
Concept explainers
Good Note Company specializes in the repair of music equipment and is owned and operated by Robin Stahl. On November 30, 2019, the end of the current year, the accountant for Good Note prepared the following
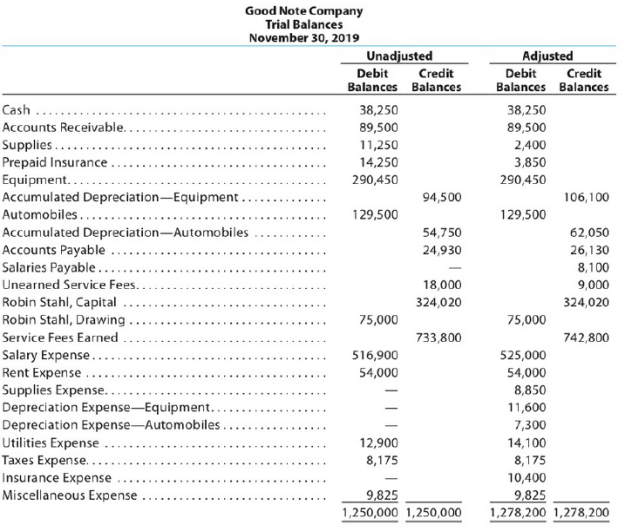
Instructions
Journalize the seven entries that adjusted the accounts at November 30. None of the accounts were affected by more than one adjusting entry.
Adjusting entries:
Adjusting entries refers to the entries that are made at the end of an accounting period in accordance with revenue recognition principle, and expenses recognition principle. All adjusting entries affect at least one income statement account (revenue or expense), and one balance sheet account (asset or liability).
Rules of Debit and Credit:
Following rules are followed for debiting and crediting different accounts while they occur in business transactions:
Ø Debit, all increase in assets, expenses and dividends, all decrease in liabilities, revenues and stockholders’ equities.
Ø Credit, all increase in liabilities, revenues, and stockholders’ equities, all decrease in assets, expenses.
To prepare: The adjusting entries in the books of Company GN at the end of the year.
Answer to Problem 3.4APR
An adjusting entry for Supplies expenses:
In this case, Company GN recognized the supplies expenses at the end of the year. So, the necessary adjusting entry that the Company GN should record to recognize the supplies expense is as follows:
| Date | Description |
Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| 2019 | Supplies expenses (1) | 8,850 | |||
| November | 30 | Supplies | 8,850 | ||
| (To record the supplies expenses incurred at the end of the year) | |||||
Table (1)
Explanation of Solution
Working note:
Calculate the value of supplies expense
Explanation:
- Supplies expense decreases the value of owner’s equity by $8,850; hence debit the supplies expenses for $8,850.
- Supplies are an asset, and it decreases the value of asset by $8,850, hence credit the supplies for $8,850.
An adjusting entry for insurance expenses:
In this case, Company GN recognized the insurance expenses at the end of the year. So, the necessary adjusting entry that the Company GN should record to recognize the prepaid expense is as follows:
| Date | Description |
Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| 2019 | Insurance expenses (2) | 10,400 | |||
| November | 30 | Prepaid insurance | 10,400 | ||
| (To record the insurance expenses incurred at the end of the year) | |||||
Table (2)
Working note:
Calculate the value of insurance expense
Explanation:
- Insurance expense decreases the value of owner’s equity by $10,400; hence debit the insurance expenses for $10,400.
- Prepaid insurance is an asset, and it decreases the value of asset by $10,400, hence credit the prepaid insurance for $10,400.
An adjusting entry for depreciation expenses-Equipment:
In this case, Company GN recognized the depreciation expenses on equipment at the end of the year. So, the necessary adjusting entry that the Company GN should record to recognize the accrued expense is as follows:
| Date | Description |
Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| 2019 | Depreciation expenses –Equipment (3) | 11,600 | |||
| November | 30 | Accumulated depreciation-Equipment | 11,600 | ||
| (To record the depreciation expenses incurred at the end of the year) | |||||
Table (3)
Working note:
Calculate the value of depreciation expense-Equipment
Explanation:
- Depreciation expense decreases the value of owner’s equity by $11,600; hence debit the depreciation expenses for $11,600.
