
| SMOLIRA GOLF. INC. 2016 Income Statement | |
| Sales | $205,227 |
| Cost of goods sold | 138,383 |
| Depreciation | 5,910 |
| EBIT | $ 60,934 |
| Interest paid | 1,617 |
| Taxable income | $ 59,317 |
| Taxes | 20,760 |
| Net income | $ 38,557 |
| Dividends | $14,300 |
| Additions to |
24,257 |
Calculating Financial Ratios. Find the following financial ratios for Smolira Golf (use year-end figures rather than average values where appropriate):
Short-term solvency ratios
a. Current ratio _____
b. Quick ratio _____
c. Cash ratio _____
Asset utilization ratios
d. Total asset turnover _____
e. Inventory turnover _____
f. Receivables turnover _____
Long-term solvency ratios
g. Total debt ratio _____
h. Debt–equity ratio _____
i. Equity multiplier _____
j. Times interest earned ratio _____
k. Cash coverage ratio _____
Profitability ratios
l. Profit margin _____
m.
n.
a)
To find: The financial ratios of Company SG
Introduction:
The process of analyzing and calculating the financial ratios for the evaluation of the performance of the firm and to find the actions that are necessary to improve the firm’s performance is the ratio analysis.
Explanation:
Given information:
The balance sheet of the Company SG shows the following information:
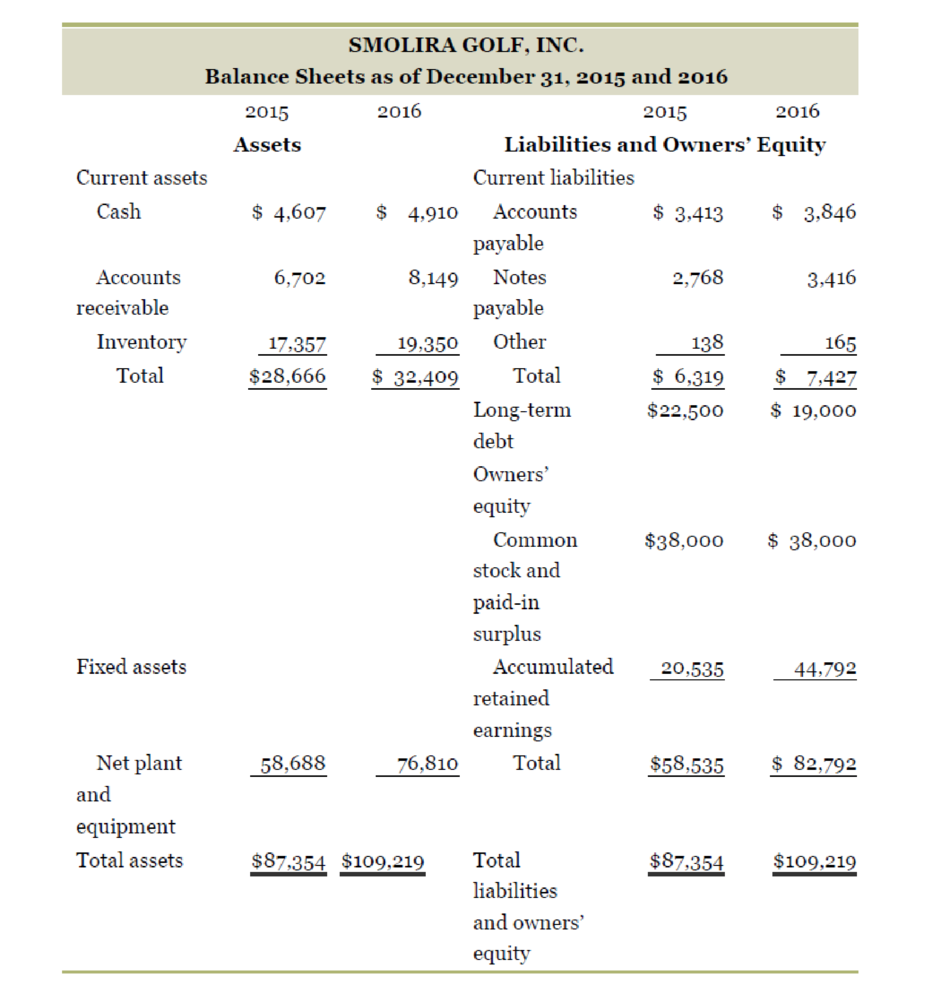
- The total assets for the year 2015 are $87,354 and for 2016 is $109,219.
