
(a)
Interpretation:
Most acidic proton should be identified in the given compounds.
Concept introduction:
Acidic strength of the molecule depends on the stability of the Conjugate ion.
- Conjugate ion is the ion, which is produced by de protonating the most acidic proton from the molecule.
This conjugate ion stability effected by four factors called ARIO (Atom Resonance Inductive effect Orbital) concept. If the conjugate anion is more stabilized, the acid considered as strong acid and the anion is weak base.
- If negative charge located atom is larger enough to hold the negative charge, the anion attains stability.
- If the anion is resonance stabilized, the corresponding acid is more acidic.
- If withdrawing inductive effect is present near to the negative charge located position, acidity increases.
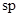 Hybridized orbital stabilizes the negative charge better than other hybridizations.
Hybridized orbital stabilizes the negative charge better than other hybridizations.
To identify: the most acidic proton in the given molecule.
(b)
Interpretation:
Most acidic proton should be identified in the given compounds.
Concept introduction:
Acidic strength of the molecule depends on the stability of the Conjugate ion.
- Conjugate ion is the ion, which is produced by de protonating the most acidic proton from the molecule.
This conjugate ion stability effected by four factors called ARIO (Atom Resonance Inductive effect Orbital) concept. If the conjugate anion is more stabilized, the acid considered as strong acid and the anion is weak base.
- If negative charge located atom is larger enough to hold the negative charge, the anion attains stability.
- If the anion is resonance stabilized, the corresponding acid is more acidic.
- If withdrawing inductive effect is present near to the negative charge located position, acidity increases.
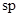 Hybridized orbital stabilizes the negative charge better than other hybridizations.
Hybridized orbital stabilizes the negative charge better than other hybridizations.
To identify: the most acidic proton in the given molecule.
(c)
Interpretation:
Most acidic proton should be identified in the given compounds.
Concept introduction:
Acidic strength of the molecule depends on the stability of the Conjugate ion.
- Conjugate ion is the ion, which is produced by de protonating the most acidic proton from the molecule.
This conjugate ion stability effected by four factors called ARIO (Atom Resonance Inductive effect Orbital) concept. If the conjugate anion is more stabilized, the acid considered as strong acid and the anion is weak base.
- If negative charge located atom is larger enough to hold the negative charge, the anion attains stability.
- If the anion is resonance stabilized, the corresponding acid is more acidic.
- If withdrawing inductive effect is present near to the negative charge located position, acidity increases.
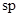 Hybridized orbital stabilizes the negative charge better than other hybridizations.
Hybridized orbital stabilizes the negative charge better than other hybridizations.
To identify: the most acidic proton in the given molecule.
(d)
Interpretation:
Most acidic proton should be identified in the given compounds.
Concept introduction:
Acidic strength of the molecule depends on the stability of the Conjugate ion.
- Conjugate ion is the ion, which is produced by de protonating the most acidic proton from the molecule.
This conjugate ion stability effected by four factors called ARIO (Atom Resonance Inductive effect Orbital) concept. If the conjugate anion is more stabilized, the acid considered as strong acid and the anion is weak base.
- If negative charge located atom is larger enough to hold the negative charge, the anion attains stability.
- If the anion is resonance stabilized, the corresponding acid is more acidic.
- If withdrawing inductive effect is present near to the negative charge located position, acidity increases.
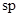 Hybridized orbital stabilizes the negative charge better than other hybridizations.
Hybridized orbital stabilizes the negative charge better than other hybridizations.
To identify: the most acidic proton in the given molecule.
(e)
Interpretation:
Most acidic proton should be identified in the given compounds.
Concept introduction:
Acidic strength of the molecule depends on the stability of the Conjugate ion.
- Conjugate ion is the ion, which is produced by de protonating the most acidic proton from the molecule.
This conjugate ion stability effected by four factors called ARIO (Atom Resonance Inductive effect Orbital) concept. If the conjugate anion is more stabilized, the acid considered as strong acid and the anion is weak base.
- If negative charge located atom is larger enough to hold the negative charge, the anion attains stability.
- If the anion is resonance stabilized, the corresponding acid is more acidic.
- If withdrawing inductive effect is present near to the negative charge located position, acidity increases.
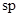 Hybridized orbital stabilizes the negative charge better than other hybridizations.
