
Introduction to Computing Systems: From Bits & Gates to C & Beyond
3rd Edition
ISBN: 9781260424751
Author: PATT, Yale
Publisher: MCGRAW-HILL HIGHER EDUCATION
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Chapter 3, Problem 29E
Program Plan Intro
OR operation:
- OR function needs two inputs and produces one output.
- It is also known as binary logical function.
- If one of the inputs or both the inputs are “1”, then one-bit OR operation produces the output as “1”.
- If both the inputs are “0”, then OR operation produces the output “0”.
- The following diagram depicts the one-bit OR operation,
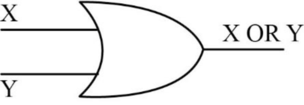
- The truth table for OR operation is as follows,
| X | Y | Z=X OR Y |
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
- In the above table, “X” and “Y” are the inputs, and “Z” is the output.
- In the above table, when “X=0”, and “Y=0”, the output “Z” is “0”, because both the inputs “X” and “Y” contains the value “0”.
- When “X=0”, and “Y=1”, the output “Z” is “1”, because one of the input “Y” contains the value “1”.
- When “X=1”, and “Y=0”, the output “Z” is “1”, because one of the input “X” contains the value “1”.
- When “X=1”, and “Y=1”, the output “Z” is “1”, because both the inputs “X” and “Y” contains the value “1”.
AND function:
- AND function needs two inputs and produces one output.
- It is also known as binary logical function.
- If one or both the inputs are “0”, then one-bit AND operation produces the output “0”.
- If both inputs are “1”, then AND operation produces the output as “1”.
- The following diagram depicts the AND operation,
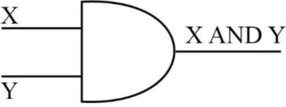
- The truth table for AND operation is as follows,
| X | Y | X AND Y |
| 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 1 |
- In the above table, “X” and “Y” are inputs, and “Z” is output.
- When “X=0”, and “Y=0”, the output is “0”, because both the inputs “X” and “Y” contains the value “0”.
- When “X=0”, and “Y=1”, the output is “0”, because one of the input “X” contains the value “0”.
- When “X=1”, and “Y=0”, the output is “0”, because one of the input “Y” contains the value “0”.
- When “X=1”, and “Y=1”, the output is “1”, because both the inputs “X” and “Y” contains the value “1”.
NOR function:
- The NOR operation produces the output which is the negation of the result of “OR” operation.
- If one or both the inputs are “1”, then NOR operation produces the output as “0”.
- If both the inputs are “0”, then NOR operation produces the output “1”.
- The following diagram depicts the NOR operation,
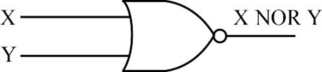
- The truth table for NOR operation is as follows,
| X | Y | Z=X OR Y |
| 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 0 |
| 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 |
NAND function:
- The NAND operation produces the output which is the negation of the result of “AND” operation.
- If one or both the inputs are “0”, then NAND operation produces the output “1”.
- If both inputs are “0”, then NAND operation produces the output as “0”.
- The following diagram depicts the NAND operation,
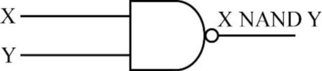
- The truth table for NAND operation is as follows,
| X | Y | X NAND Y |
| 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 0 | 1 | 1 |
| 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 1 | 1 | 0 |
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
I want to solve 13.2 using matlab please help
a) Show a possible trace of the OSPF algorithm for computing the routing table in Router 2 forthis network.b) Show the messages used by RIP to compute routing tables.
using r language to answer question 4 Question 4: Obtain a 95% standard normal bootstrap confidence interval, a 95% basic bootstrap confidence interval, and a percentile confidence interval for the ρb12 in Question 3.
Chapter 3 Solutions
Introduction to Computing Systems: From Bits & Gates to C & Beyond
Ch. 3 - Prob. 1ECh. 3 - Replace the missing parts in the following circuit...Ch. 3 - A two-input AND and a two-input OR are both...Ch. 3 - Replace the missing parts in the following circuit...Ch. 3 - Complete a truth table for the transistor-level...Ch. 3 - For the transistor-level circuit in Figure 3.38,...Ch. 3 - Prob. 7ECh. 3 - The transistor-level circuit below implements the...Ch. 3 - What does the following transistor circuit do?
