
Concept explainers
Requirement – 1
To record: The
Requirement – 1
Explanation of Solution
Journal:
Journal is the method of recording monetary business transactions in chronological order. It records the debit and credit aspects of each transaction to abide by the double-entry system.
Rules of Debit and Credit:
Following rules are followed for debiting and crediting different accounts while they occur in business transactions:
- Debit, all increase in assets, expenses and dividends, all decrease in liabilities, revenues and stockholders’ equities.
- Credit, all increase in liabilities, revenues, and stockholders’ equities, all decrease in assets, expenses.
Journal entries for given transactions are as follows:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| 2018 | Prepaid rent | 6,000 | |
| January 2 | Cash | 6,000 | |
| (To record advance rent received for one year) | |||
| 2018 | Supplies | 3,500 | |
| January 9 | Accounts payable | 3,500 | |
| (To record purchase of additional supplied) | |||
| 2018 | Accounts receivable | 25,500 | |
| January 13 | Service revenue | 25,500 | |
| (To record service provided on account) | |||
| 2018 | Cash | 3,700 | |
| January 17 | Deferred revenue | 3,700 | |
| (To record cash received from customer for future service) | |||
| 2018 | Salaries expense | 11,500 | |
| January 20 | Cash | 11,500 | |
| (To record incurred of salaries expense) | |||
| 2018 | Cash | 24,100 | |
| January 22 | Accounts receivable | 24,100 | |
| (To record cash received from customer) | |||
| 2018 | Accounts payable | 4,000 | |
| January 29 | Cash | 4,000 | |
| (To record cash paid to suppliers) | |||
Table (1)
Requirement – 2 (a)
To record: The adjusting entry for prepaid rent.
Requirement – 2 (a)
Answer to Problem 3.21E
Adjusting entry for prepaid rent is as follows:
| Date | Accounts title and explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| January 31, 2018 | Rent expense | 500 | ||
| Prepaid rent | 500 | |||
| (To record the rent expense incurred at the end of the accounting year) |
Table (2)
Explanation of Solution
Adjusting entries refers to the entries that are made at the end of an accounting period in accordance with revenue recognition principle, and expenses recognition principle. The purpose of adjusting entries is to adjust the revenue, and the expenses during the period in which they actually occurs.
Following is the rules of debit and credit of above transaction:
- Rent expense is an expense, and it decreased the value of
stockholder’s equity. Therefore, it is debited. - Prepaid rent is an asset account. There is a decrease in assets, therefore it is credited.
Requirement – 2 (b)
To record: The adjusting entry for supplies expense.
Requirement – 2 (b)
Answer to Problem 3.21E
Adjusting entry for supplies expense is as follows:
| Date | Accounts title and explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| January 31, 2018 | Supplies expense (1) | 3,800 | ||
| Supplies | 3,800 | |||
| (To record the supplies expense incurred at the end of the accounting year) |
Table (3)
Explanation of Solution
Explanation:
Adjusting entries:
Adjusting entries refers to the entries that are made at the end of an accounting period in accordance with revenue recognition principle, and expenses recognition principle. The purpose of adjusting entries is to adjust the revenue, and the expenses during the period in which they actually occurs.
Following is the rules of debit and credit of above transaction:
- Supplies expense is an expense, and it decreased the value of stockholder’s equity. Therefore, it is debited.
- Supplies are an asset account. There is a decrease in assets, therefore it is credited.
Working note:
Calculate the value of supplies expense at end of the October month
Requirement – 2 (c)
To record: The adjusting entry for service revenue recognized at the end of the accounting year.
Requirement – 2 (c)
Answer to Problem 3.21E
Adjusting entry for service revenue is as follows:
| Date | Accounts title and explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| January 31, 2018 | Deferred revenue | 3,200 | ||
| Service revenue | 3,200 | |||
| (To record the service revenue recognized at the end of the accounting year) |
Table (4)
Explanation of Solution
Explanation:
Adjusting entries:
Adjusting entries refers to the entries that are made at the end of an accounting period in accordance with revenue recognition principle, and expenses recognition principle. The purpose of adjusting entries is to adjust the revenue, and the expenses during the period in which they actually occurs.