- Accumulated depreciation is a contra-asset account, and it decreases the value of asset by $11,600, hence credit the accumulated depreciation for $11,600.
An adjusting entry for depreciation expenses-Automobiles:
In this case, Company GN recognized the depreciation expenses on automobiles at the end of the year. So, the necessary adjusting entry that the Company GN should record to recognize the accrued expense is as follows:
| Date | Description |
Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| 2019 | Depreciation expenses –Automobiles (4) | 7,300 | |||
| November | 30 | Accumulated depreciation-Automobiles | 7,300 | ||
| (To record the depreciation expenses incurred at the end of the year) | |||||
Table (4)
Working note:
Calculate the value of depreciation expense-Automobiles
Explanation:
- Depreciation expense decreases the value of owner’s equity by $7,300; hence debit the depreciation expenses for $7,300.
- Accumulated depreciation is a contra-asset account, and it decreases the value of asset by $7,300, hence credit the accumulated depreciation for $7,300.
An adjusting entry for utilities expenses:
In this case, Company GN recognized the utilities expenses at the end of the year. So, the necessary adjusting entry that the Company GN should record to recognize the accrued expense is as follows:
| Date | Description |
Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| 2019 | Utilities expenses (5) | 1,200 | |||
| November | 30 | Accounts payable | 1,200 | ||
| (To record the utilities expenses incurred at the end of the year) | |||||
Table (5)
Working note:
Calculate the value of utilities expense
Explanation:
- Utilities expense decreases the value of owner’s equity by $1,200; hence debit the utilities expenses for $1,200.
- Accounts payable is a liability, and it increases the value of liability by $1,200, hence credit the accounts payable for $1,200.
An adjusting entry for salaries expenses:
In this case, Company GN recognized the salaries expenses at the end of the year. So, the necessary adjusting entry that the Company GN should record to recognize the accrued expense is as follows:
| Date | Description |
Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| 2019 | Salaries expenses (6) | 8,100 | |||
| November | 30 | Salaries payable | 8,100 | ||
| (To record the salaries expenses incurred at the end of the year) | |||||
Table (6)
Working note:
Calculate the value of salaries expense
Explanation:
- Salaries expense decreases the value of owner’s equity by $8,100; hence debit the salaries expenses for $8,100.
- Salaries payable is a liability, and it increases the value of liability by $8,100, hence credit the salaries payable for $8,100.
An adjusting entry for unearned service fees:
In this case, Company GN received cash in advance before the service provided to customer. So, the necessary adjusting entry that the Company GN should record for the unearned fees revenue at the end of the year is as follows:
| Date | Description |
Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| 2019 | Unearned service fees | 9,000 | |||
| November | 30 | Service fees earned (7) | 9,000 | ||
| (To record the unearned service fees at the end of the year) | |||||
Table (7)
Working note:
Calculate the value of service fees earned
Explanation:
- Unearned service fees are a liability, and it decreases the value of liability by $9,000, hence debit the unearned service fees for $9,000.
- Service fees earned increases owner’s equity by $9,000; hence credit the service fees earned for $9,000.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Accounting
- Can you explain the correct methodology to solve this financial accounting problem?arrow_forwardCan you help me solve this general accounting problem with the correct methodology?arrow_forwardPlease provide the solution to this general accounting question using proper accounting principles.arrow_forward
- Please provide the correct answer to this general accounting problem using accurate calculations.arrow_forwardI need help with this financial accounting question using standard accounting techniques.arrow_forwardI need help with this general accounting question using standard accounting techniques.arrow_forward
- I am trying to find the accurate solution to this financial accounting problem with the correct explanation.arrow_forwardPlease help me solve this financial accounting question using the right financial principles.arrow_forwardPlease explain the solution to this financial accounting problem with accurate explanations.arrow_forward
- Please explain the correct approach for solving this financial accounting question.arrow_forwardPlease provide the answer to this financial accounting question with proper steps.arrow_forwardI am searching for the correct answer to this financial accounting problem with proper accounting rules.arrow_forward
- Century 21 Accounting Multicolumn JournalAccountingISBN:9781337679503Author:GilbertsonPublisher:Cengage
 Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning  Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning



