
(a)
Interpretation:
Most acidic proton should be identified in the given compounds.
Concept introduction:
Acidic strength of the molecule depends on the stability of the Conjugate ion.
- Conjugate ion is the ion, which is produced by de protonating the most acidic proton from the molecule.
This conjugate ion stability effected by four factors called ARIO (Atom Resonance Inductive effect Orbital) concept. If the conjugate anion is more stabilized, the acid considered as strong acid and the anion is weak base.
- If negative charge located atom is larger enough to hold the negative charge, the anion attains stability.
- If the anion is resonance stabilized, the corresponding acid is more acidic.
- If withdrawing inductive effect is present near to the negative charge located position, acidity increases.
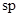 Hybridized orbital stabilizes the negative charge better than other hybridizations.
Hybridized orbital stabilizes the negative charge better than other hybridizations.
To identify: the most acidic proton in the given molecule.
(b)
Interpretation:
Most acidic proton should be identified in the given compounds.
Concept introduction:
Acidic strength of the molecule depends on the stability of the Conjugate ion.
- Conjugate ion is the ion, which is produced by de protonating the most acidic proton from the molecule.
This conjugate ion stability effected by four factors called ARIO (Atom Resonance Inductive effect Orbital) concept. If the conjugate anion is more stabilized, the acid considered as strong acid and the anion is weak base.
- If negative charge located atom is larger enough to hold the negative charge, the anion attains stability.
- If the anion is resonance stabilized, the corresponding acid is more acidic.
- If withdrawing inductive effect is present near to the negative charge located position, acidity increases.
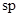 Hybridized orbital stabilizes the negative charge better than other hybridizations.
Hybridized orbital stabilizes the negative charge better than other hybridizations.
To identify: the most acidic proton in the given molecule.
(c)
Interpretation:
Most acidic proton should be identified in the given compounds.
Concept introduction:
Acidic strength of the molecule depends on the stability of the Conjugate ion.
- Conjugate ion is the ion, which is produced by de protonating the most acidic proton from the molecule.
This conjugate ion stability effected by four factors called ARIO (Atom Resonance Inductive effect Orbital) concept. If the conjugate anion is more stabilized, the acid considered as strong acid and the anion is weak base.
- If negative charge located atom is larger enough to hold the negative charge, the anion attains stability.
- If the anion is resonance stabilized, the corresponding acid is more acidic.
- If withdrawing inductive effect is present near to the negative charge located position, acidity increases.
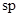 Hybridized orbital stabilizes the negative charge better than other hybridizations.
Hybridized orbital stabilizes the negative charge better than other hybridizations.
To identify: the most acidic proton in the given molecule.
(d)
Interpretation:
Most acidic proton should be identified in the given compounds.
Concept introduction:
Acidic strength of the molecule depends on the stability of the Conjugate ion.
- Conjugate ion is the ion, which is produced by de protonating the most acidic proton from the molecule.
This conjugate ion stability effected by four factors called ARIO (Atom Resonance Inductive effect Orbital) concept. If the conjugate anion is more stabilized, the acid considered as strong acid and the anion is weak base.
- If negative charge located atom is larger enough to hold the negative charge, the anion attains stability.
- If the anion is resonance stabilized, the corresponding acid is more acidic.
- If withdrawing inductive effect is present near to the negative charge located position, acidity increases.
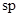 Hybridized orbital stabilizes the negative charge better than other hybridizations.
Hybridized orbital stabilizes the negative charge better than other hybridizations.
To identify: the most acidic proton in the given molecule.
(e)
Interpretation:
Most acidic proton should be identified in the given compounds.
Concept introduction:
Acidic strength of the molecule depends on the stability of the Conjugate ion.
- Conjugate ion is the ion, which is produced by de protonating the most acidic proton from the molecule.
This conjugate ion stability effected by four factors called ARIO (Atom Resonance Inductive effect Orbital) concept. If the conjugate anion is more stabilized, the acid considered as strong acid and the anion is weak base.
- If negative charge located atom is larger enough to hold the negative charge, the anion attains stability.
- If the anion is resonance stabilized, the corresponding acid is more acidic.
- If withdrawing inductive effect is present near to the negative charge located position, acidity increases.
 Hybridized orbital stabilizes the negative charge better than other hybridizations.
Hybridized orbital stabilizes the negative charge better than other hybridizations.
To identify: the most acidic proton in the given molecule.
(f)
Interpretation:
Most acidic proton should be identified in the given compounds.
Concept introduction:
Acidic strength of the molecule depends on the stability of the Conjugate ion.
- Conjugate ion is the ion, which is produced by de protonating the most acidic proton from the molecule.
This conjugate ion stability effected by four factors called ARIO (Atom Resonance Inductive effect Orbital) concept. If the conjugate anion is more stabilized, the acid considered as strong acid and the anion is weak base.
- If negative charge located atom is larger enough to hold the negative charge, the anion attains stability.
- If the anion is resonance stabilized, the corresponding acid is more acidic.
- If withdrawing inductive effect is present near to the negative charge located position, acidity increases.
 Hybridized orbital stabilizes the negative charge better than other hybridizations.
Hybridized orbital stabilizes the negative charge better than other hybridizations.
