
INTRO.TO COMPUTING SYSTEMS >INTL.ED.<
3rd Edition
ISBN: 9781260565911
Author: PATT
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Chapter 3, Problem 29E
Program Plan Intro
OR operation:
- OR function needs two inputs and produces one output.
- It is also known as binary logical function.
- If one of the inputs or both the inputs are “1”, then one-bit OR operation produces the output as “1”.
- If both the inputs are “0”, then OR operation produces the output “0”.
- The following diagram depicts the one-bit OR operation,
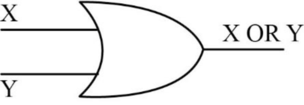
- The truth table for OR operation is as follows,
| X | Y | Z=X OR Y |
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
- In the above table, “X” and “Y” are the inputs, and “Z” is the output.
- In the above table, when “X=0”, and “Y=0”, the output “Z” is “0”, because both the inputs “X” and “Y” contains the value “0”.
- When “X=0”, and “Y=1”, the output “Z” is “1”, because one of the input “Y” contains the value “1”.
- When “X=1”, and “Y=0”, the output “Z” is “1”, because one of the input “X” contains the value “1”.
- When “X=1”, and “Y=1”, the output “Z” is “1”, because both the inputs “X” and “Y” contains the value “1”.
AND function:
- AND function needs two inputs and produces one output.
- It is also known as binary logical function.
- If one or both the inputs are “0”, then one-bit AND operation produces the output “0”.
- If both inputs are “1”, then AND operation produces the output as “1”.
- The following diagram depicts the AND operation,
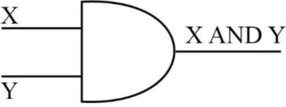
- The truth table for AND operation is as follows,
| X | Y | X AND Y |
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
- In the above table, “X” and “Y” are inputs, and “Z” is output.
- When “X=0”, and “Y=0”, the output is “0”, because both the inputs “X” and “Y” contains the value “0”.
- When “X=0”, and “Y=1”, the output is “0”, because one of the input “X” contains the value “0”.
- When “X=1”, and “Y=0”, the output is “0”, because one of the input “Y” contains the value “0”.
- When “X=1”, and “Y=1”, the output is “1”, because both the inputs “X” and “Y” contains the value “1”.
NOR function:
- The NOR operation produces the output which is the negation of the result of “OR” operation.
- If one or both the inputs are “1”, then NOR operation produces the output as “0”.
- If both the inputs are “0”, then NOR operation produces the output “1”.
- The following diagram depicts the NOR operation,
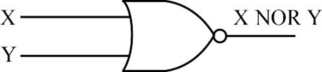
- The truth table for NOR operation is as follows,
| X | Y | Z=X OR Y |
| 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 |
NAND function:
- The NAND operation produces the output which is the negation of the result of “AND” operation.
- If one or both the inputs are “0”, then NAND operation produces the output “1”.
- If both inputs are “0”, then NAND operation produces the output as “0”.
- The following diagram depicts the NAND operation,
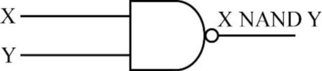
- The truth table for NAND operation is as follows,
| X | Y | X NAND Y |
| 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 |
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
15 OF 25 QUESTIONS REMAININ
Consider the following code. You want to print the array values in the div as an ordered list. What statement would you use to
replace the comment in the code below?
Two
J
// what statement goes here?
-
لبية للالكالا
const app = Vue.createApp({
data ((
return (
lunch: [
'Burrito',
'Soup',
'Pizza',
'Rice'
})
app.mount ('#app6')
-
-
Please answer JAVA OOP problem below:
Assume you have three data definition classes, Person, Student and Faculty. The Student and Faculty classes extend Person. Given the code snippet below, in Java, complete the method determinePersonTypeCount to print out how many Student and Faculty objects exist within the Person array. You may assume that each object within the Person[] is either referencing a Student or Faculty object.
public static void determinePersonTypeCount(Person[] people){
// Place your code here
}
Please answer JAVA OOP question below:
Consider the following relationship diagram between the Game and VideoGame data defintion classes.
Game has a constructor that takes in two parameters, title (String) and cost (double). The VideoGame constructor has an additional parameter, genre (String). In Java, efficiently write the constructors needed within the Game class and VideoGame classes.
Hint: Remember to think about the appropriate validation
Chapter 3 Solutions
INTRO.TO COMPUTING SYSTEMS >INTL.ED.<
Ch. 3 - Prob. 1ECh. 3 - Replace the missing parts in the following circuit...Ch. 3 - A two-input AND and a two-input OR are both...Ch. 3 - Replace the missing parts in the following circuit...Ch. 3 - Complete a truth table for the transistor-level...Ch. 3 - For the transistor-level circuit in Figure 3.38,...Ch. 3 - Prob. 7ECh. 3 - The transistor-level circuit below implements the...Ch. 3 - What does the following transistor circuit do?
Ch. 3 - For what values of A, B, C, D, E, and F will the...
Ch. 3 - A student knew that an inverter contained one...Ch. 3 - The following logic diagram produces the logical...Ch. 3 - The following logic circuits consist of two...Ch. 3 - Fill in the truth table for the logical expression...Ch. 3 - Fill in the truth table for a two-input NOR...Ch. 3 - Prob. 19ECh. 3 - How many output lines will a 16-input multiplexer...Ch. 3 - Prob. 21ECh. 3 - Given the following truth table, generate the...Ch. 3 - Prob. 23ECh. 3 - Prob. 24ECh. 3 - Logic circuit 1 in Figure 3.39 has inputs A, B, C....Ch. 3 - You know a byte is eight bits. We call a four-bit...Ch. 3 - Prob. 28ECh. 3 - Prob. 29ECh. 3 - Say the speed of a logic structure depends on the...Ch. 3 - Recall that the adder was built with individual...Ch. 3 - For this question, refer to the figure that...Ch. 3 - Prob. 35ECh. 3 - A comparator circuit has two 1-bit inputs A and B...Ch. 3 - If a computer has eight-byte addressability and...Ch. 3 - Prob. 38ECh. 3 - Refer to Figure 3.21, the diagram of the...Ch. 3 - Given a memory that is addressed by 22 bits and is...Ch. 3 - Prob. 42ECh. 3 - Prob. 43ECh. 3 - Prob. 44ECh. 3 - Prob. 47ECh. 3 - Refer to Figure 3.32. Why are lights 1 and 2...Ch. 3 - Prob. 49ECh. 3 - We have learned that we can write one bit of...Ch. 3 - A student decided to design a latch as shown...