
(a)
Interpretation:
The element that is highlighted in yellow in the periodic table is present in p area or d area has to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Periodic law states that if the elements are arranged in increasing order of
Location of an element in a periodic table can be given by the period number and the group number. The horizontal row in a periodic table where the elements are present is known as Period. The vertical column in a periodic table where the elements are present is known as Group.
Chemical properties of the elements repeat themselves at regular intervals because of the electronic configuration. The elements that are present in a Group have similar chemical properties. This is because the outer-shell electronic configuration will be the same.
The periodic table has all the elements that can be distinguished based on the outer-shell electron. If the outer-shell electron is present in s subshell, then the elements are present in s area of periodic table. If the outer-shell electron is present in p subshell, then the elements are present in p area of periodic table. If the outer-shell electron is present in d subshell, then the elements are present in d area of periodic table. If the outer-shell electron is present in f subshell, then the elements are present in f area of periodic table.
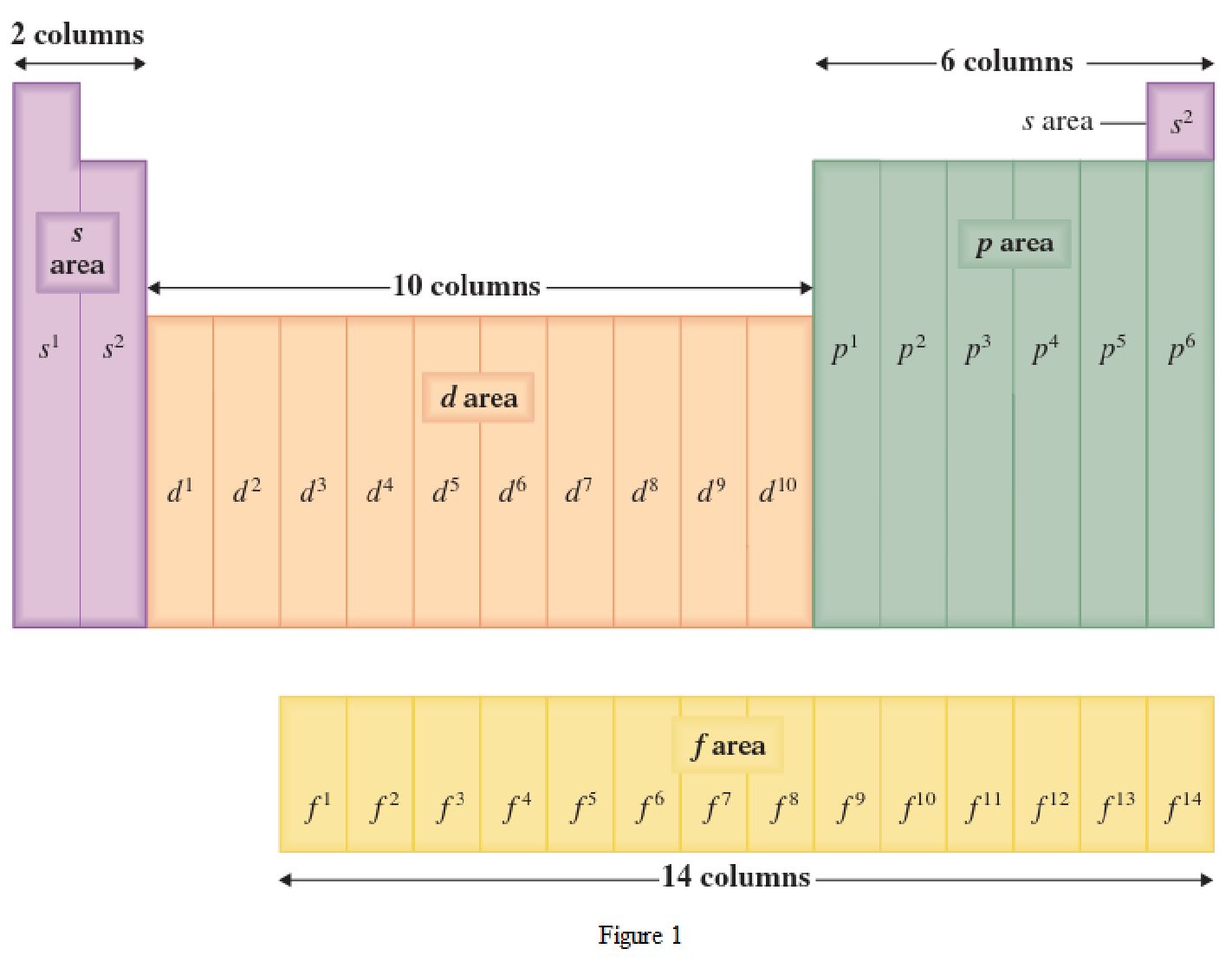
Distinguishing electron is the one that is the last electron added to the electronic configuration of an element when the electron subshells are filled in the order of increasing energy. This distinguishing electron determines the area of the element in the periodic table. This is because this only causes the element electronic configuration to differ from other elements.
(b)
Interpretation:
The element that is highlighted in blue in the periodic table is present in s area or d area has to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Periodic law states that if the elements are arranged in increasing order of atomic number, then the elements with similar chemical properties occur at regular intervals or periodic intervals. The elements are arranged in a periodic table in which the arrangement was based on the atomic number of the elements and the elements that have similar chemical properties are positioned in vertical columns.
Location of an element in a periodic table can be given by the period number and the group number. The horizontal row in a periodic table where the elements are present is known as Period. The vertical column in a periodic table where the elements are present is known as Group.
Chemical properties of the elements repeat themselves at regular intervals because of the electronic configuration. The elements that are present in a Group have similar chemical properties. This is because the outer-shell electronic configuration will be the same.
The periodic table has all the elements that can be distinguished based on the outer-shell electron. If the outer-shell electron is present in s subshell, then the elements are present in s area of periodic table. If the outer-shell electron is present in p subshell, then the elements are present in p area of periodic table. If the outer-shell electron is present in d subshell, then the elements are present in d area of periodic table. If the outer-shell electron is present in f subshell, then the elements are present in f area of periodic table.
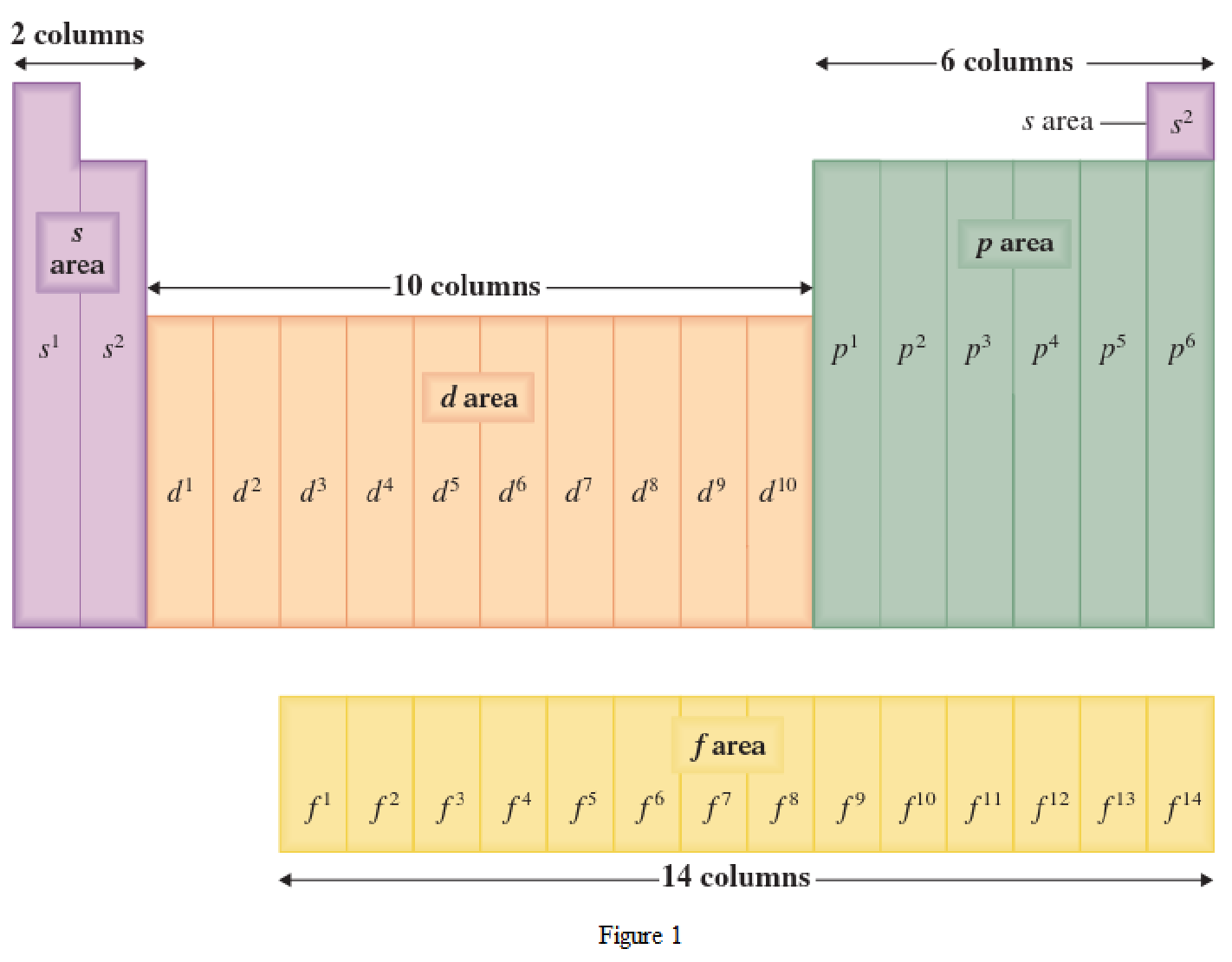
Distinguishing electron is the one that is the last electron added to the electronic configuration of an element when the electron subshells are filled in the order of increasing energy. This distinguishing electron determines the area of the element in the periodic table. This is because this only causes the element electronic configuration to differ from other elements.