- The total liabilities and equity for the year 2015 are $87,354 and for 2016 is $109,219.
- The cash at the beginning and end of the year are $4,607 and $4,910 respectively.
- The accounts receivable for the year 2015 and 2016 are $6,702 and $8,149 respectively.
- The inventory for the year 2015 and 2016 are $17,357 and $19,350 respectively.
- The fixed asset for the year 2015 and 2016 are $58,688 and $76,810 respectively.
- The accounts payable for the year 2015 and 2016 are $3,413 and $3,846 respectively.
- The other current liabilities for the year 2015 and 2016 are $138 and $165 respectively.
- The notes payable for the year 2015 and 2016 are $2,768 and $3,416 respectively.
- The long-term debt for the year 2015 and 2016 are $22,500 and $19,000.
- The common stock and paid in surplus for 2015 are $38,000 and for 2016 are $38,000.
- The accumulated retained earnings for 2015 are $20,535 and 2016 are $44,792.
- The net income is $38,557.
- The depreciation is $5,910.
- The dividend paid is $14,300.
- The cost of goods sold amounts to $138,383.
- The sales are $205,227.
- The earnings before interest and taxes are $60,934.
- The interest paid is $1,617.
- The addition to retained earnings is $24,257.
- The taxable income is $59,317.
Explanation of Solution
Formula to calculate the current ratio:
Compute the current ratio:
Hence, the current ratio for 2015 is 4.54 times.
Hence, the current ratio for 2016 is 4.36 times.
b)
To find: The financial ratios of Company SG
Introduction:
The process of analyzing and calculating the financial ratios for the evaluation of the performance of the firm and to find the actions that are necessary to improve the firm’s performance is the ratio analysis.
Explanation:
Given information:
The balance sheet of the Company SG shows the following information:
- The total assets for the year 2015 are $87,354 and for 2016 is $109,219.
- The total liabilities and equity for the year 2015 are $87,354 and for 2016 is $109,219.
- The cash at the beginning and end of the year are $4,607 and $4,910 respectively.
- The accounts receivable for the year 2015 and 2016 are $6,702 and $8,149 respectively.
- The inventory for the year 2015 and 2016 are $17,357 and $19,350 respectively.
- The fixed asset for the year 2015 and 2016 are $58,688 and $76,810 respectively.
- The accounts payable for the year 2015 and 2016 are $3,413 and $3,846 respectively.
- The other current liabilities for the year 2015 and 2016 are $138 and $165 respectively.
- The notes payable for the year 2015 and 2016 are $2,768 and $3,416 respectively.
- The long-term debt for the year 2015 and 2016 are $22,500 and $19,000.
- The common stock and paid in surplus for 2015 are $38,000 and for 2016 are $38,000.
- The accumulated retained earnings for 2015 are $20,535 and 2016 are $44,792.
- The net income is $38,557.
- The depreciation is $5,910.
- The dividend paid is $14,300.
- The cost of goods sold amounts to $138,383.
- The sales are $205,227.
- The earnings before interest and taxes are $60,934.
- The interest paid is $1,617.
- The addition to retained earnings is $24,257.
- The taxable income is $59,317.
Explanation of Solution
Formula to calculate Quick ratio:
Compute the quick ratio:
Hence, the quick ratio for 2015 is 1.79 times.
Hence, the quick ratio for 2016 is 1.76 times.
c)
To find: The financial ratios of Company SG
Introduction:
The process of analyzing and calculating the financial ratios for the evaluation of the performance of the firm and to find the actions that are necessary to improve the firm’s performance is the ratio analysis.
Explanation:
Given information:
The balance sheet of the Company SG shows the following information:
- The total assets for the year 2015 are $87,354 and for 2016 is $109,219.
- The total liabilities and equity for the year 2015 are $87,354 and for 2016 is $109,219.
- The cash at the beginning and end of the year are $4,607 and $4,910 respectively.
- The accounts receivable for the year 2015 and 2016 are $6,702 and $8,149 respectively.
- The inventory for the year 2015 and 2016 are $17,357 and $19,350 respectively.
