
Concept explainers
1
To record: The
1
Explanation of Solution
Journal:
Journal is the method of recording monetary business transactions in chronological order. It records the debit and credit aspects of each transaction to abide by the double-entry system.
Rules of Debit and Credit:
Following rules are followed for debiting and crediting different accounts while they occur in business transactions:
- Debit, all increase in assets, expenses and dividends, all decrease in liabilities, revenues and stockholders’ equities.
- Credit, all increase in liabilities, revenues, and stockholders’ equities, all decrease in assets, expenses.
The journal entries for given transactions of Company G are as follows:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | PostRef. | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| 2015 | Cash | 10,000 | ||
| July 1 | Common stock | 10,000 | ||
| (To record the issuance of common stock in cash to Company S) | ||||
| 2015 | Cash | 10,000 | ||
| July, 2 | Common stock | 10,000 | ||
| (To record the issuance of common stock in cash to Company T) | ||||
| 2015 | Prepaid insurance | 4,800 | ||
| July 1 | Cash | 4,800 | ||
| (To record the purchase of one year insurance policy in cash) | ||||
| 2015 | Legal fees expense | 1,500 | ||
| July, 2 | Cash | 1,500 | ||
| (To record the payment of legal fees) | ||||
| 2015 | Supplies (office) | 1,800 | ||
| July, 4 | Accounts payable | 1,800 | ||
| (To record purchase of office supplies on account) | ||||
| 2015 | Advertising expense | 300 | ||
| July, 7 | Cash | 300 | ||
| (To record payment of advertising expense) | ||||
| 2015 | Equipment (Bikes) | 12,000 | ||
| July, 7 | Cash | 12,000 | ||
| (To record the purchase of mountain bike) | ||||
| 2015 | Cash | 2,000 | ||
| July, 15 | Service revenue (Clinic) | 2,000 | ||
| ( To record the cash received for service revenue) | ||||
| 2015 | Cash | 2,300 | ||
| July, 22 | Service revenue (Clinic) | 2,300 | ||
| ( To record the cash received for service revenue) | ||||
| 2015 | Advertising expense | 700 | ||
| July, 22 | Cash | 700 | ||
| (To record the payment of advertising expense in cash) | ||||
| 2015 | Cash | 4,000 | ||
| July, 30 | Deferred revenue | 4,000 | ||
| (To record advance cash received from customer) | ||||
| 2015 | Cash | 30,000 | ||
| August, 1 | Notes payable | 30,000 | ||
| (To record loan received from city council) | ||||
| 2015 | Equipment (Kayaks) | 28,000 | ||
| August, 4 | Cash | 28,000 | ||
| (To record the purchase of equipment in cash) | ||||
| 2015 | Cash | 3,000 | ||
| August, 10 | Deferred revenue | 4,000 | ||
| Service revenue | 7,000 | |||
| (To record the cash received from service revenue and recognized service revenue) | ||||
| 2015 | Cash | 10,500 | ||
| August, 17 | Service revenue | 10,500 | ||
| (To record cash received from service revenue) | ||||
| 2015 | Accounts payable | 1,800 | ||
| August, 24 | Cash | 1,800 | ||
| ( To record payment of cash to creditors) | ||||
| 2015 | Prepaid rent | 2,400 | ||
| September 1 | Cash | 2,400 | ||
| (To record the payment of one year advance rent) | ||||
| 2015 | Cash | 13,200 | ||
| September 21 | Service revenue (Clinic) | 13,200 | ||
| (To record the cash received from customer) | ||||
| 2015 | Cash | 17,900 | ||
| October 17 | Service revenue (Clinic) | 17,900 | ||
| (To record the cash received from customer) | ||||
| 2015 | Miscellaneous expense | 1,200 | ||
| December 8 | Cash | 1,200 | ||
| (To record the payment of miscellaneous expense) | ||||
| 2015 | Supplies (Racing) | 2,800 | ||
| December 12 | Accounts payable |
| 2,800 | |
| (To record purchase of supplies on account) | ||||
| 2015 | Cash | 20,000 | ||
| December 15 | Service revenue (Racing) | 20,000 | ||
| (To record cash received from service revenue) | ||||
| 2015 | Salaries expense | 2,000 | ||
| December 16 | Cash | 2,000 | ||
| (To record the supplies expense incurred) | ||||
| 2015 | Dividend | 4,000 | ||
| December 31 | Cash | 4,000 | ||
| (To record the payment of cash dividends) |
Table (1)
2
To record: The adjusting journal entries on December 31.
2
Explanation of Solution
Adjusting entries refers to the entries that are made at the end of an accounting period in accordance with revenue recognition principle, and expenses recognition principle. The purpose of adjusting entries is to adjust the revenue, and the expenses during the period in which they actually occurs.
The adjusting journal entries for given transactions of Company G are as follows:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post Ref. | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| 2015 |
| 8,000 | ||
| December 31 |
| 8,000 | ||
| (To record depreciation expense incurred at the end of the accounting year) | ||||
| 2015 | Insurance expense | 2,400 | ||
| December 31 | Prepaid insurance | 2,400 | ||
| (To record the insurance expense incurred at the end of the accounting period) | ||||
| 2015 | Rent expense | 800 | ||
| December 31 | Prepaid rent | 800 | ||
| (To record the rent expense incurred at the end of the accounting year) | ||||
| 2015 | Supplies expense (Office) | 1,500 | ||
| December 31 | Supplies | 1,500 | ||
| (To record supplies expense incurred at the end of the accounting year) | ||||
| 2015 | Interest expense | 750 | ||
| December 31 | Interest payable | 750 | ||
| (To record interest expense incurred at the end of the accounting year) | ||||
| 2015 | Supplies expense (Racing) | 2,600 | ||
| December 31 | Supplies | 2,600 | ||
| (To record supplies expense incurred at the end of the accounting year) | ||||
| 2015 | Income tax expense | 14,000 | ||
| December 31 | Income tax payable | 14,000 | ||
| (To record the income tax expense incurred at the end of the accounting year) |
Table (2)
3
To post: The Transactions to T-accounts of Company G.
3
Explanation of Solution
T-account:
T-account refers to an individual account, where the increases or decreases in the value of specific asset, liability,
This account is referred to as the T-account, because the alignment of the components of the account resembles the capital letter ‘T’.’ An account consists of the three main components which are as follows:
- (a) The title of the account
- (b) The left or debit side
- (c) The right or credit side
T-accounts for above transactions are as follows:
| Cash | |
| 10,000 | 4,800 |
| 10,000 | 1,500 |
| 2,000 | 300 |
| 2,300 | 12,000 |
| 4,000 | 700 |
| 30,000 | 28,000 |
| 3,000 | 1,800 |
| 10,500 | 2,400 |
| 13,200 | 1,200 |
| 17,900 | 2,000 |
| 20,000 | 4,000 |
| 64,200 | |
| Prepaid Insurance | |
| 4,800 | 2,400 |
| 2,400 | |
| Supplies (Racing) | |
| 2,800 | 2,600 |
| 200 | |
| Prepaid Rent | |
| 2,400 | 800 |
| 1,600 | |
| Supplies (Office) | |
| 1,800 | 1,500 |
| 300 | |
| Equipment (Bikes) | |
| 12,000 | |
| 12,000 | |
| Equipment (Kayaks) | |
| 28,000 | |
| 28,000 | |
| Accumulated Depreciation | |
| 8,000 | |
| 8,000 | |
| Accounts Payable | |
| 1800 | 1,800 |
| 2,800 | |
| 2,800 | |
| Deferred Revenue | |
| 4,000 | 4,000 |
| 0 | |
| Interest Payable | |
| 750 | |
| 750 | |
| Income Tax Payable | |
| 14,000 | |
| 14,000 | |
| Notes Payable | |
| 30,000 | |
| 30,000 | |
| Common Stock | |
| 10,000 | |
| 10,000 | |
| 20,000 | |
| Dividends | |
| 4,000 | |
| 4,000 | |
| Service Revenue (Clinic) | |
| 2,000 | |
| 2,300 | |
| 7,000 | |
| 10,500 | |
| 13,200 | |
| 17,900 | |
| 52,900 | |
| Service Revenue (Racing) | |
| 20,000 | |
| 20,000 | |
| Legal Fees Expense | |
| 1,500 | |
| 1,500 | |
| Advertising Expense | |
| 300 | |
| 700 | |
| 1,000 | |
| Rent Expense | |
| 800 | |
| 800 | |
| Salaries Expense | |
| 2,000 | |
| 2,000 | |
| Depreciation Expense | |
| 8,000 | |
| 8,000 | |
| Insurance Expense | |
| 2,400 | |
| 2,400 | |
| Supplies Expense (Office) | |
| 1,500 | |
| 1,500 | |
| Supplies Expense (Racing) | |
| 2,600 | |
| 2,600 | |
| Interest Expense | |
| 750 | |
| 750 | |
| Income Tax Expense | |
| 14,000 | |
| 14,000 | |
| Miscellaneous Expense | |
| 1,200 | |
| 1,200 | |
4
To prepare: The adjusted
4
Explanation of Solution
Adjusted trial balance:
Adjusted trial balance is a summary of all the ledger accounts, and it contains the balances of all the accounts after the adjustment entries are journalized, and posted.
Adjusted trial balance of Company G is as follows:
| Company G | ||
| Adjusted Trial Balance | ||
| December 31, 2015 | ||
| Accounts | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| Cash | 64,200 | |
| Prepaid Insurance | 2,400 | |
| Prepaid Rent | 1,600 | |
| Supplies (Office) | 300 | |
| Supplies (Racing) | 200 | |
| Equipment (Bikes) | 12,000 | |
| Equipment (Kayaks) | 28,000 | |
| Accumulated Depreciation | $8,000 | |
| Accounts Payable | 2,800 | |
| Income Tax Payable | 14,000 | |
| Interest Payable | 750 | |
| Notes Payable | 30,000 | |
| Common Stock | 20,000 | |
| Dividends | 4,000 | |
| Service Revenue (Clinic) | 52,900 | |
| Service Revenue (Racing) | 20,000 | |
| Advertising Expense | 1,000 | |
| Depreciation Expense | 8,000 | |
| Income Tax Expense | 14,000 | |
| Insurance Expense | 2,400 | |
| Interest Expense | 750 | |
| Legal Fees Expense | 1,500 | |
| Miscellaneous Expense | 1,200 | |
| Rent Expense | 800 | |
| Salaries Expense | 2,000 | |
| Supplies Expense (Office) | 1,500 | |
| Supplies Expense (Racing) | 2,600 | |
| Totals | 148,450 | 148,450 |
Table (3)
5
To prepare: The income statement and classified
5
Explanation of Solution
Income statement:
This is the financial statement of a company which shows all the revenues earned and expenses incurred by the company over a period of time.
Statement of stockholders’ equity:
This statement reports the beginning stockholder’s equity and all the changes, which led to ending stockholder’s’ equity. Additional capital, net income from income statement is added to and drawings are deducted from beginning stockholder’s equity to arrive at the result of closing balance of stockholders’ equity.
Classified balance sheet:
This is the financial statement of a company which shows the grouping of similar assets and liabilities under subheadings.
Income statement:
Income statement of Company G is as follows:
| Company G | ||
| Income Statement | ||
| For the year ended December 31, 2015 | ||
| ($) | ($) | |
| Revenues: | ||
| Service revenue (clinic) | 52,900 | |
| Service revenue (racing) | 20,000 | |
| Total revenues | 72,900 | |
| Expenses: | ||
| Advertising expense | 1,000 | |
| Depreciation expense | 8,000 | |
| Income tax expense | 14,000 | |
| Insurance expense | 2,400 | |
| Interest expense | 750 | |
| Legal fees expense | 1,500 | |
| Miscellaneous expense | 1,200 | |
| Rent expense | 800 | |
| Salaries expense | 2,000 | |
| Supplies expense (office) | 1,500 | |
| Supplies expense (racing) | 2,600 | |
| Total expenses | 35,750 | |
| Net income | 37,150 | |
Table (4)
Therefore, the net income of Company G is $37,150.