Following is the rules of debit and credit of above transaction:
- Deferred revenue is a liability account. There is a decrease in liability, therefore it is debited.
- Service revenue is revenue, and it increased the value of stockholder’s equity. Therefore, it is credited
Requirement – 2 (d)
To record: The adjusting entry for salaries expense.
Requirement – 2 (d)
Answer to Problem 3.21E
Adjusting entry for salaries expense is as follows:
| Date | Accounts title and explanation | Post Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| January 31, 2018 | Salaries expense | 5,800 | ||
| Salaries payable | 5,800 | |||
| (To record the salaries expense incurred at the end of the accounting year) |
Table (5)
Explanation of Solution
Adjusting entries:
Adjusting entries refers to the entries that are made at the end of an accounting period in accordance with revenue recognition principle, and expenses recognition principle. The purpose of adjusting entries is to adjust the revenue, and the expenses during the period in which they actually occurs.
Following is the rules of debit and credit of above transaction:
- Salaries expense is an expense, and it decreased the value of stockholder’s equity. Therefore, it is debited.
- Salaries payable is a liability account. There is a decrease in liability, therefore it is credited.
Requirement – 3
To prepare: The adjusted
Requirement – 3
Explanation of Solution
Adjusted trial balance:
Adjusted trial balance is a summary of all the ledger accounts, and it contains the balances of all the accounts after the adjustment entries are journalized, and posted.
The adjusted trial balance of Company D is as follows:
| Company D | ||
| Adjusted Trial Balance | ||
| January 31, 2018 | ||
| Accounts (Refer working note (2) ) | Debit | Credit |
| Cash | $30,100 | |
| Accounts Receivable | 6,600 | |
| Supplies | 2,800 | |
| Prepaid Rent | 5,500 | |
| Land | 50,000 | |
| Accounts Payable | $2,700 | |
| Deferred Revenue | 500 | |
| Salaries Payable | 5,800 | |
| Common Stock | 65,000 | |
| 13,900 | ||
| Service Revenue | 28,700 | |
| Salaries Expense | 17,300 | |
| Rent Expense | 500 | |
| Supplies Expense | 3,800 | |
| Totals | $116,600 | $116,600 |
Table (6)
Working note:
Calculate the ending balance of all accounts:
| Accounts | Beginning balance +Adjustment | Ending balance | ||
| Cash | = |
| = | 30,100 |
| Accounts Receivable | = |
| = | 6,600 |
| Supplies | = |
| = | 2,800 |
| Prepaid Rent | = |
| = | 5,500 |
| Land | = |
| = | 50,000 |
| Accounts Payable | = |
| = | 2,700 |
| Deferred Revenue | = |
| = | 500 |
| Salaries Payable | = |
| = | 5,800 |
| Common Stock | = |
| = | 65,000 |
| Retained Earnings | = |
| = | 13,900 |
| Service Revenue | = |
| = | 28,700 |
| Salaries Expense | = |
| = | 17,300 |
| Rent Expense | = |
| = | 500 |
| Supplies Expense | = |
| = | 3,800 |
(2)
Thus, the total of debit, and credit columns of an adjusted trial balance is $116,600 and agreed.
Requirement – 4
To prepare: The income statement of Company D for the year ended January 31, 2018.
Requirement – 4
Explanation of Solution
Income statement:
This is the financial statement of a company which shows all the revenues earned and expenses incurred by the company over a period of time.
The income statement of Company D for the year ended January 31, 2018 is as follows:
| Company D | ||
| Income statement | ||
| For the year ended January 31, 2018 | ||
| $ | $ | |
| Service revenue (A) | 28,700 | |
| Expenses: | ||
| Salaries expense | 17,300 | |
| Rent expense | 500 | |
| Supplies expense | 3,800 | |
| Total expense (B) | 21,600 | |
| Net income | 7,100 | |
Table (7)
Therefore, the net income of Company D is $7,100.