- The fixed asset for the year 2015 and 2016 are $58,688 and $76,810 respectively.
- The accounts payable for the year 2015 and 2016 are $3,413 and $3,846 respectively.
- The other current liabilities for the year 2015 and 2016 are $138 and $165 respectively.
- The notes payable for the year 2015 and 2016 are $2,768 and $3,416 respectively.
- The long-term debt for the year 2015 and 2016 are $22,500 and $19,000.
- The common stock and paid in surplus for 2015 are $38,000 and for 2016 are $38,000.
- The accumulated retained earnings for 2015 are $20,535 and 2016 are $44,792.
- The net income is $38,557.
- The depreciation is $5,910.
- The dividend paid is $14,300.
- The cost of goods sold amounts to $138,383.
- The sales are $205,227.
- The earnings before interest and taxes are $60,934.
- The interest paid is $1,617.
- The addition to retained earnings is $24,257.
- The taxable income is $59,317.
Explanation of Solution
Formula to calculate the cash ratio:
Compute the cash ratio:
Hence, the cash ratio for 2015 is 0.73 times.
Hence, the cash ratio for 2016 is 0.42 times.
d)
To find: The financial ratios of Company SG
Introduction:
The process of analyzing and calculating the financial ratios for the evaluation of the performance of the firm and to find the actions that are necessary to improve the firm’s performance is the ratio analysis.
Explanation:
Given information:
The balance sheet of the Company SG shows the following information:
- The total assets for the year 2015 are $87,354 and for 2016 is $109,219.
- The total liabilities and equity for the year 2015 are $87,354 and for 2016 is $109,219.
- The cash at the beginning and end of the year are $4,607 and $4,910 respectively.
- The accounts receivable for the year 2015 and 2016 are $6,702 and $8,149 respectively.
- The inventory for the year 2015 and 2016 are $17,357 and $19,350 respectively.
- The fixed asset for the year 2015 and 2016 are $58,688 and $76,810 respectively.
- The accounts payable for the year 2015 and 2016 are $3,413 and $3,846 respectively.
- The other current liabilities for the year 2015 and 2016 are $138 and $165 respectively.
- The notes payable for the year 2015 and 2016 are $2,768 and $3,416 respectively.
- The long-term debt for the year 2015 and 2016 are $22,500 and $19,000.
- The common stock and paid in surplus for 2015 are $38,000 and for 2016 are $38,000.
- The accumulated retained earnings for 2015 are $20,535 and 2016 are $44,792.
- The net income is $38,557.
- The depreciation is $5,910.
- The dividend paid is $14,300.
- The cost of goods sold amounts to $138,383.
- The sales are $205,227.
- The earnings before interest and taxes are $60,934.
- The interest paid is $1,617.
- The addition to retained earnings is $24,257.
- The taxable income is $59,317.
Explanation of Solution
Formula to calculate the total asset turnover ratio:
Compute the total asset turnover ratio:
Hence, the total asset turnover ratio is 1.88 times.
e)
To find: The financial ratios of Company SG
Introduction:
The process of analyzing and calculating the financial ratios for the evaluation of the performance of the firm and to find the actions that are necessary to improve the firm’s performance is the ratio analysis.
Explanation:
Given information:
The balance sheet of the Company SG shows the following information:
- The total assets for the year 2015 are $87,354 and for 2016 is $109,219.
- The total liabilities and equity for the year 2015 are $87,354 and for 2016 is $109,219.
- The cash at the beginning and end of the year are $4,607 and $4,910 respectively.
- The accounts receivable for the year 2015 and 2016 are $6,702 and $8,149 respectively.
- The inventory for the year 2015 and 2016 are $17,357 and $19,350 respectively.
- The fixed asset for the year 2015 and 2016 are $58,688 and $76,810 respectively.
- The accounts payable for the year 2015 and 2016 are $3,413 and $3,846 respectively.
- The other current liabilities for the year 2015 and 2016 are $138 and $165 respectively.
- The notes payable for the year 2015 and 2016 are $2,768 and $3,416 respectively.
- The long-term debt for the year 2015 and 2016 are $22,500 and $19,000.
- The common stock and paid in surplus for 2015 are $38,000 and for 2016 are $38,000.
- The accumulated retained earnings for 2015 are $20,535 and 2016 are $44,792.
- The net income is $38,557.
- The depreciation is $5,910.
- The dividend paid is $14,300.
- The cost of goods sold amounts to $138,383.
- The sales are $205,227.
- The earnings before interest and taxes are $60,934.
- The interest paid is $1,617.
- The addition to retained earnings is $24,257.
- The taxable income is $59,317.
Explanation of Solution
Formula to calculate the inventory turnover ratio:
Compute the inventory turnover ratio:
Hence, the inventory turnover ratio is 7.15 times.
f)
To find: The financial ratios of Company SG
Introduction:
The process of analyzing and calculating the financial ratios for the evaluation of the performance of the firm and to find the actions that are necessary to improve the firm’s performance is the ratio analysis.
Explanation:
Given information:
The balance sheet of the Company SG shows the following information:
- The total assets for the year 2015 are $87,354 and for 2016 is $109,219.
- The total liabilities and equity for the year 2015 are $87,354 and for 2016 is $109,219.
- The cash at the beginning and end of the year are $4,607 and $4,910 respectively.
- The accounts receivable for the year 2015 and 2016 are $6,702 and $8,149 respectively.
- The inventory for the year 2015 and 2016 are $17,357 and $19,350 respectively.
- The fixed asset for the year 2015 and 2016 are $58,688 and $76,810 respectively.
- The accounts payable for the year 2015 and 2016 are $3,413 and $3,846 respectively.
- The other current liabilities for the year 2015 and 2016 are $138 and $165 respectively.
- The notes payable for the year 2015 and 2016 are $2,768 and $3,416 respectively.
- The long-term debt for the year 2015 and 2016 are $22,500 and $19,000.
- The common stock and paid in surplus for 2015 are $38,000 and for 2016 are $38,000.
- The accumulated retained earnings for 2015 are $20,535 and 2016 are $44,792.
- The net income is $38,557.
- The depreciation is $5,910.
- The dividend paid is $14,300.
- The cost of goods sold amounts to $138,383.
- The sales are $205,227.
- The earnings before interest and taxes are $60,934.
- The interest paid is $1,617.
- The addition to retained earnings is $24,257.
- The taxable income is $59,317.
Explanation of Solution
Formula to calculate the receivables turnover ratio:
Compute the receivables turnover ratio:
Hence, the receivables turnover ratio is 25.18 times.
g)
To find: The financial ratios of Company SG
Introduction:
The process of analyzing and calculating the financial ratios for the evaluation of the performance of the firm and to find the actions that are necessary to improve the firm’s performance is the ratio analysis.
Explanation:
Given information:
The balance sheet of the Company SG shows the following information:
- The total assets for the year 2015 are $87,354 and for 2016 is $109,219.
- The total liabilities and equity for the year 2015 are $87,354 and for 2016 is $109,219.
- The cash at the beginning and end of the year are $4,607 and $4,910 respectively.
- The accounts receivable for the year 2015 and 2016 are $6,702 and $8,149 respectively.
- The inventory for the year 2015 and 2016 are $17,357 and $19,350 respectively.
- The fixed asset for the year 2015 and 2016 are $58,688 and $76,810 respectively.
- The accounts payable for the year 2015 and 2016 are $3,413 and $3,846 respectively.
- The other current liabilities for the year 2015 and 2016 are $138 and $165 respectively.
- The notes payable for the year 2015 and 2016 are $2,768 and $3,416 respectively.
- The long-term debt for the year 2015 and 2016 are $22,500 and $19,000.
- The common stock and paid in surplus for 2015 are $38,000 and for 2016 are $38,000.
- The accumulated retained earnings for 2015 are $20,535 and 2016 are $44,792.
- The net income is $38,557.
- The depreciation is $5,910.
- The dividend paid is $14,300.
- The cost of goods sold amounts to $138,383.
- The sales are $205,227.
- The earnings before interest and taxes are $60,934.
- The interest paid is $1,617.
- The addition to retained earnings is $24,257.
- The taxable income is $59,317.
Explanation of Solution
Formula to calculate the total debt ratio:
Compute the total debt ratio:
Hence, the total debt ratio for 2015 is 0.33 times.
