
Concept explainers
The Signage Company specializes in the maintenance and repair of signs, such as billboards. On March 31, 2019, the accountant for The Signage Company prepared the
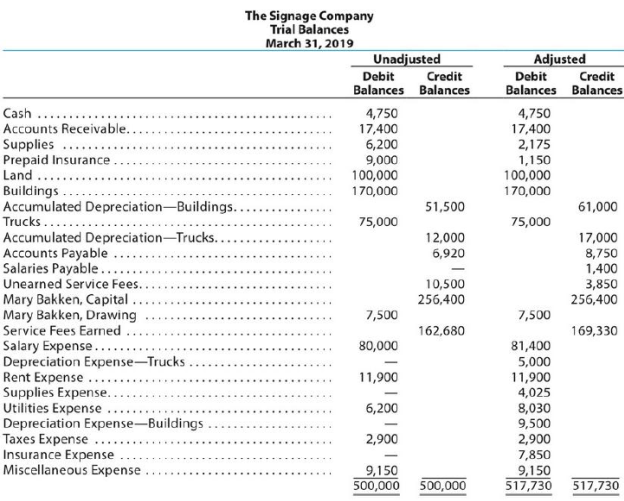
Instructions
Journalize the seven entries that adjusted the accounts at March 31. None of the accounts were affected by more than one adjusting entry.
Adjusting entries:
Adjusting entries refers to the entries that are made at the end of an accounting period in accordance with revenue recognition principle, and expenses recognition principle. All adjusting entries affect at least one income statement account (revenue or expense), and one balance sheet account (asset or liability).
Rules of Debit and Credit:
Following rules are followed for debiting and crediting different accounts while they occur in business transactions:
Ø Debit, all increase in assets, expenses and dividends, all decrease in liabilities, revenues and owner’s equities.
Ø Credit, all increase in liabilities, revenues, and owners’ equities, all decrease in assets, expenses.
To prepare: The adjusting entries in the books of Company S at the end of the year.
Answer to Problem 3.4BPR
An adjusting entry for Supplies expenses:
In this case, Company S recognized the supplies expenses at the end of the year. So, the necessary adjusting entry that the Company S should record to recognize the supplies expense is as follows:
| Date | Description |
Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| 2019 | Supplies expenses (1) | 4,025 | |||
| March | 31 | Supplies | 4,025 | ||
| (To record the supplies expenses incurred at the end of the year) | |||||
Table (1)
Explanation of Solution
Working note:
Calculate the value of supplies expense
Explanation:
- Supplies expense decreased the value of owner’s equity by $4,025; hence debit the supplies expenses for $4,025.
- Supplies are an asset, and it decreased the value of asset by $4,025, hence credit the supplies for $4,025.
An adjusting entry for insurance expenses:
In this case, Company S recognized the insurance expenses at the end of the year. So, the necessary adjusting entry that the Company S should record to recognize the prepaid expense is as follows:
| Date | Description |
Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| 2019 | Insurance expenses (2) | 7,850 | |||
| March | 31 | Prepaid insurance | 7,850 | ||
| (To record the insurance expenses incurred at the end of the year) | |||||
Table (2)
Working note:
Calculate the value of insurance expense
Explanation:
- Insurance expense decreased the value of owner’s equity by $7,850; hence debit the insurance expenses for $7,850.
- Prepaid insurance is an asset, and it decreased the value of asset by $7,850, hence credit the prepaid insurance for $7,850.
An adjusting entry for depreciation expenses-Buildings:
In this case, Company S recognized the depreciation expenses on buildings at the end of the year. So, the necessary adjusting entry that the Company S should record to recognize the accrued expense is as follows:
| Date | Description |
Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| 2019 | Depreciation expenses –Buildings (3) | 9,500 | |||
| March | 31 | Accumulated depreciation-Buildings | 9,500 | ||
| (To record the depreciation expenses incurred at the end of the year) | |||||
Table (3)
Working note:
Calculate the value of depreciation expense-Equipment
Explanation:
- Depreciation expense decreased the value of owner’s equity by $9,500; hence debit the depreciation expenses for $9,500.
- Accumulated depreciation is a contra-asset account, and it decreased the value of asset by $9,500, hence credit the accumulated depreciation for $9,500.
An adjusting entry for depreciation expenses-Trucks:
In this case, Company S recognized the depreciation expenses on trucks at the end of the year. So, the necessary adjusting entry that the Company S should record to recognize the accrued expense is as follows:
| Date | Description |
Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| 2019 | Depreciation expenses –Trucks(4) | 5,000 | |||
| March | 31 | Accumulated depreciation-Trucks | 5,000 | ||
| (To record the depreciation expenses incurred at the end of the year) | |||||
Table (4)
Working note:
Calculate the value of depreciation expense-Trucks
Explanation:
- Depreciation expense decreased the value of owner’s equity by $5,000; hence debit the depreciation expenses for $5,000.
- Accumulated depreciation is a contra-asset account, and it decreased the value of asset by $5,000, hence credit the accumulated depreciation for $5,000.
An adjusting entry for utilities expenses:
In this case, Company S recognized the utilities expenses at the end of the year. So, the necessary adjusting entry that the Company S should record to recognize the accrued expense is as follows:
| Date | Description |
Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| 2019 | Utilities expenses (5) | 1,830 | |||
| March | 31 | Accounts payable | 1,830 | ||
| (To record the utilities expenses incurred at the end of the year) | |||||
Table (5)
Working note:
Calculate the value of utilities expense
Explanation:
- Utilities expense decreased the value of owner’s equity by $1,830; hence debit the utilities expenses for $1,830.
- Accounts payable is a liability, and it increased the value of liability by $1,830, hence credit the accounts payable for $1,830.
An adjusting entry for salaries expenses:
In this case, Company S recognized the salaries expenses at the end of the year. So, the necessary adjusting entry that the Company S should record to recognize the accrued expense is as follows:
| Date | Description |
Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| 2019 | Salaries expenses (6) | 1,400 | |||
| March | 31 | Salaries payable | 1,400 | ||
| (To record the salaries expenses incurred at the end of the year) | |||||
Table (6)
Working note:
Calculate the value of salaries expense
Explanation:
- Salaries expense decreased the value of owner’s equity by $1,400; hence debit the salaries expenses for $1,400.
- Salaries payable is a liability, and it increased the value of liability by $1,400, hence credit the salaries payable for $1,400.
An adjusting entry for unearned service fees:
In this case, Company S received cash in advance before the service provided to customer. So, the necessary adjusting entry that the Company S should record for the unearned fees revenue at the end of the year is as follows:
| Date | Description |
Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| 2019 | Unearned service fees | 6,650 | |||
| March | 31 | Service fees earned (7) | 6,650 | ||
| (To record the unearned service fees at the end of the year) | |||||
Table (7)
Working note:
Calculate the value of service fees earned
Explanation:
- Unearned service fees are a liability, and it decreased the value of liability by $6,650, hence debit the unearned service fees for $6,650.
- Service fees earned increased owner’s equity by $6,650; hence credit the service fees earned for $6,650.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Accounting
- I am looking for the correct answer to this general accounting problem using valid accounting standards.arrow_forwardRahul Consulting Services expects its consultants to work 25,000 direct labor hours per year. The company's estimated total indirect costs are $350,000. The direct labor rate is $95 per hour. The company uses direct labor hours as the allocation base for indirect costs. If Rahul performs a job requiring 40 hours of direct labor, what is the total job cost?arrow_forwardCan you help me solve this general accounting question using the correct accounting procedures?arrow_forward
- Calculate the ending balance of the accountarrow_forwardHems worth Electronics company has a beginning finished goods inventory of $24,500, raw material purchases of $35,600, cost of goods manufactured of $42,800, and an ending finished goods inventory of$27,300. The cost of goods sold for this company is?arrow_forwardWhich of the following is an example of an accrual accounting principle?a) Revenue is recognized when cash is receivedb) Revenue is recognized when it is earned, not when cash is receivedc) Expenses are recognized when paidd) Revenue and expenses are recorded only at year-endarrow_forward
- I am searching for the accurate solution to this financial accounting problem with the right approach.arrow_forwardBergen Corporation has an employee earning $8,400 per month. The FICA tax rate for Social Security is 6.2%, and the FICA tax rate for Medicare is 1.45%. The current FUTA tax rate is 0.6%, and the SUTA tax rate is 5.2%. Both unemployment taxes are applied to the first $7,000 of an employee's pay. The employee has $320 in federal income taxes withheld. The employee also has voluntary deductions for health insurance of $245 and contributes $180 to a retirement plan each month. What is the employee's net pay for the month of January?arrow_forwardCan you demonstrate the proper approach for solving this financial accounting question with valid techniques?arrow_forward
 Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning- Century 21 Accounting Multicolumn JournalAccountingISBN:9781337679503Author:GilbertsonPublisher:Cengage
 Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,