Requirement – 5
To prepare: The classified balance sheet of Company D at January 31, 2018.
Requirement – 5
Explanation of Solution
Classified balance sheet:
This is the financial statement of a company which shows the grouping of similar assets and liabilities under subheadings.
The classified balance sheet of Company D at January 31, 2018 is as follows:
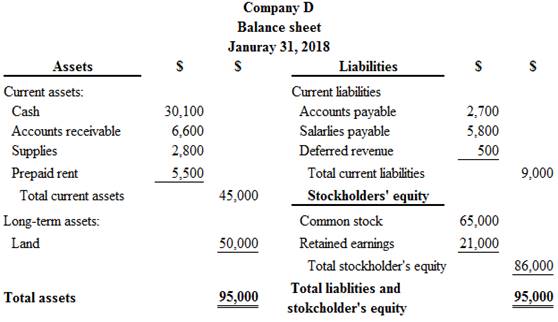
Figure (1)
Therefore, the total assets of Company D are $95,000, and the total liabilities and stockholders’ equity are $95,000.
Requirement – 6
To record: The closing entries of Company D.
Requirement – 6
Answer to Problem 3.21E
The closing entries of Company D are as follows:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| 2018 | Service revenue | 28,700 | |
| January 31 | Retained earnings | 28,700 | |
| (To close revenue account) | |||
| 2018 | Retained earnings | 21,600 | |
| January 31 | Salaries expense | 17,300 | |
| Rent expense | 500 | ||
| Supplies expense | 3,800 | ||
| (To close all expense account) | |||
Table (7)
Explanation of Solution
Closing entries:
Closing entries are those journal entries, which are passed to transfer the final balances of temporary accounts, (all revenues account, all expenses account and dividend) to the income summary account. Closing entries produce a zero balance in each temporary account.
Closing entry for revenue account:
In this closing entry, the service revenue account is closed by transferring the amount of service revenue to the retained earnings in order to bring the revenue accounts balance to zero.
Closing entry for expenses account:
In this closing entry, salaries expense, rent expense, and supplies expense are closed by transferring the amount of all expenses to the retained earnings in order to bring all the expense accounts balance to zero.
Requirement – 7 (a)
the amount of profit reported for the month of January.
Requirement – 7 (a)
Explanation of Solution
Net income:
Net income is the excess amount of revenue which is arises after deducting all the expenses of a company. In simply, it is the difference between total revenue and total expenses of the company.
The amount of reported profit is $7,100 (Refer Requirement – 4).
Requirement – 7 (b)
To calculate: The ratio of current assets to current liabilities at the end of January.
Requirement – 7 (b)
Explanation of Solution
A part of
Current ratio of the Company D is as follows:
Here,
Current assets is $45,000
Current liabilities is $9,000
Requirement – 7 (c)
To indicate: Whether Company D appears good or bad in financial condition.
Requirement – 7 (c)
Explanation of Solution
Financial condition of Company D is good, because profit is greater than zero and current assets is greater than its current liability. So, the company can earn revenue from its customer and able to pay obligation.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTINGLL W/CONNECT >IC<
- Can you help me solve this general accounting problem with the correct methodology?arrow_forwardSalvador Manufacturing estimates that annual manufacturing overhead costs will be $842,400. Estimated annual operating activity bases are direct labor costs of $496,000, direct labor hours of 41,200, and machine hours of 90,400. Compute the predetermined overhead rate for each activity base: a. Overhead rate per direct labor cost b. Overhead rate per direct labor hour c. Overhead rate per machine hourarrow_forwardFinancial Accountingarrow_forward
- Please explain the solution to this financial accounting problem with accurate explanations.arrow_forwardCan you demonstrate the accurate steps for solving this financial accounting problem with valid procedures?arrow_forwardI need help with this financial accounting problem using proper accounting guidelines.arrow_forward
 Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College