Statement of stockholder’s equity:
The statement of stockholder’s equity of Company G for the year ended December 31, 2015 is as follows:
| Company G | |||
| Statement of Stockholders’ Equity | |||
| For the period ended December 31, 2015 | |||
| Common stock ($) |
| Total stockholders' equity ($) | |
| Balance at July 1 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Issuance of common stock | 20,000 | 20,000 | |
| Add: Net income for 2018 | 37,150 | 37,150 | |
| Less: Dividends | -4,000 | -4,000 | |
| Balance at December 31 | $20,000 | $33,150 | $53,150 |
Table (5)
Therefore, the total stockholder’s equity of Company G for the year ended December 31, 2015 is $53,150.
Classified balance sheet:
Classified balance sheet of Company G is as follows:
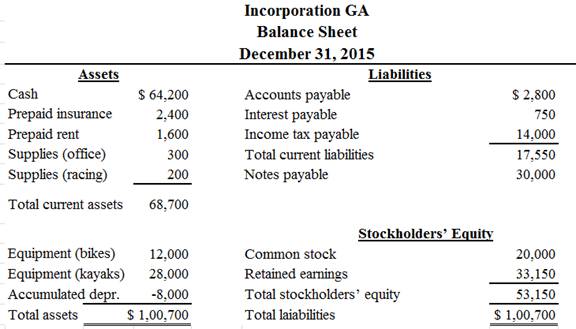
Figure (1)
Therefore, the total assets of Company G are $100,700, and the total liabilities and stockholders’ equity are $100,700.
6
To record: The necessary closing entries of Company G.
6
Explanation of Solution
Closing entries:
Closing entries are those journal entries, which are passed to transfer the final balances of temporary accounts, (all revenues account, all expenses account and dividend) to the retained earnings. Closing entries produce a zero balance in each temporary account.
Closing entries of Company G is as follows:
| Date | Account Title and Explanation |
Post Ref. |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| 2015 | Service revenue (Clinic) | 52,900 | ||
| December 31 | Service revenue (Racing) | 20,000 | ||
| Retained earnings | 72,900 | |||
| (To close all revenue account) | ||||
| 2015 | Retained earnings | 37,750 | ||
| December 31 | Advertising expense | 1,000 | ||
| Depreciation expense | 8,000 | |||
| Income tax expense | 14,000 | |||
| Insurance expense | 2,400 | |||
| Interest expense | 750 | |||
| Legal fees expense | 1,500 | |||
| Miscellaneous expense | 1,200 | |||
| Rent expense | 800 | |||
| Salaries expense | 2,000 | |||
| Supplies expense (office) | 1,500 | |||
| Supplies expense (Racing) | 2,600 | |||
| (To close all the expenses account) | ||||
| 2015 | Retained earnings | 4,000 | ||
| December 31 | Dividends | 4,000 | ||
| (To close the dividends account) | ||||
Table (6)
7
To post: The closing entries to the T-accounts.
7
Explanation of Solution
| Service Revenue (Clinic) | |
| 2,000 | |
| 2,300 | |
| 7,000 | |
| 10,500 | |
| 13,200 | |
| 52,900 | 17,900 |
| 0 | |
| Service Revenue (Racing) | |
| 20,000 | 20,000 |
| 0 | |
| Legal Fees Expense | |
| 1,500 | 1,500 |
| 0 | |
| Advertising Expense | |
| 300 | |
| 700 | 1,000 |
| 0 | |
| Rent Expense | |
| 800 | 800 |
| 0 | |
| Salaries Expense | |
| 2,000 | 2,000 |
| 0 | |
| Depreciation Expense | |
| 8,000 | 8,000 |
| 0 | |
| Insurance Expense | |
| 2,400 | 2,400 |
| 0 | |
| Supplies Expense (Office) | |
| 1,500 | 1,500 |
| 0 | |
| Supplies Expense (Racing) | |
| 2,600 | 2,600 |
| 0 | |
| Interest Expense | |
| 750 | 0 |
| 750 | |
| Income Tax Expense | |
| 14,000 | 14,000 |
| 0 | |
| Miscellaneous Expense | |
| 1,200 | 1,200 |
| 0 | |
| Dividends | |
| 4,000 | 4,000 |
| 0 | |
| Retained Earnings | |
| 35,750 | 72,900 |
| 4,000 | |
| 33,150 | |
8
To prepare: A post-closing trial balance of Company G.
