
AND gate:
The AND gate is denoted by “AND”, “.” or no symbol. The AND gate is always opposite to the OR gate.

Truth table:
Consider the truth table of AND gate is as follows:
| A | B | C = AB |
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
Here, the Boolean expressions “AB” is equivalent to the expression “A.B” is read “A and B”. The result of the given expression is 1 only when both the inputs are 1, and 0 otherwise.
OR gate:
The OR gate is denoted by “OR” or “+”. The result of OR gate is 0 when both the inputs are 0, otherwise 1.
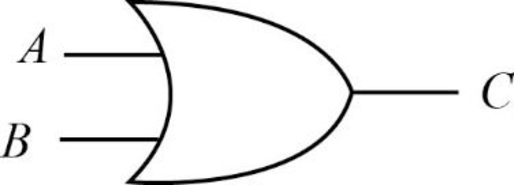
Truth table:
Consider the truth table of OR gate is as follows:
| A | B | C = A+B |
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
Here, the Boolean expressions “A+B” then it is read “A or B”. The result of the given expression is 0 only when both the inputs are 0, and 1 otherwise.
NOT gate:
The NOT gate denoted by negation symbol like “B’”. The result of NOT gate is 0 if the input is 1 and vice versa.
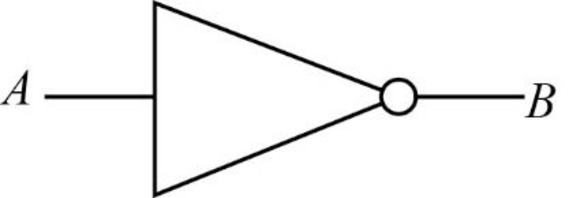
Truth table:
The truth table for NOT gate is given below:
| A | B' |
| 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 |
Here, the “B’” is simply opposite value of the input variable “A”.
Ex-OR gate:
The result of Ex-OR gate will be 1, if any of the input is 0. Otherwise 1.
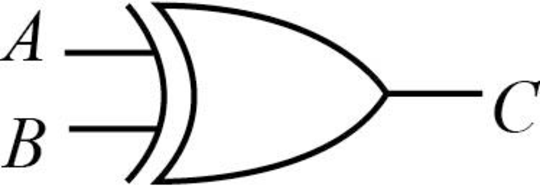
The truth table for XOR gate is given below:
| A | B | C = A |
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 |
Here, the Boolean expression of “A
NAND gate:
The NAND gate is always opposite to the AND gate which means the result of NAND gate is 0 if both inputs are 1, otherwise 0.
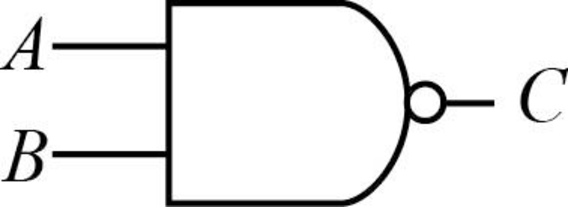
Truth table:
Consider the truth table of NAND gate is as follows:
| A | B | C = (AB)’ |
| 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 |
The result of the given expression is 0 only when both the inputs are 1, and 0 otherwise.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 3 Solutions
Essentials of Computer Organization and Architecture
- Could you help me to know features of the following concepts: - defragmenting. - dynamic disk. - hardware RAIDarrow_forwardwhat is a feature in the Windows Server Security Compliance Toolkit, thank you.arrow_forwardYou will write a program that allows the user to keep track of college locations and details about each location. To begin you will create a College python class that keeps track of the csollege's unique id number, name, address, phone number, maximum students, and average tuition cost. Once you have built the College class, you will write a program that stores College objects in a dictionary while using the College's unique id number as the key. The program should display a menu in this order that lets the user: 1) Add a new College 2) Look up a College 4) Delete an existing College 5) Change an existing College's name, address, phone number, maximum guests, and average tuition cost. 6) Exit the programarrow_forward
- Show all the workarrow_forwardShow all the workarrow_forward[5 marks] Give a recursive definition for the language anb2n where n = 1, 2, 3, ... over the alphabet Ó={a, b}. 2) [12 marks] Consider the following languages over the alphabet ={a ,b}, (i) The language of all words that begin and end an a (ii) The language where every a in a word is immediately followed by at least one b. (a) Express each as a Regular Expression (b) Draw an FA for each language (c) For Language (i), draw a TG using at most 3 states (d) For Language (ii), construct a CFG.arrow_forward
- Question 1 Generate a random sample of standard lognormal data (rlnorm()) for sample size n = 100. Construct histogram estimates of density for this sample using Sturges’ Rule, Scott’s Normal Reference Rule, and the FD Rule. Question 2 Construct a frequency polygon density estimate for the sample in Question 1, using bin width determined by Sturges’ Rule.arrow_forwardGenerate a random sample of standard lognormal data (rlnorm()) for sample size n = 100. Construct histogram estimates of density for this sample using Sturges’ Rule, Scott’s Normal Reference Rule, and the FD Rule.arrow_forwardCan I get help with this case please, thank youarrow_forward
 Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON
Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON
Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON
C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