Hence, the total debt ratio for 2016 is 0.24 times.
h)
To find: The financial ratios of Company SG
Introduction:
The process of analyzing and calculating the financial ratios for the evaluation of the performance of the firm and to find the actions that are necessary to improve the firm’s performance is the ratio analysis.
Explanation:
Given information:
The balance sheet of the Company SG shows the following information:
- The total assets for the year 2015 are $87,354 and for 2016 is $109,219.
- The total liabilities and equity for the year 2015 are $87,354 and for 2016 is $109,219.
- The cash at the beginning and end of the year are $4,607 and $4,910 respectively.
- The accounts receivable for the year 2015 and 2016 are $6,702 and $8,149 respectively.
- The inventory for the year 2015 and 2016 are $17,357 and $19,350 respectively.
- The fixed asset for the year 2015 and 2016 are $58,688 and $76,810 respectively.
- The accounts payable for the year 2015 and 2016 are $3,413 and $3,846 respectively.
- The other current liabilities for the year 2015 and 2016 are $138 and $165 respectively.
- The notes payable for the year 2015 and 2016 are $2,768 and $3,416 respectively.
- The long-term debt for the year 2015 and 2016 are $22,500 and $19,000.
- The common stock and paid in surplus for 2015 are $38,000 and for 2016 are $38,000.
- The accumulated retained earnings for 2015 are $20,535 and 2016 are $44,792.
- The net income is $38,557.
- The depreciation is $5,910.
- The dividend paid is $14,300.
- The cost of goods sold amounts to $138,383.
- The sales are $205,227.
- The earnings before interest and taxes are $60,934.
- The interest paid is $1,617.
- The addition to retained earnings is $24,257.
- The taxable income is $59,317.
Explanation of Solution
Formula to calculate the debt-equity ratio:
Compute the debt-equity:
Hence, the debt-equity ratio for the year 2015 is 0.49 times.
Hence, the debt-equity ratio for the year 2016 is 0.32 times.
Note: The total debt is calculated by adding the total-long term debt and total current liabilities.
i)
To find: The financial ratios of Company SG
Introduction:
The process of analyzing and calculating the financial ratios for the evaluation of the performance of the firm and to find the actions that are necessary to improve the firm’s performance is the ratio analysis.
Explanation:
Given information:
The balance sheet of the Company SG shows the following information:
- The total assets for the year 2015 are $87,354 and for 2016 is $109,219.
- The total liabilities and equity for the year 2015 are $87,354 and for 2016 is $109,219.
- The cash at the beginning and end of the year are $4,607 and $4,910 respectively.
- The accounts receivable for the year 2015 and 2016 are $6,702 and $8,149 respectively.
- The inventory for the year 2015 and 2016 are $17,357 and $19,350 respectively.
- The fixed asset for the year 2015 and 2016 are $58,688 and $76,810 respectively.
- The accounts payable for the year 2015 and 2016 are $3,413 and $3,846 respectively.
- The other current liabilities for the year 2015 and 2016 are $138 and $165 respectively.
- The notes payable for the year 2015 and 2016 are $2,768 and $3,416 respectively.
- The long-term debt for the year 2015 and 2016 are $22,500 and $19,000.
- The common stock and paid in surplus for 2015 are $38,000 and for 2016 are $38,000.
- The accumulated retained earnings for 2015 are $20,535 and 2016 are $44,792.
- The net income is $38,557.
- The depreciation is $5,910.
- The dividend paid is $14,300.
- The cost of goods sold amounts to $138,383.
- The sales are $205,227.
- The earnings before interest and taxes are $60,934.
- The interest paid is $1,617.
- The addition to retained earnings is $24,257.
- The taxable income is $59,317.
Explanation of Solution
Formula to calculate the equity multiplier:
Compute the equity multiplier ratio for the year 2015:
Hence, the equity multiplier ratio for the year 2015 is 1.49 times.
Hence, the equity multiplier ratio for the year 2016 is 1.32 times.
j)
To find: The financial ratios of Company SG
Introduction:
The process of analyzing and calculating the financial ratios for the evaluation of the performance of the firm and to find the actions that are necessary to improve the firm’s performance is the ratio analysis.
Explanation:
Given information:
The balance sheet of the Company SG shows the following information:
- The total assets for the year 2015 are $87,354 and for 2016 is $109,219.
- The total liabilities and equity for the year 2015 are $87,354 and for 2016 is $109,219.
- The cash at the beginning and end of the year are $4,607 and $4,910 respectively.
- The accounts receivable for the year 2015 and 2016 are $6,702 and $8,149 respectively.
- The inventory for the year 2015 and 2016 are $17,357 and $19,350 respectively.
- The fixed asset for the year 2015 and 2016 are $58,688 and $76,810 respectively.
- The accounts payable for the year 2015 and 2016 are $3,413 and $3,846 respectively.
- The other current liabilities for the year 2015 and 2016 are $138 and $165 respectively.
- The notes payable for the year 2015 and 2016 are $2,768 and $3,416 respectively.
- The long-term debt for the year 2015 and 2016 are $22,500 and $19,000.
- The common stock and paid in surplus for 2015 are $38,000 and for 2016 are $38,000.
- The accumulated retained earnings for 2015 are $20,535 and 2016 are $44,792.
- The net income is $38,557.
- The depreciation is $5,910.
- The dividend paid is $14,300.
- The cost of goods sold amounts to $138,383.
- The sales are $205,227.
- The earnings before interest and taxes are $60,934.
- The interest paid is $1,617.
- The addition to retained earnings is $24,257.
- The taxable income is $59,317.
Explanation of Solution
Formula to calculate the times interest earned ratio:
Compute the times interest earned ratio:
Hence, the times interest earned is 37.68 times.
k)
To find: The financial ratios of Company SG
Introduction:
The process of analyzing and calculating the financial ratios for the evaluation of the performance of the firm and to find the actions that are necessary to improve the firm’s performance is the ratio analysis.
Explanation:
Given information:
The balance sheet of the Company SG shows the following information:
- The total assets for the year 2015 are $87,354 and for 2016 is $109,219.
- The total liabilities and equity for the year 2015 are $87,354 and for 2016 is $109,219.
- The cash at the beginning and end of the year are $4,607 and $4,910 respectively.
- The accounts receivable for the year 2015 and 2016 are $6,702 and $8,149 respectively.
- The inventory for the year 2015 and 2016 are $17,357 and $19,350 respectively.
- The fixed asset for the year 2015 and 2016 are $58,688 and $76,810 respectively.
- The accounts payable for the year 2015 and 2016 are $3,413 and $3,846 respectively.
- The other current liabilities for the year 2015 and 2016 are $138 and $165 respectively.
- The notes payable for the year 2015 and 2016 are $2,768 and $3,416 respectively.
- The long-term debt for the year 2015 and 2016 are $22,500 and $19,000.
- The common stock and paid in surplus for 2015 are $38,000 and for 2016 are $38,000.
- The accumulated retained earnings for 2015 are $20,535 and 2016 are $44,792.
- The net income is $38,557.
- The depreciation is $5,910.
- The dividend paid is $14,300.
- The cost of goods sold amounts to $138,383.
- The sales are $205,227.
- The earnings before interest and taxes are $60,934.
- The interest paid is $1,617.
- The addition to retained earnings is $24,257.
- The taxable income is $59,317.
Explanation of Solution
Formula to calculate the cash coverage ratio:
Compute the cash coverage ratio:
Hence, the cash coverage ratio is 41.34 times.
l)
To find: The financial ratios of Company SG
Introduction:
The process of analyzing and calculating the financial ratios for the evaluation of the performance of the firm and to find the actions that are necessary to improve the firm’s performance is the ratio analysis.
Explanation:
Given information:
The balance sheet of the Company SG shows the following information:
- The total assets for the year 2015 are $87,354 and for 2016 is $109,219.
- The total liabilities and equity for the year 2015 are $87,354 and for 2016 is $109,219.
- The cash at the beginning and end of the year are $4,607 and $4,910 respectively.
- The accounts receivable for the year 2015 and 2016 are $6,702 and $8,149 respectively.
- The inventory for the year 2015 and 2016 are $17,357 and $19,350 respectively.
- The fixed asset for the year 2015 and 2016 are $58,688 and $76,810 respectively.
- The accounts payable for the year 2015 and 2016 are $3,413 and $3,846 respectively.
- The other current liabilities for the year 2015 and 2016 are $138 and $165 respectively.
- The notes payable for the year 2015 and 2016 are $2,768 and $3,416 respectively.