Ch. 3 - For what values of A, B, C, D, E, and F will the...
Ch. 3 - A student knew that an inverter contained one...Ch. 3 - The following logic diagram produces the logical...Ch. 3 - The following logic circuits consist of two...Ch. 3 - Fill in the truth table for the logical expression...Ch. 3 - Fill in the truth table for a two-input NOR...Ch. 3 - Prob. 19ECh. 3 - How many output lines will a 16-input multiplexer...Ch. 3 - Prob. 21ECh. 3 - Given the following truth table, generate the...Ch. 3 - Prob. 23ECh. 3 - Prob. 24ECh. 3 - Logic circuit 1 in Figure 3.39 has inputs A, B, C....Ch. 3 - You know a byte is eight bits. We call a four-bit...Ch. 3 - Prob. 28ECh. 3 - Prob. 29ECh. 3 - Say the speed of a logic structure depends on the...Ch. 3 - Recall that the adder was built with individual...Ch. 3 - For this question, refer to the figure that...Ch. 3 - Prob. 35ECh. 3 - A comparator circuit has two 1-bit inputs A and B...Ch. 3 - If a computer has eight-byte addressability and...Ch. 3 - Prob. 38ECh. 3 - Refer to Figure 3.21, the diagram of the...Ch. 3 - Given a memory that is addressed by 22 bits and is...Ch. 3 - Prob. 42ECh. 3 - Prob. 43ECh. 3 - Prob. 44ECh. 3 - Prob. 47ECh. 3 - Refer to Figure 3.32. Why are lights 1 and 2...Ch. 3 - Prob. 49ECh. 3 - We have learned that we can write one bit of...Ch. 3 - A student decided to design a latch as shown...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, computer-science and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- using r language Obtain a bootstrap t confidence interval estimate for the correlation statistic in Example 8.2 (law data in bootstrap).arrow_forwardusing r language Compute a jackknife estimate of the bias and the standard error of the correlation statistic in Example 8.2.arrow_forwardusing r languagearrow_forward
- using r languagearrow_forwardThe assignment here is to write an app using a database named CIT321 with a collection named students; we will provide a CSV file of the data. You need to use Vue.js to display 2 pages. You should know that this assignment is similar, all too similar in fact, to the cars4sale2 example in the lecture notes for Vue.js 2. You should study that program first. If you figure out cars4sale2, then program 6 will be extremely straightforward. It is not my intent do drop a ton of new material here in the last few days of class. The database contains 51 documents. The first rows of the CSV file look like this: sid last_name 1 Astaire first_name Humphrey CIT major hrs_attempted gpa_points 10 34 2 Bacall Katharine EET 40 128 3 Bergman Bette EET 42 97 4 Bogart Cary CIT 11 33 5 Brando James WEB 59 183 6 Cagney Marlon CIT 13 40 GPA is calculated as gpa_points divided by hrs_attempted. GPA points would have been arrived at by adding 4 points for each credit hour of A, 3 points for each credit hour of…arrow_forwardI need help to solve the following case, thank youarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON
Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON
Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON
C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Database System Concepts
Computer Science
ISBN:9780078022159
Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. Sudarshan
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780134444321
Author:Tony Gaddis
Publisher:PEARSON

Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780132737968
Author:Thomas L. Floyd
Publisher:PEARSON

C How to Program (8th Edition)
Computer Science
ISBN:9780133976892
Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey Deitel
Publisher:PEARSON

Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...
Computer Science
ISBN:9781337627900
Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven Morris
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Computer Science
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Boolean Algebra - Digital Logic and Logic Families - Industrial Electronics; Author: Ekeeda;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=u7XnJos-_Hs;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Boolean Algebra 1 – The Laws of Boolean Algebra; Author: Computer Science;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EPJf4owqwdA;License: Standard Youtube License