
(a)
Interpretation:
Conjugate bases of given acids are needed to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
According to Bronsted-Lowry concept, acid is a proton donor. The deprotonated acids are called conjugate base. The stability of this conjugate base determines the location of deprotonation in an acid.

In a conjugate base where the negative charge is carried by a more electronegative atom will show more stability. The greater electronegativity makes lone pair closer to the nucleus hence more stabilized.
The conjugate base having resonance will have greater stability as compared to conjugate base having single anion. Because of the resonance conjugate base will get resonance stabilization.
(a)
Answer to Problem 37PP
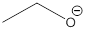
Explanation of Solution
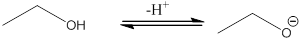
The most acidic proton of the given acid (a) is
(b)
Interpretation:
Conjugate bases of given acids are needed to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
According to Bronsted-Lowry concept, acid is a proton donor. The deprotonated acids are called conjugate base. The stability of this conjugate base determines the location of deprotonation in an acid.

In a conjugate base where the negative charge is carried by a more electronegative atom will show more stability. The greater electronegativity makes lone pair closer to the nucleus hence more stabilized.
The conjugate base having resonance will have greater stability as compared to conjugate base having single anion. Because of the resonance conjugate base will get resonance stabilization.
(b)
Answer to Problem 37PP
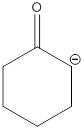
Explanation of Solution
The most acidic hydrogen atom presented in the given acid is
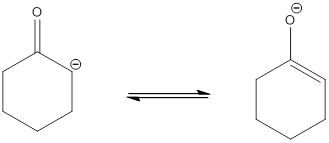 .
.
No other
(c)
Interpretation:
Conjugate bases of given acids are needed to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
According to Bronsted-Lowry concept, acid is a proton donor. The deprotonated acids are called conjugate base. The stability of this conjugate base determines the location of deprotonation in an acid.

In a conjugate base where the negative charge is carried by a more electronegative atom will show more stability. The greater electronegativity makes lone pair closer to the nucleus hence more stabilized.
The conjugate base having resonance will have greater stability as compared to conjugate base having single anion. Because of the resonance conjugate base will get resonance stabilization.
(c)
Answer to Problem 37PP

Explanation of Solution
Deprotonation of
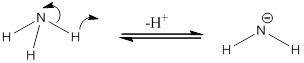
(d)
Interpretation:
Conjugate bases of given acids are needed to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
According to Bronsted-Lowry concept, acid is a proton donor. The deprotonated acids are called conjugate base. The stability of this conjugate base determines the location of deprotonation in an acid.

In a conjugate base where the negative charge is carried by a more electronegative atom will show more stability. The greater electronegativity makes lone pair closer to the nucleus hence more stabilized.
The conjugate base having resonance will have greater stability as compared to conjugate base having single anion. Because of the resonance conjugate base will get resonance stabilization.
(d)
Answer to Problem 37PP
Explanation of Solution
Deprotonation of
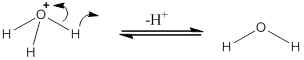
(e)
Interpretation:
Conjugate bases of given acids are needed to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
According to Bronsted-Lowry concept, acid is a proton donor. The deprotonated acids are called conjugate base. The stability of this conjugate base determines the location of deprotonation in an acid.

In a conjugate base where the negative charge is carried by a more electronegative atom will show more stability. The greater electronegativity makes lone pair closer to the nucleus hence more stabilized.
The conjugate base having resonance will have greater stability as compared to conjugate base having single anion. Because of the resonance conjugate base will get resonance stabilization.
(e)
Answer to Problem 37PP
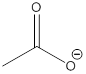
Explanation of Solution
The most acidic proton of the given acid (e) is
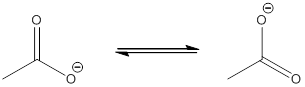
(f)
Interpretation:
Conjugate bases of given acids are needed to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
According to Bronsted-Lowry concept, acid is a proton donor. The deprotonated acids are called conjugate base. The stability of this conjugate base determines the location of deprotonation in an acid.

In a conjugate base where the negative charge is carried by a more electronegative atom will show more stability. The greater electronegativity makes lone pair closer to the nucleus hence more stabilized.
The conjugate base having resonance will have greater stability as compared to conjugate base having single anion. Because of the resonance conjugate base will get resonance stabilization.
(f)
Answer to Problem 37PP
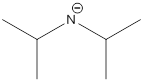
Explanation of Solution
The most acidic proton of the given acid (e) is
(g)
Interpretation:
Conjugate bases of given acids are needed to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
According to Bronsted-Lowry concept, acid is a proton donor. The deprotonated acids are called conjugate base. The stability of this conjugate base determines the location of deprotonation in an acid.

In a conjugate base where the negative charge is carried by a more electronegative atom will show more stability. The greater electronegativity makes lone pair closer to the nucleus hence more stabilized.
The conjugate base having resonance will have greater stability as compared to conjugate base having single anion. Because of the resonance conjugate base will get resonance stabilization.
(g)
Answer to Problem 37PP

Explanation of Solution
Deprotonation of

Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- For each of the substituted benzene molecules below, determine the inductive and resonance effects the substituent will have on the benzene ring, as well as the overall electron-density of the ring compared to unsubstituted benzene. Molecule Inductive Effects O donating O withdrawing O no inductive effects Resonance Effects Overall Electron-Density ○ donating ○ withdrawing O no resonance effects O electron-rich O electron-deficient O similar to benzene Cl O donating O withdrawing ○ donating ○ withdrawing O no inductive effects O no resonance effects O Explanation Check O electron-rich O electron-deficient similar to benzene X © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessarrow_forwardIdentifying electron-donating and For each of the substituted benzene molecules below, determine the inductive and resonance effects the substituent will have on the benzene ring, as well as the overall electron-density of the ring compared to unsubstituted benzene. Molecule Inductive Effects NH2 ○ donating NO2 Explanation Check withdrawing no inductive effects Resonance Effects Overall Electron-Density ○ donating O withdrawing O no resonance effects O donating O withdrawing O donating withdrawing O no inductive effects Ono resonance effects O electron-rich electron-deficient O similar to benzene O electron-rich O electron-deficient O similar to benzene olo 18 Ar 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibilityarrow_forwardRank each of the following substituted benzene molecules in order of which will react fastest (1) to slowest (4) by electrophilic aromatic substitution. Explanation Check Х (Choose one) OH (Choose one) OCH3 (Choose one) OH (Choose one) © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Centerarrow_forward
- Assign R or S to all the chiral centers in each compound drawn below porat bg 9 Br Brarrow_forwarddescrive the energy levels of an atom and howan electron moces between themarrow_forwardRank each set of substituents using the Cahn-Ingold-Perlog sequence rules (priority) by numbering the highest priority substituent 1.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