- The long-term debt for the year 2015 and 2016 are $22,500 and $19,000.
- The common stock and paid in surplus for 2015 are $38,000 and for 2016 are $38,000.
- The accumulated retained earnings for 2015 are $20,535 and 2016 are $44,792.
- The net income is $38,557.
- The depreciation is $5,910.
- The dividend paid is $14,300.
- The cost of goods sold amounts to $138,383.
- The sales are $205,227.
- The earnings before interest and taxes are $60,934.
- The interest paid is $1,617.
- The addition to retained earnings is $24,257.
- The taxable income is $59,317.
Explanation of Solution
Formula to calculate the profit margin ratio:
Compute the profit margin:
Hence, the profit margin is 18.79%.
m)
To find: The financial ratios of Company SG
Introduction:
The process of analyzing and calculating the financial ratios for the evaluation of the performance of the firm and to find the actions that are necessary to improve the firm’s performance is the ratio analysis.
Explanation:
Given information:
The balance sheet of the Company SG shows the following information:
- The total assets for the year 2015 are $87,354 and for 2016 is $109,219.
- The total liabilities and equity for the year 2015 are $87,354 and for 2016 is $109,219.
- The cash at the beginning and end of the year are $4,607 and $4,910 respectively.
- The accounts receivable for the year 2015 and 2016 are $6,702 and $8,149 respectively.
- The inventory for the year 2015 and 2016 are $17,357 and $19,350 respectively.
- The fixed asset for the year 2015 and 2016 are $58,688 and $76,810 respectively.
- The accounts payable for the year 2015 and 2016 are $3,413 and $3,846 respectively.
- The other current liabilities for the year 2015 and 2016 are $138 and $165 respectively.
- The notes payable for the year 2015 and 2016 are $2,768 and $3,416 respectively.
- The long-term debt for the year 2015 and 2016 are $22,500 and $19,000.
- The common stock and paid in surplus for 2015 are $38,000 and for 2016 are $38,000.
- The accumulated retained earnings for 2015 are $20,535 and 2016 are $44,792.
- The net income is $38,557.
- The depreciation is $5,910.
- The dividend paid is $14,300.
- The cost of goods sold amounts to $138,383.
- The sales are $205,227.
- The earnings before interest and taxes are $60,934.
- The interest paid is $1,617.
- The addition to retained earnings is $24,257.
- The taxable income is $59,317.
Explanation of Solution
Formula to calculate the Return on assets (ROA):
Compute the Return on assets (ROA):
Hence, the return on assets is 35.30%.
n)
To find: The financial ratios of Company SG
Introduction:
The process of analyzing and calculating the financial ratios for the evaluation of the performance of the firm and to find the actions that are necessary to improve the firm’s performance is the ratio analysis.
Explanation:
Given information:
The balance sheet of the Company SG shows the following information:
- The total assets for the year 2015 are $87,354 and for 2016 is $109,219.
- The total liabilities and equity for the year 2015 are $87,354 and for 2016 is $109,219.
- The cash at the beginning and end of the year are $4,607 and $4,910 respectively.
- The accounts receivable for the year 2015 and 2016 are $6,702 and $8,149 respectively.
- The inventory for the year 2015 and 2016 are $17,357 and $19,350 respectively.
- The fixed asset for the year 2015 and 2016 are $58,688 and $76,810 respectively.
- The accounts payable for the year 2015 and 2016 are $3,413 and $3,846 respectively.
- The other current liabilities for the year 2015 and 2016 are $138 and $165 respectively.
- The notes payable for the year 2015 and 2016 are $2,768 and $3,416 respectively.
- The long-term debt for the year 2015 and 2016 are $22,500 and $19,000.
- The common stock and paid in surplus for 2015 are $38,000 and for 2016 are $38,000.
- The accumulated retained earnings for 2015 are $20,535 and 2016 are $44,792.
- The net income is $38,557.
- The depreciation is $5,910.
- The dividend paid is $14,300.
- The cost of goods sold amounts to $138,383.
- The sales are $205,227.
- The earnings before interest and taxes are $60,934.
- The interest paid is $1,617.
- The addition to retained earnings is $24,257.
- The taxable income is $59,317.
