
Concept explainers
a & b
Prepare the necessary journal entries and post to the ledger accounts.
a & b
Explanation of Solution
Prepare the journal entries in the books of W Catering Service.
| Date | Account titles and Explanation | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| July 1 | Cash (A+) | 15,000 | |
| Common stock (E+) | 15,000 | ||
| (To record the issuance of common stock) | |||
| July 2 | Delivery van (A+) | 3,780 | |
| Equipment (A+) | 3,240 | ||
| Supplies (A+) | 1,600 | ||
| Cash(A-) | 8,620 | ||
| (To record the purchase of asset) | |||
| July 3 | Prepaid insurance (A+) | 1,080 | |
| Cash (A-) | 1,080 | ||
| (To record the payment of insurance premium) | |||
| July 4 | Cash (A+) | 4,500 | |
| Unearned catering fees revenue (L+) | 4,500 | ||
| (To record the receipt of cash in advance for unearned catering fees revenue) | |||
| July 5 | Prepaid rent (A+) | 2,340 | |
| Cash (A-) | 2,340 | ||
| (To record the prepaid rent) | |||
| July 6 | Wages expense (E-) | 1,700 | |
| Cash (A-) | 1,700 | ||
| (To record the wages expense) | |||
| July 7 | 4,500 | ||
| Catering fees revenue (E+) | 4,500 | ||
| (To record the revenue on account) | |||
| July 8 | Supplies (A+) | 3,400 | |
| Accounts payable ((L+) | 3,400 | ||
| (To record the purchase of supplies on account) | |||
| July 9 | Wages expense(E+) | 1,700 | |
| Cash (A-) | 1,700 | ||
| (To record the payment of wages) | |||
| July 10 | Delivery van expense(E+) | 690 | |
| Cash (A-) | 690 | ||
| (To record the payment of delivery van expense) | |||
| July 11 | Cash (A+) | 3,700 | |
| Accounts receivable (A-) | 3,700 | ||
| (To record the collection of cash from customers) | |||
| July 12 | Accounts receivable (A+) | 4,800 | |
| Catering Fees Revenue (E+) | 4,800 | ||
| (To record the revenues on account) | |||
| July 13 | Dividends (E-) | 1,900 | |
| Cash(A-) | 1,900 | ||
| (To record the payment of cash dividends) |
Table (1)
T-account:
T-account is the form of the ledger account, where the journal entries are posted to this account. It is referred to as the T-account, because the alignment of the components of the account resembles the capital letter ‘T’.
The components of the T-account are as follows:
a) The title of the account
b) The left or debit side
c) The right or credit side
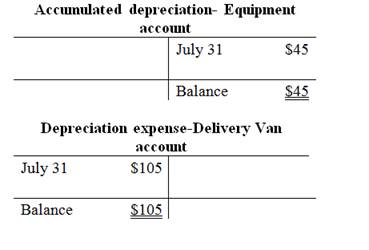
Prepare the T-accounts:

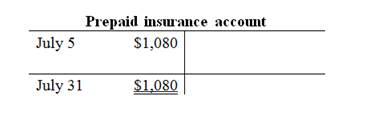
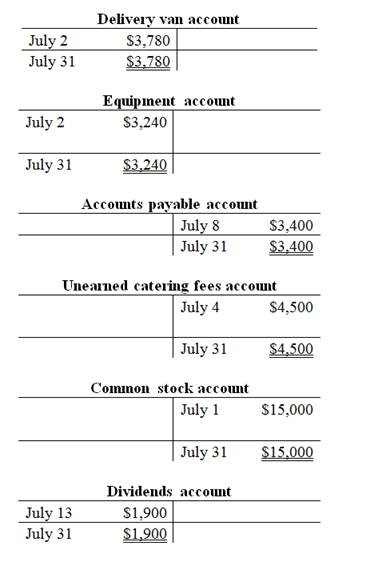
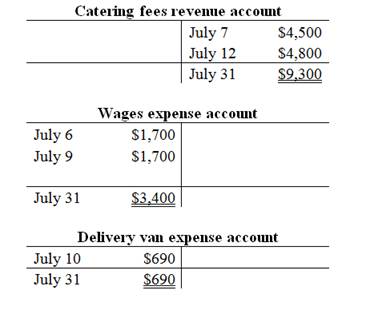
c.
Prepare an unadjusted
c.
Explanation of Solution
Unadjusted trial balance:
Unadjusted trial balance is that statement which contains complete list of accounts with their unadjusted balances. This statement is prepared at the end of every financial period.
Prepare the unadjusted trial balance as of 31st July.
| W Catering Services | ||
| Unadjusted Trial Balance | ||
| For the year ended 31st July | ||
| Accounts | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| Cash | 5,170 | |
| Supplies | 5,000 | |
| Accounts receivable | 5,600 | |
| Prepaid insurance | 1,080 | |
| Prepaid rent | 2,340 | |
| Equipment | 3,240 | |
| Delivery Van | 3,780 | |
| Accounts Payable | 3,400 | |
| Common Stock | 15,000 | |
| Dividends | 1,900 | |
| Catering Fees Revenue | 9,300 | |
| Unearned Catering Fees Revenue | 4,500 | |
| Wages Expense | 3,400 | |
| Delivery Van Expenses | 690 | |
| Total | 32,200 | 32,200 |
Table (2)
The debit column and credit column of the unadjusted trial balance are agreed, both having balance of $32,000.
d.