Hybridized orbital stabilizes the negative charge better than other hybridizations.
To identify: the most acidic proton in the given molecule.
(f)
Interpretation:
Most acidic proton should be identified in the given compounds.
Concept introduction:
Acidic strength of the molecule depends on the stability of the Conjugate ion.
- Conjugate ion is the ion, which is produced by de protonating the most acidic proton from the molecule.
This conjugate ion stability effected by four factors called ARIO (Atom Resonance Inductive effect Orbital) concept. If the conjugate anion is more stabilized, the acid considered as strong acid and the anion is weak base.
- If negative charge located atom is larger enough to hold the negative charge, the anion attains stability.
- If the anion is resonance stabilized, the corresponding acid is more acidic.
- If withdrawing inductive effect is present near to the negative charge located position, acidity increases.
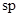 Hybridized orbital stabilizes the negative charge better than other hybridizations.
Hybridized orbital stabilizes the negative charge better than other hybridizations.
To identify: the most acidic proton in the given molecule.
(g)
Interpretation:
Most acidic proton should be identified in the given compounds.
Concept introduction:
Acidic strength of the molecule depends on the stability of the Conjugate ion.
- Conjugate ion is the ion, which is produced by de protonating the most acidic proton from the molecule.
This conjugate ion stability effected by four factors called ARIO (Atom Resonance Inductive effect Orbital) concept. If the conjugate anion is more stabilized, the acid considered as strong acid and the anion is weak base.
- If negative charge located atom is larger enough to hold the negative charge, the anion attains stability.
- If the anion is resonance stabilized, the corresponding acid is more acidic.
- If withdrawing inductive effect is present near to the negative charge located position, acidity increases.
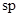 Hybridized orbital stabilizes the negative charge better than other hybridizations.
Hybridized orbital stabilizes the negative charge better than other hybridizations.
To identify: the most acidic proton in the given molecule.
(h)
Interpretation:
Most acidic proton should be identified in the given compounds.
Concept introduction:
Acidic strength of the molecule depends on the stability of the Conjugate ion.
- Conjugate ion is the ion, which is produced by de protonating the most acidic proton from the molecule.
This conjugate ion stability effected by four factors called ARIO (Atom Resonance Inductive effect Orbital) concept. If the conjugate anion is more stabilized, the acid considered as strong acid and the anion is weak base.
- If negative charge located atom is larger enough to hold the negative charge, the anion attains stability.
- If the anion is resonance stabilized, the corresponding acid is more acidic.
- If withdrawing inductive effect is present near to the negative charge located position, acidity increases.
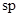 Hybridized orbital stabilizes the negative charge better than other hybridizations.
Hybridized orbital stabilizes the negative charge better than other hybridizations.
To identify: the most acidic proton in the given molecule.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 3 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY LL PRINT UPGRADE
- Synthesize 2-Ethyl-3-methyloxirane from dimethyl(propyl)sulfonium iodide using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize 2-Hydroxy-2-phenylacetonitrile from phenylmethanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardSynthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forward
- Synthesize N-Methylcyclohexylamine from cyclohexanol using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forwardIf possible, please provide the formula of the compound 3,3-dimethylbut-2-enal.arrow_forwardSynthesize 1,4-dibromobenzene from acetanilide (N-phenylacetamide) using the necessary organic or inorganic reagents. Draw the structures of the compounds.arrow_forward
- Indicate the products obtained by mixing (3-oxo-3-phenylpropyl)triphenylphosphonium bromide with sodium hydride.arrow_forwardWe mix N-ethyl-2-hexanamine with excess methyl iodide and followed by heating with aqueous Ag2O. Indicate the major products obtained.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by mixing acetophenone with iodine and NaOH.arrow_forward
- Indicate the products obtained by mixing 2-Propanone and ethyllithium and performing a subsequent acid hydrolysis.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained if (E)-2-butenal and 3-oxo-butanenitrile are mixed with sodium ethoxide in ethanol.arrow_forwardQuestion 3 (4 points), Draw a full arrow-pushing mechanism for the following reaction Please draw all structures clearly. Note that this intramolecular cyclization is analogous to the mechanism for halohydrin formation. COH Br + HBr Brarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