Explanation of Solution
Formulae to calculate the Return on equity (ROE):
Compute the Return on equity (ROE):
Hence, the return on equity is 0.4657 or 46.57%.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
ESSENTIALS CORPORATE FINANCE + CNCT A.
- The continuous conditional probability density function pc(S, t; S', t') for a risk neutral lognormal random walk is given by Pc(S, t; S', t') = 1 σS'√2π(t' - t) - (log(S/S) (ro²)(t − t)] exp 202 (t't) In the binomial method, the value of the underlying is Sm at time step môt and the value of the underlying at time step (m + 1)St is Sm+1. For this case evaluate Ec[(Sm+1)k|Sm] = [°° (S')*pc(S™, mdt; S', (m + 1)8t)dS' showing all steps, where k is a positive integer with k ≥ 1. You may assume that 1 e (x-n)2 2s2dx = 1 for all real numbers n and s with s > 0.arrow_forwardJohn and Jane Doe, a married couple filing jointly, have provided you with their financial information for the year, including details of federal income tax withheld. They need assistance in preparing their tax return. W-2 Income: John earns $150,000 with $35,000 withheld for federal income tax. Jane earns $85,000 with $15,500 withheld for federal income tax. Interest Income: They received $2500 in interest from a savings account, with no tax withheld. Child Tax Credit: They have two children under the age of 17. Mortgage Interest: Paid $28,000 in mortgage interest on their primary residence. Property Taxes: Paid $4,800 in property taxes on their primary residence. Charitable Donations: Donated $22,000 to qualifying charitable organizations. Other Deductions: They have no other deductions to claim. You will gather the appropriate information and complete the forms provided in Blackboard (1040, Schedule A, and Schedule B in preparation of their tax file.arrow_forwardOn the issue date, you bought a 20-year maturity, 5.85% semi-annual coupon bond. The bond then sold at YTM of 6.25%. Now, 5 years later, the similar bond sells at YTM of 5.25%. If you hold the bond now, what is your realized rate of return for the 5-year holding period?arrow_forward
- Bond Valuation with Semiannual Payments Renfro Rentals has issued bonds that have an 11% coupon rate, payable semiannually. The bonds mature in 17 years, have a face value of $1,000, and a yield to maturity of 9.5%. What is the price of the bonds? Round your answer to the nearest cent.arrow_forwardanalyze at least three financial banking products from both the liability side (like time deposits, fixed income, stocks, structure products, etc). You will need to examine aspects such as liquidity, risk, and profitability from a company and an individual point of view.arrow_forwardHow a does researcher ensure that consulting recommendations are data-driven? What does make it effective, and sustainable? Please help explain and give the example How does DMAC help researchers to improve their business processes? How to establish feedback loops for ongoing refinement. Please give the examplesarrow_forward
- Could you please help to explain the DMAIC phases and how a researcher would use them to conduct a consulting project? What is a measure process performance and how to analyze the process? What is an improve process performance and how the control improves process and future process performance?arrow_forwardConsider the two stocks below. Graph the frontier of combinations of the two stocks. Show the effect on the frontier of varying the correlation from −1 to +1. 1 2 3 Mean A B C D TWO STOCKS Varying the correlation coefficient Stock A Stock B 3.00% 8.00% 4 Sigma 15.00% 22.00% 5 Correlation 0.3000 Farrow_forwardLindsay is 30 years old and has a new job in web development. She wants to make sure that she is financially sound by the age of 55, so she plans to invest the same amount into a retirement account at the end of every year for the next 25 years. (a) Construct a data table in Excel that will show Lindsay the balance of her retirement account for various levels of annual investment and return. If Lindsay invests $10,000 at return of 6%, what would be the balance at the end of the 25th year? Note that because Lindsay invests at the end of the year, there is no interest earned on the contribution for the year in which she contributes. Round your answer to a whole dollar amount. $ (b) Develop a two-way table for annual investment amounts of $5,000 to $20,000 in increments of $1,000 and for returns of 0% to 12% in increments of 1%. From the 2-way table, what are the minimum annual investments Lindsay must contribute for annual rates ranging from 6% to 11%, if she wants to…arrow_forward
 Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Accounting: The Cornerstone of Busines...AccountingISBN:9781337115773Author:Maryanne M. Mowen, Don R. Hansen, Dan L. HeitgerPublisher:Cengage Learning