(c)
Interpretation:
The element that is highlighted in red in the periodic table is a
Concept Introduction:
Periodic law states that if the elements are arranged in increasing order of atomic number, then the elements with similar chemical properties occur at regular intervals or periodic intervals. The elements are arranged in a periodic table in which the arrangement was based on the atomic number of the elements and the elements that have similar chemical properties are positioned in vertical columns.
Location of an element in a periodic table can be given by the period number and the group number. The horizontal row in a periodic table where the elements are present is known as Period. The vertical column in a periodic table where the elements are present is known as Group.
Chemical properties of the elements repeat themselves at regular intervals because of the electronic configuration. The elements that are present in a Group have similar chemical properties. This is because the outer-shell electronic configuration will be the same.
The periodic table has all the elements that can be distinguished based on the outer-shell electron. If the outer-shell electron is present in s subshell, then the elements are present in s area of periodic table. If the outer-shell electron is present in p subshell, then the elements are present in p area of periodic table. If the outer-shell electron is present in d subshell, then the elements are present in d area of periodic table. If the outer-shell electron is present in f subshell, then the elements are present in f area of periodic table.
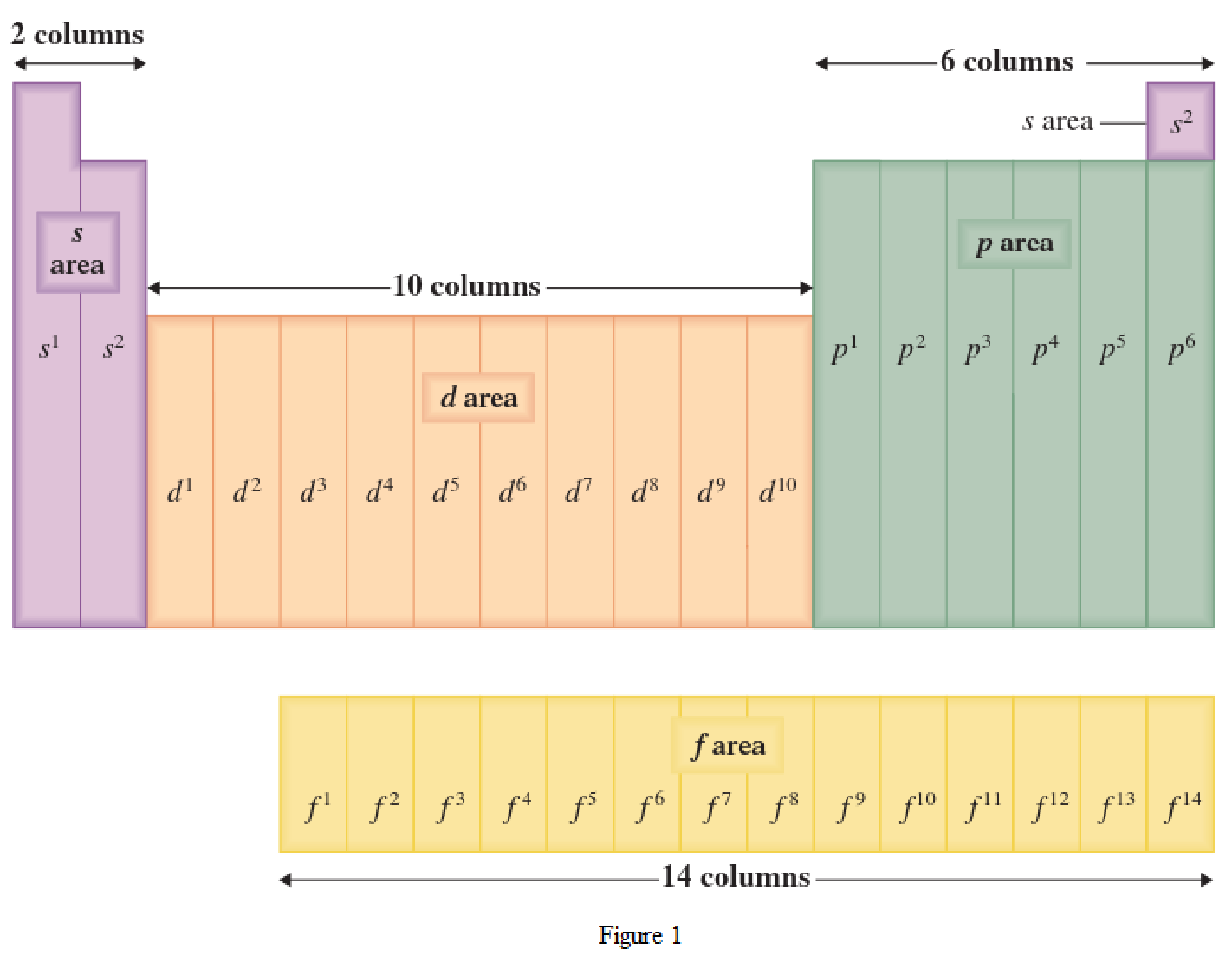
Distinguishing electron is the one that is the last electron added to the electronic configuration of an element when the electron subshells are filled in the order of increasing energy. This distinguishing electron determines the area of the element in the periodic table. This is because this only causes the element electronic configuration to differ from other elements.
(d)
Interpretation:
The element that is highlighted in green in the periodic table is a