8
Explanation of Solution
Post-closing trial balance:
The post-closing trial balance is a summary of all ledger accounts, and it shows the debit and the credit balances after the closing entries are journalized and posted. The post-closing trial balance contains only permanent (balance sheet) accounts, and the debit and the credit balances of permanent accounts should agree.
Post-closing trial balance of Company G is as follows:
| Company G | ||
| Post-closing Trial Balance | ||
| For the year ended December 31, 2015 | ||
| Accounts | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| Cash | $64,200 | |
| Prepaid Insurance | 2,400 | |
| Prepaid Rent | 1,600 | |
| Supplies (Office) | 300 | |
| Supplies (Racing) | 200 | |
| Equipment (Bikes) | 12,000 | |
| Equipment (Kayaks) | 28,000 | |
| Accumulated Depreciation | $8,000 | |
| Accounts Payable | 2,800 | |
| Income Tax Payable | 14,000 | |
| Interest Payable | 750 | |
| Notes Payable | 30,000 | |
| Common Stock | 20,000 | |
| Retained Earnings | 33,150 | |
| Total | $108,700 | $108,700 |
Table (7)
Therefore, the total of debit, and credit columns of post-closing trial balance is $108,700 and agree.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Financial Accounting
- Blossom Corporation issues 72000 shares of $50 par value preferred stock for cash at $60 per share. The entry to record the transaction will consist of a debit to Cash for $4320000 and a credit or credits to ○ Preferred Stock for $4320000 ○ Preferred Stock for $3600000 and Paid-in Capital in Excess of Par-Preferred Stock for $720000 ○ Preferred Stock for $3600000 and Retained Earnings for $720000 ○ Paid-in Capital from Preferred Stock for $4320000arrow_forwardThe current sections of Kingbird Inc's balance sheets at December 31, 2024 and 2025, are presented here. Kingbird's net income for 2025 was $107,100. Depreciation expense was $18,900. 2025 2024 Current assets Cash $73,500 $69,300 Accounts receivable 56,000 62,300 Inventory 117,600 120,400 Prepaid expenses 18,900 15,400 Total current assets $266,000 $267,400 Current liabilities Accrued expenses payable $10,500 $3,500 Accounts payable 59,500 64,400 Total current liabilities $70,000 $67,900 Prepare the operating activities section of the company's statement of cash flows for the year ended December 31, 2025, using the indirect method. (Show amounts that decrease cash flow with either a-sign eg.-15,000 or in parenthesis e.g. (15,000).) KINGBIRD INC. Statement of Cash Flows (Partial) - Indirect Method For the Year Ended December 31, 2025 Cash Flows from Operating Activities Net Income Adjustments to reconcile net income to Depreciation Expense 18900 6300 Decrease In Accounts Receivable…arrow_forwardWrong answer will get unhelpful ratearrow_forward
- Metlock Lawn Service Company reported a net loss of $15300 for the year ended December 31, 2025. During the year, accounts receivable decreased $25000, inventory increased $20000, accounts payable increased by $30600, and depreciation expense of $26400 was recorded. During 2025, operating activities provided net cash of $77000 O provided net cash of $46700. O used net cash of $46700. ○ used net cash of $9200.arrow_forwardPlease help me solve this financial accounting question using the right financial principles.arrow_forwardDon't use aiarrow_forward
- General accounting Problemarrow_forwardA company purchased for cash a machine with a list price of $85,000. The machine was shipped FOB shipping point at a cost of $6,500. Installation and test runs of the machine cost $4,500. The recorded acquisition cost of the machine is which amount? Need helparrow_forwardJersey Manufacturing applies manufacturing overhead to its cost objects based on 80% of direct material cost. If Job 22B had $64,000 of manufacturing overhead applied to it during June, what was the amount for direct materials assigned to Job 22B? Answerarrow_forward
- Net income is $145,000, accounts payable increased $12,000 during the year, inventory decreased $8,000, and accounts receivable increased $15,000 during the year. Under the indirect method, what is net cash provided by operations?arrow_forwardHelparrow_forwardThe following data is available for Ivanhoe Corporation at December 31, 2025: Common stock, par $10 (authorized 32500 shares) $292500 Treasury stock (at cost $15 per share) $1110 Based on the data, how many shares of common stock are outstanding? 32500 32426 29250 ○ 29176arrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