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, computer-science and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- In a shopping cart, there are various items, which can either belong to the category of household items or electronic items. The following UML diagram illustrates the relationship between items, household items, and electronic items. //Implementation Class public class ShoppingCart{ public static void main(String[] args){ final int MAX_ITEM = 50; Item cart = new Item[MAX_ITEM]; addItem(cart); // populate the item array printItem(cart); } } Considering that all the data definition classes and the implementation class are complete, which of the following Object-Oriented Programming (OOP) concepts do you need to use in the above context? i) Polymorphism ii) Method Overloading iii) Method Overriding iv) Dynamic Binding v) Abstract Class Explain, using course terminology, how you would use any of the above concepts to model the given scenario.arrow_forwardAnswer this JAVA OOP question below: An Employee has a name, employee ID, and department. An Employee object must be created with all its attributes. The UML diagram is provided below: - name: String - employeeId: String - department: String + Employee(name: String, employeeId: String, department: String) + setName(name: String): void + setEmployeeId(employeeId: String): void + setDepartment(department: String): void + getName(): String + getEmployeeId(): String + getDepartment(): String + toString(): String A faculty is an Employee with an additional field String field: rank public class TestImplementation{ public static void main(String[] args){ Employee[] allEmployee = new Employee[100]; // create an employee object with name Tom Evan, employee ID 001 and department IST and store it in allEmployee // create a faculty object with name Adam Scott, employee ID 002, department IST and rank Professor and store it in allEmployee } }arrow_forwardPlease answer this JAVA OOP question that is given below: An Employee has a name, employee ID, and department. An Employee object must be created with all its attributes. The UML diagram is provided below: - name: String - employeeId: String - department: String + Employee(name: String, employeeId: String, department: String) + setName(name: String): void + setEmployeeId(employeeId: String): void + setDepartment(department: String): void + getName(): String + getEmployeeId(): String + getDepartment(): String + toString(): String A faculty is an Employee with an additional field String field: rank Assuming the Employee class is fully implemented, define a Professor class in Java with the following: A toString() method that includes both the inherited attributes and the specializationarrow_forward
- Please answer JAVA OOP question below: An Employee has a name, employee ID, and department. An Employee object must be created with all its attributes. The UML diagram is provided below: - name: String - employeeId: String - department: String + Employee(name: String, employeeId: String, department: String) + setName(name: String): void + setEmployeeId(employeeId: String): void + setDepartment(department: String): void + getName(): String + getEmployeeId(): String + getDepartment(): String + toString(): String A faculty is an Employee with an additional field String field: rank Assuming the Employee class is fully implemented, define a Professor class in Java with the following: Instance variable(s) A Constructorarrow_forwardDevelop a C++ program that execute the operation as stated by TM for addition of two binary numbers (see attached image). Your code should receive two binary numbers and output the resulting sum (also in binary). Make sure your code mimics the TM operations (dealing with the binary numbers as a string of characters 1 and 0, and following the logic to increase the first number and decreasing the second one. Try your TM for the following examples: 1101 and 101, resulting 10010; and 1101 and 11, resulting 10000.arrow_forwardI need to define and discuss the uses of one monitoring or troubleshooting tool in Windows Server 2019. thank youarrow_forward
- I would likr toget help with the following concepts: - Windows Server features - Windows Server versus Windows 10 used as a client-server networkarrow_forwardI need to define and discuss the uses of one monitoring or troubleshooting tool in Windows Server 2019. thank youarrow_forwardWhy is planning for the retirement system and transition critical?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON
Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON
Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON
C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Database System Concepts
Computer Science
ISBN:9780078022159
Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780134444321
Author:Tony Gaddis
Publisher:PEARSON

Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780132737968
Author:Thomas L. Floyd
Publisher:PEARSON

C How to Program (8th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780133976892
Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey Deitel
Publisher:PEARSON

Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...
Computer Science
ISBN:9781337627900
Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven Morris
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Computer Science
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Boolean Algebra - Digital Logic and Logic Families - Industrial Electronics; Author: Ekeeda;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=u7XnJos-_Hs;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Boolean Algebra 1 – The Laws of Boolean Algebra; Author: Computer Science;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EPJf4owqwdA;License: Standard Youtube License