Concept Introduction:
Periodic law states that if the elements are arranged in increasing order of atomic number, then the elements with similar chemical properties occur at regular intervals or periodic intervals. The elements are arranged in a periodic table in which the arrangement was based on the atomic number of the elements and the elements that have similar chemical properties are positioned in vertical columns.
Location of an element in a periodic table can be given by the period number and the group number. The horizontal row in a periodic table where the elements are present is known as Period. The vertical column in a periodic table where the elements are present is known as Group.
Chemical properties of the elements repeat themselves at regular intervals because of the electronic configuration. The elements that are present in a Group have similar chemical properties. This is because the outer-shell electronic configuration will be the same.
The periodic table has all the elements that can be distinguished based on the outer-shell electron. If the outer-shell electron is present in s subshell, then the elements are present in s area of periodic table. If the outer-shell electron is present in p subshell, then the elements are present in p area of periodic table. If the outer-shell electron is present in d subshell, then the elements are present in d area of periodic table. If the outer-shell electron is present in f subshell, then the elements are present in f area of periodic table.
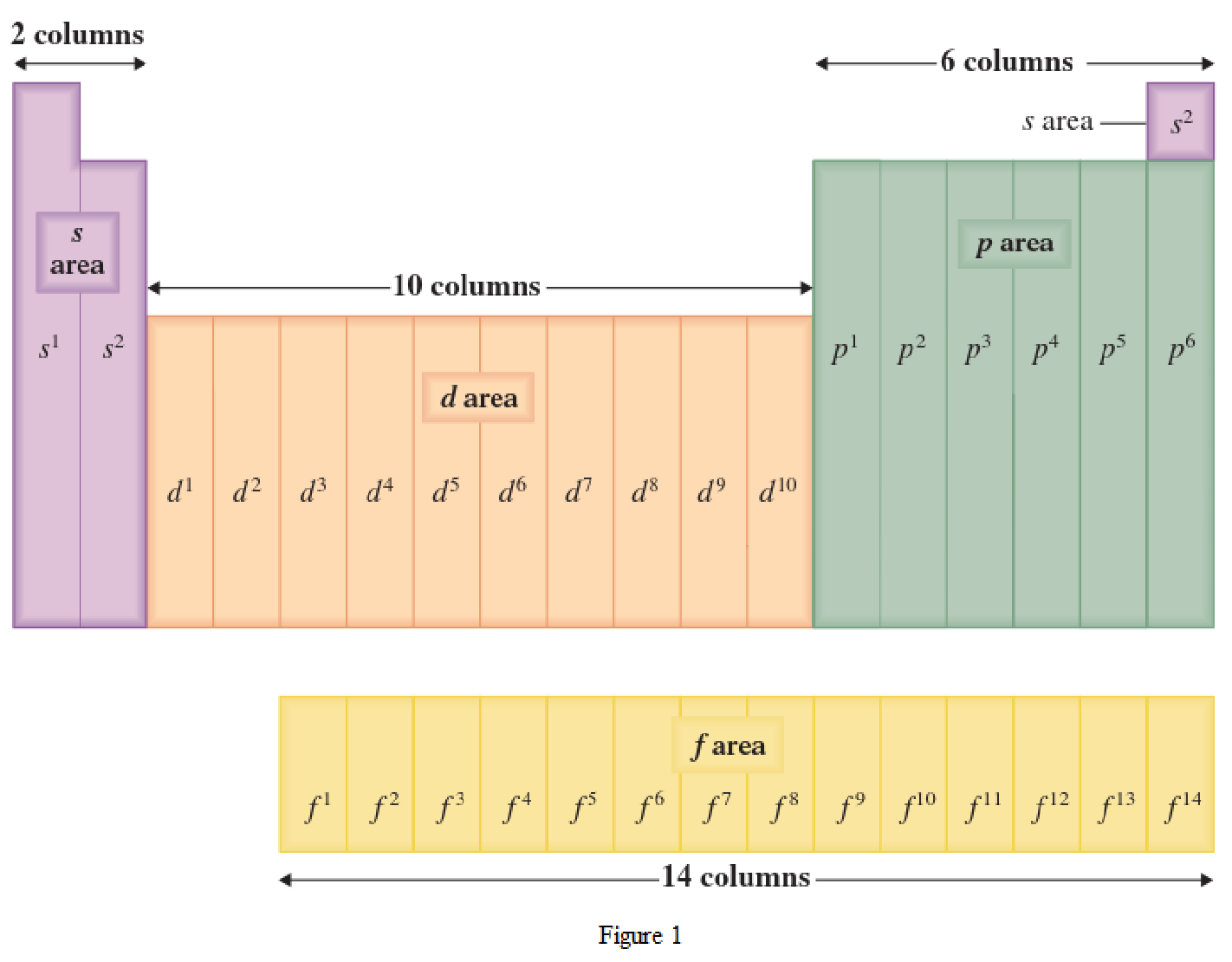
Distinguishing electron is the one that is the last electron added to the electronic configuration of an element when the electron subshells are filled in the order of increasing energy. This distinguishing electron determines the area of the element in the periodic table. This is because this only causes the element electronic configuration to differ from other elements.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 3 Solutions