To identify: the most acidic proton in the given molecule.
(g)
Interpretation:
Most acidic proton should be identified in the given compounds.
Concept introduction:
Acidic strength of the molecule depends on the stability of the Conjugate ion.
- Conjugate ion is the ion, which is produced by de protonating the most acidic proton from the molecule.
This conjugate ion stability effected by four factors called ARIO (Atom Resonance Inductive effect Orbital) concept. If the conjugate anion is more stabilized, the acid considered as strong acid and the anion is weak base.
- If negative charge located atom is larger enough to hold the negative charge, the anion attains stability.
- If the anion is resonance stabilized, the corresponding acid is more acidic.
- If withdrawing inductive effect is present near to the negative charge located position, acidity increases.
 Hybridized orbital stabilizes the negative charge better than other hybridizations.
Hybridized orbital stabilizes the negative charge better than other hybridizations.
To identify: the most acidic proton in the given molecule.
(h)
Interpretation:
Most acidic proton should be identified in the given compounds.
Concept introduction:
Acidic strength of the molecule depends on the stability of the Conjugate ion.
- Conjugate ion is the ion, which is produced by de protonating the most acidic proton from the molecule.
This conjugate ion stability effected by four factors called ARIO (Atom Resonance Inductive effect Orbital) concept. If the conjugate anion is more stabilized, the acid considered as strong acid and the anion is weak base.
- If negative charge located atom is larger enough to hold the negative charge, the anion attains stability.
- If the anion is resonance stabilized, the corresponding acid is more acidic.
- If withdrawing inductive effect is present near to the negative charge located position, acidity increases.
 Hybridized orbital stabilizes the negative charge better than other hybridizations.
Hybridized orbital stabilizes the negative charge better than other hybridizations.
To identify: the most acidic proton in the given molecule.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 3 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY (LL) W/ACCESS
- Propose a synthesis pathway for the following transformations. b) c) d)arrow_forwardThe rate coefficient of the gas-phase reaction 2 NO2 + O3 → N2O5 + O2 is 2.0x104 mol–1 dm3 s–1 at 300 K. Indicate whether the order of the reaction is 0, 1, or 2.arrow_forward8. Draw all the resonance forms for each of the following molecules or ions, and indicate the major contributor in each case, or if they are equivalent. (4.5 pts) (a) PH2 سمةarrow_forward
- 3. Assign absolute configuration (Rors) to each chirality center. a. H Nitz C. он b. 0 H-C. C H 7 C. ་-4 917-417 refs H 1つ ८ ડુ d. Но f. -2- 01 Ho -OH 2HNarrow_forwardHow many signals do you expect in the H NMR spectrum for this molecule? Br Br Write the answer below. Also, in each of the drawing areas below is a copy of the molecule, with Hs shown. In each copy, one of the H atoms is colored red. Highlight in red all other H atoms that would contribute to the same signal as the H already highlighted red. Note for advanced students: In this question, any multiplet is counted as one signal. Number of signals in the 'H NMR spectrum. For the molecule in the top drawing area, highlight in red any other H atoms that will contribute to the same signal as the H atom already highlighted red. If no other H atoms will contribute, check the box at right. No additional Hs to color in top molecule For the molecule in the bottom drawing area, highlight in red any other H atoms that will contribute to the same signal as the H atom already highlighted red. If no other H atoms will contribute, check the box at right. No additional Hs to color in bottom moleculearrow_forwardIn the drawing area below, draw the major products of this organic reaction: 1. NaOH ? 2. CH3Br If there are no major products, because nothing much will happen to the reactant under these reaction conditions, check the box under the drawing area instead. No reaction. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. ☐ : A คarrow_forward
- Predict the major products of the following organic reaction: NC Δ ? Some important Notes: • Draw the major product, or products, of the reaction in the drawing area below. • If there aren't any products, because no reaction will take place, check the box below the drawing area instead. • Be sure to draw bonds carefully to show important geometric relationships between substituents. Note: if your answer contains a complicated ring structure, you must use one of the molecular fragment stamps (available in the menu at right) to enter the ring structure. You can add any substituents using the pencil tool in the usual way. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Х аarrow_forwardPredict the major products of this organic reaction. Be sure you use dash and wedge bonds to show stereochemistry where it's important. + ☑ OH 1. TsCl, py .... 文 P 2. t-BuO K Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forwardConsider this organic reaction: ( Draw the major products of the reaction in the drawing area below. If there won't be any major products, because this reaction won't happen at a significant rate, check the box under the drawing area instead. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Х : а ค 1arrow_forward
- In the drawing area below, draw the major products of this organic reaction: If there are no major products, because nothing much will happen to the reactant under these reaction conditions, check the box under the drawing area instead. 1. NaH 2. CH3Br ? Click and drag to start drawing a structure. No reaction. : ☐ Narrow_forward+ Predict the major product of the following reaction. : ☐ + ☑ ค OH H₂SO4 Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forwardConsider this organic reaction: ... OH CI Draw the major products of the reaction in the drawing area below. If there won't be any major products, because this reaction won't happen at a significant rate, check the box under the drawing area instead. ☐ No Reaction. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. : аarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





