
Concept explainers
Different materials rest on a table.
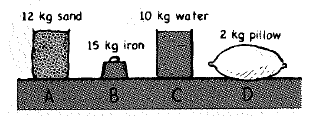
a. From greatest to least, rank them by how much they resist being set into motion.
b. From greatest to least, rank them by weight.
c. From greatest to least, rank them by the support (normal) force the table exerts on them.
(a)
Ranking of the materials from greatest to least by how much they resist being set into motion.
Answer to Problem 21A
Ranking of materials by how much they resist is given as:
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Mass of sand,
Mass of iron,
Mass of water,
Mass of pillow,
Formula used:
Force of friction is given by:
Calculation:
According to the given formula, the force of friction is directly proportional to the mass, because
Hence, the resistance of the materials being set into motion is ranked according to the masses:
So, the final result will be:
Conclusion:
Ranking of materials by how much they resist is given as:
(b)
Ranking of materials by their weight.
Answer to Problem 21A
The ranking of materials according to their weight is:
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Mass of sand,
Mass of iron,
Mass of water,
Mass of pillow,
Formula used:
Weight of an object is given by:
Calculation:
According to the formula, the weight is directly proportional to the mass of the object, because the acceleration due to gravity is constant. So,
Hence, the ranking is given as follows:
Conclusion:
The ranking of materials according to their weight is:
(c)
Ranking of materials by the normal force the table exerts on them.
Answer to Problem 21A
The ranking of materials by the normal force the table exerts on them is:
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Mass of sand,
Mass of iron,
Mass of water,
Mass of pillow,
Formula used:
The normal force is given by:
Calculation:
According to the formula, the normal force is directly proportional to the force of friction, because
Hence, the ranking is given as follows:
Conclusion:
The ranking of materials by the normal force the table exerts on them is:
Chapter 3 Solutions
EP CONCEPTUAL PHYSICS-ITEXT ACCESS
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
Chemistry: The Central Science (14th Edition)
Cosmic Perspective Fundamentals
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
- 1. A charge of -25 μC is distributed uniformly throughout a spherical volume of radius 11.5 cm. Determine the electric field due to this charge at a distance of (a) 2 cm, (b) 4.6 cm, and (c) 25 cm from the center of the sphere. (a) = = (b) E = (c)Ẻ = = NC NC NCarrow_forward1. A long silver rod of radius 3.5 cm has a charge of -3.9 ис on its surface. Here ŕ is a unit vector ст directed perpendicularly away from the axis of the rod as shown in the figure. (a) Find the electric field at a point 5 cm from the center of the rod (an outside point). E = N C (b) Find the electric field at a point 1.8 cm from the center of the rod (an inside point) E=0 Think & Prepare N C 1. Is there a symmetry in the charge distribution? What kind of symmetry? 2. The problem gives the charge per unit length 1. How do you figure out the surface charge density σ from a?arrow_forward1. Determine the electric flux through each surface whose cross-section is shown below. 55 S₂ -29 S5 SA S3 + 9 Enter your answer in terms of q and ε Φ (a) s₁ (b) s₂ = -29 (C) Φ զ Ερ (d) SA = (e) $5 (f) Sa $6 = II ✓ -29 S6 +39arrow_forward
- No chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardthe cable may break and cause severe injury. cable is more likely to break as compared to the [1] ds, inclined at angles of 30° and 50° to the vertical rings by way of a scaled diagram. [4] I 30° T₁ 3cm 3.8T2 cm 200 N 50° at it is headed due North and its airspeed indicat 240 km/h. If there is a wind of 100 km/h from We e relative to the Earth? [3]arrow_forwardCan you explain this using nodal analysis With the nodes I have present And then show me how many KCL equations I need to write, I’m thinking 2 since we have 2 dependent sourcesarrow_forward
- The shear leg derrick is used to haul the 200-kg net of fish onto the dock as shown in. Assume the force in each leg acts along its axis. 5.6 m. 4 m- B Part A Determine the compressive force along leg AB. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. FAB = Value Submit Request Answer Part B Units ? Determine the compressive force along leg CB. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. FCB= Value Submit Request Answer Part C ? Units Determine the tension in the winch cable DB. Express your answer with the appropriate units. 2marrow_forwardPart A (Figure 1) shows a bucket suspended from a cable by means of a small pulley at C. If the bucket and its contents have a mass of 10 kg, determine the location of the pulley for equilibrium. The cable is 6 m long. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. Figure 4 m B НА x = Value Submit Request Answer Provide Feedback < 1 of 1 T 1 m Units ?arrow_forwardThe particle in is in equilibrium and F4 = 165 lb. Part A Determine the magnitude of F1. Express your answer in pounds to three significant figures. ΑΣΦ tvec F₁ = Submit Request Answer Part B Determine the magnitude of F2. Express your answer in pounds to three significant figures. ΑΣΦ It vec F2 = Submit Request Answer Part C Determine the magnitude of F3. Express your answer in pounds to three significant figures. ? ? lb lb F₂ 225 lb 135° 45° 30° -60°-arrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