Study Guide with Selected Solutions for Stoker's General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry, 7th
- 8:16 PM Sun Mar 30 K Draw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Proble 1. CH3MgBr 2. H3O+ F Drawingarrow_forwardо но оarrow_forwardName the major organic product of the following action of 4-chloro-4-methyl-1-pentanol in neutral pollution 10+ Now the product. The product has a molecular formula f b. In a singly hain, the starting, material again converts into a secule with the molecular kormula CIO. but with comply Draw the major organic structure inhalationarrow_forward
- Macmillan Learning Alcohols can be oxidized by chromic acid derivatives. One such reagent is pyridinium chlorochromate, (C,H,NH*)(CICTO3), commonly known as PCC. Draw the proposed (neutral) intermediate and the organic product in the oxidation of 1-butanol by PCC when carried out in an anhydrous solvent such as CH₂C₁₂. PCC Intermediate OH CH2Cl2 Draw the intermediate. Select Draw Templates More с H Cr о Product Draw the product. Erase Select Draw Templates More H о Erasearrow_forwardIf I have 1-bromopropene, to obtain compound A, I have to add NaOH and another compound. Indicate which compound that would be. A C6H5 CH3arrow_forwardProvide the reagents for the following reactions.arrow_forward
- If I have 1-bromopropene, to obtain compound Z, I have to add two compounds A1 and A2. Indicate which compounds are needed. P(C6H5)3arrow_forwardDraw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Assume that the water side product is continuously removed to drive the reaction toward products. O CH3CH2NH2, TSOH Select to Draw >arrow_forwardPredict the major organic product(s) for the following reaction.arrow_forward
- Predict the major organic product(s) for the following reactions.arrow_forwardProvide the complete mechanism for the reactions below. You must include appropriate arrows,intermediates, and formal charges.arrow_forwardIndicate the products obtained by reacting fluorobenzene with a sulfonitric mixture.arrow_forward
 General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning





