what sequence should the…arrow_forwardGalaxy Co. sells virtual reality (VR) goggles, particularly targeting customers who like to play video games. Galaxy procures each pair of goggles for $150 from its supplier and sells each pair of goggles for $300. Monthly demand for the VR goggles is a normal random variable with a mean of 157 units and a standard deviation of 41 units. At the beginning of each month, Galaxy orders enough goggles from its supplier to bring the inventory level up to 140 goggles. If the monthly demand is less than 140, Galaxy pays $20 per pair of goggles that remains in inventory at the end of the month. If the monthly demand exceeds 140, Galaxy sells only the 140 pairs of goggles in stock. Galaxy assigns a shortage cost of $40 for each unit of demand that is unsatisfied to represent a loss-of-goodwill among its customers. Management would like to use a simulation model to analyze this situation. (Use at least 1,000 trials.) (a) What is the average monthly profit (in dollars)? (Round your answer to the…arrow_forwardHospital administrators must schedule nurses so that the hospital's patients are provided adequate care. At the same time, careful attention must be paid to keeping costs down. From historical records, administrators can project the minimum number of nurses required to be on hand for various times of day and days of the week. The objective is to find the minimum total number of nurses required to provide adequate care. Nurses start work at the beginning of one of the four-hour shifts given below (except for shift 6) and work for 8 consecutive hours. Hence, possible start times are the start of shifts 1 through 5. Also, assume that the projected required number of nurses factors in time for each nurse to have a meal break. Formulate and solve the nurse scheduling problem as an integer program for one day for the data given below. (Let x = number of nurses who start work at the beginning of shift t, t = 1, 2, 3, 4, 5.) Shift Time Minimum Number of Nurses Needed 1 12:00 A.M. - 4:00 A.M.…arrow_forward
- The Kolkmeyer Manufacturing Company uses a group of six identical machines, each of which operates an average of 23 hours between breakdowns. With randomly occurring breakdowns, the Poisson probability distribution is used to describe the machine breakdown arrival process. One person from the maintenance department provides the single-server repair service for the six machines. Management is now considering adding two machines to its manufacturing operation. This addition will bring the number of machines to eight. The president of Kolkmeyer asked for a study of the need to add a second employee to the repair operation. The service rate for each individual assigned to the repair operation is 0.40 machines per hour. (a) Compute the operating characteristics if the company retains the single-employee repair operation. (Round your answers to four decimal places. Report time in hours.) W L = q W = ✓ X h × h (b) Compute the operating characteristics if a second employee is added to the…arrow_forwardConsider the nonlinear optimization model stated below. Min 2x²-18x + 2XY + y² 14Y + 51 s.t. X + 4Y ≤7 (a) Find the minimum solution to this problem. at (X, Y) = (b) If the right-hand side of the constraint is increased from 7 to 8, how much do you expect the objective function to change? Based on the dual value on the constraint X + 4Y ≤7, we expect the optimal objective function value to decrease by (c) Resolve the problem with a new right-hand side of the constraint of 8. How does the actual change compare with your estimate? If we resolve the problem with a new right-hand-side of 8 the new optimal objective function value is , so the actual change is a decrease of rather than what we expected in part (b).arrow_forwardBurger Dome sells hamburgers, cheeseburgers, french fries, soft drinks, and milk shakes, as well as a limited number of specialty items and dessert selections. Although Burger Dome would like to serve each customer immediately, at times more customers arrive than can be handled by the Burger Dome food service staff. Thus, customers wait in line to place and receive their orders. Burger Dome analyzed data on customer arrivals and concluded that the arrival rate is 40 customers per hour. Burger Dome also studied the order-filling process and found that a single employee can process an average of 56 customer orders per hour. Burger Dome is concerned that the methods currently used to serve customers are resulting in excessive waiting times and a possible loss of sales. Management wants to conduct a waiting line study to help determine the best approach to reduce waiting times and improve service. Suppose Burger Dome establishes two servers but arranges the restaurant layout so that an…arrow_forward
- >>>> e 自 A ? ↑ G סוי - C Mind Tap Cengage Learning CENGAGE MINDTAP Chapter 12 Homework: Managing Inventories in Supply Chains Assignment: Chapter 12 Homework: Managing Inventories in Supply Chains Questions Problem 12-70 Algo (Managing Fixed-Quantity Inventory Systems) 6. 7. ng.cengage.com + O C Excel Online Student Work Q Search this course ? Save Assignment Score: 91.34% Submit Assignment for Grading e Question 8 of 11 ▸ A-Z Hint(s) Check My Work 8. 9. 10. 11. Spreadsheet Environmental considerations, material losses, and waste disposal can be included in the EOQ model to improve inventory-management decisions. Assume that the annual demand for an industrial chemical is 1,600 lb, item cost is $2/lb, order cost is $45, inventory holding cost rate (percent of item cost) is 15 percent. Use the EOQ Model Excel template in MindTap to answer the following: a. Find the EOQ and total cost, assuming no waste disposal. Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer for the EOQ to…arrow_forward>>>> G סוי - C Mind Tap Cengage Learning CENGAGE MINDTAP Chapter 12 Homework: Managing Inventories in Supply Chains Questions Problem 12-44 Algo (Managing Fixed-Quantity Inventory Systems) 1. e 2. 3. 自 4. 5. ? ↑ 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. ng.cengage.com + O C Excel Online Student Work Q Search this course ? Question 3 of 11 ► Hint(s) Check My Work Brenda opened a pool and spa store in a lively shopping mall and finds business to be booming but she often stocks out of key items customers want. The 28-ounce bottle of Super Algaecide (SA) is a high margin SKU, but it stocks out frequently. Ten SA bottles come in each box, and she orders boxes from a vendor 160 miles away. Brenda is busy running the store and seldom has time to review store inventory status and order the right quantity at the right time. She collected the following data: Demand = 9 boxes per week Order cost = $90/order Store open = 48 weeks/year Lead-time = 3 weeks Item cost = $180/box Inventory-holding cost = 10 percent per…arrow_forwardווח CENGAGE MINDTAP G Chapter 09 Excel Activity: Exponential Smoothing Question 1 3.33/10 A e Submit 自 ? G→ Video Excel Online Tutorial Excel Online Activity: Exponential Smoothing ng.cengage.com Q Search this course ? A retail store records customer demand during each sales period. The data has been collected in the Microsoft Excel Online file below. Use the Microsoft Excel Online file below to develop the single exponential smoothing forecast and answer the following questions. X Open spreadsheet Questions 1. What is the forecast for the 13th period based on the single exponential smoothing? Round your answer to two decimal places. 91.01 2. What is the MSE for the single exponential smoothing forecast? Round your answer to two decimal places. 23.50 3. Choose the correct graph for the single exponential smoothing forecast. The correct graph is graph A ☑ Back Observation Exponential Smoothing Forecast 100 Forecast 95 95 90 90 A-Z Office Next A+arrow_forward
 Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,MarketingMarketingISBN:9780357033791Author:Pride, William MPublisher:South Western Educational Publishing
Practical Management ScienceOperations ManagementISBN:9781337406659Author:WINSTON, Wayne L.Publisher:Cengage,MarketingMarketingISBN:9780357033791Author:Pride, William MPublisher:South Western Educational Publishing Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Purchasing and Supply Chain ManagementOperations ManagementISBN:9781285869681Author:Robert M. Monczka, Robert B. Handfield, Larry C. Giunipero, James L. PattersonPublisher:Cengage Learning