Prepare the
d.
Explanation of Solution
Adjusting entries: Adjusting entries are the journal entries which are recorded at the end of the accounting period to correct or adjust the revenue and expense accounts, to concede with the accrual principle of accounting.
Prepare the adjusting entries in the books of W Catering Service.
| Date | Account titles and Explanation | Debit ($) | Credit ($) |
| July 31 | Office Supplies Expense (E+) (1) | 3,500 | |
| Office Supplies (A–) | 3,500 | ||
| (To record the adjusting entry for office supplies expense) | |||
| July 31 | Wages Expense (E+) | 510 | |
| Wages Payable (L+) | 510 | ||
| (To record the adjusting entry for wages expense | |||
| July 31 | 45 | ||
| 45 | |||
| (To record the amount of depreciation for July) | |||
| July 31 | Depreciation Expense- Delivery van (E+) (3) | 105 | |
| Accumulated Depreciation - Delivery van (A–) | 105 | ||
| (To record the amount of depreciation for July) | |||
| July 31 | Rent Expense (E+) (4) | 780 | |
| Prepaid Rent(A–) | 780 | ||
| (To record the adjusting entry for rent expense) | |||
| July 31 | Insurance Expense (E+) (4) | 90 | |
| Prepaid Insurance(A–) | 90 | ||
| (To record the adjusting entry for insurance expense) | |||
| July 31 | Unearned Catering Fees (L–) | 750 | |
| Catering Fees Revenue (E+) | 750 | ||
| (To record the adjusting entry for unearned catering fees) |
Table (3)
Working note:
Calculate the amount of office supplies used during the year:
Calculate the amount of depreciation on equipment for the month July:
Calculate the amount of depreciation on delivery van for the month July:
Calculate the rent expense for the month of July:
Calculate the insurance expense for the month of July:
T-account:
T-account is the form of the ledger account, where the journal entries are posted to this account. It is referred to as the T-account, because the alignment of the components of the account resembles the capital letter ‘T’.
The components of the T-account are as follows:
a) The title of the account
b) The left or debit side
c) The right or credit side
Prepare the T-accounts:
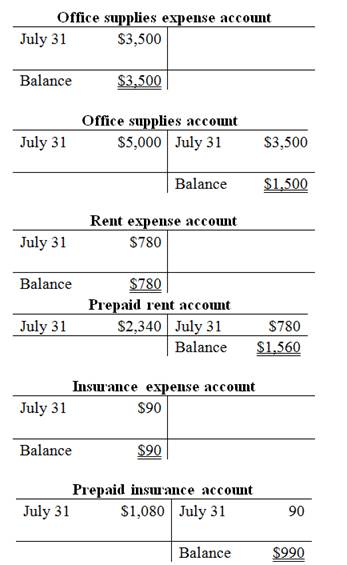
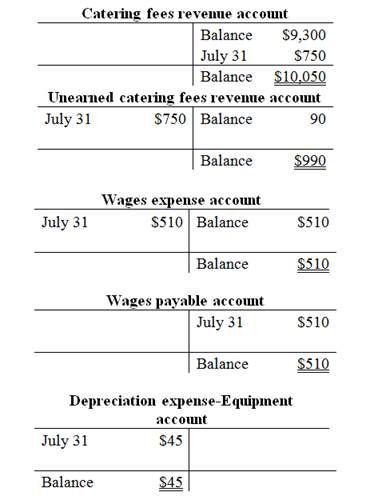

Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Financial Accounting for Undergraduates
- Joe transferred land worth $200,000, with a tax basis of $40,000, to JH Corporation, an existing entity, for 100 shares of its stock. JH Corporation has two other shareholders, Ethan and Young, each of whom holds 100 shares. With respect to the transfer:a. Joe has no recognized gain. b. JH Corporation has a basis of $160,000 in the land.c. Joe has a basis of $200,000 in his 100 shares in JH Corporation. d. Joe has a basis of $40,000 in his 100 shares in JH Corporation. e. None of the above.arrow_forwardI need help with this general accounting problem using proper accounting guidelines.arrow_forwardI am looking for the correct answer to this general accounting problem using valid accounting standards.arrow_forward
- accounting question?arrow_forwardThree individuals form JEY Corporation with the following contributions: Joe, cash of $50,000 for 50 shares; Ethan, land worth $20,000 (basis of $11,000) for 20 shares; and Young, cattle worth $9,000 (basis of $6,000) for 9 shares and services worth $21,000 for 21 shares. a. These transfers are fully taxable and not subject to § 351. b. Young’s basis in her stock is $27,000. c. Young’s basis in her stock is $6,000. d. Ethan’s basis in his stock is $20,000. e. None of the above.arrow_forwardNonearrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





