
Principles of Corporate Finance (Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series in Finance, Insurance, and Real Estate)
12th Edition
ISBN: 9781259144387
Author: Richard A Brealey, Stewart C Myers, Franklin Allen
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 3, Problem 1SQ
(PRICE) In February 2009, Treasury 8.5s of 2020 yielded 3.2976%. What was their price? If the yield rose to 4%, what would happen to the price?
Expert Solution
Summary Introduction
To determine: The price of bond at a yield of 3.2976%.
Answer to Problem 1SQ
The price of bond at a yield of 3.2976% is $147.67.
Explanation of Solution
Determine the price of bond at a yield of 3.2976%
Excel Spreadsheet:
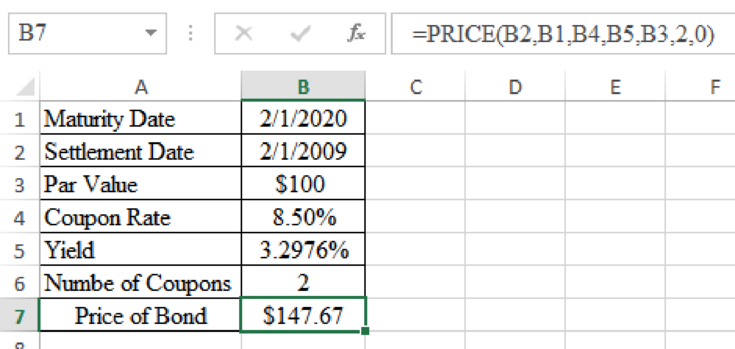
Therefore the price of bond at a yield of 3.2976% is $147.67.
Expert Solution
Summary Introduction
To determine: The price of bond at a yield of 4%.
Answer to Problem 1SQ
The price of bond at a yield of 4% is $139.73.
Explanation of Solution
Determine the price of bond at a yield of 4%
Excel Spreadsheet:
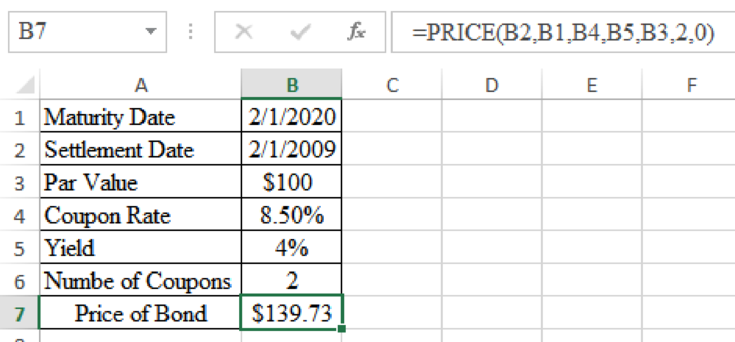
Therefore the price of bond at a yield of 4% is $139.73.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Subscribe now to access step-by-step solutions to millions of textbook problems written by subject matter experts!
Students have asked these similar questions
Suppose that you are a U.S.-based importer of goods from the United Kingdom. You expect the value of the pound to increase against the U.S. dollar over the next 30 days. You will be making payment on a shipment of imported goods in 30 days and want to hedge your currency exposure. The U.S. risk-free rate is 5.5 percent, and the U.K. risk-free rate is 4.5 percent. These rates are expected to remain unchanged over the next month. The current spot rate is $1.90.
1.Move forward 10 days. The spot rate is $1.93. Interest rates are unchanged. Calculate the value of your forward position. Do not round intermediate calculations. Round your answer to 4 decimal places.
Don't solve.
I mistakenly submitted blurr image please comment i will write values.
please dont Solve with incorrect values otherwise unhelpful.
The image is blurr please comment i will write values.
please dont Solve with incorrect values otherwise unhelpful.
Chapter 3 Solutions
Principles of Corporate Finance (Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series in Finance, Insurance, and Real Estate)
Ch. 3 - (PRICE) In February 2009, Treasury 8.5s of 2020...Ch. 3 - (YLD) On the same day, Treasury 3.5s of 2018 were...Ch. 3 - (DURATION) What was the duration of the Treasury...Ch. 3 - (MDURATION) What was the modified duration of the...Ch. 3 - Prob. 1PSCh. 3 - Bond prices and yields The following statements...Ch. 3 - Prob. 3PSCh. 3 - Bond prices and yields A 10-year German government...Ch. 3 - Bond prices and yields Construct some simple...Ch. 3 - Spot interest rates and yields Which comes first...
Ch. 3 - Prob. 7PSCh. 3 - Spot interest rates and yields Assume annual...Ch. 3 - Prob. 9PSCh. 3 - Prob. 10PSCh. 3 - Duration True or false? Explain. a....Ch. 3 - Duration Calculate the durations and volatilities...Ch. 3 - Term-structure theories The one-year spot interest...Ch. 3 - Real interest rates The two-year interest rate is...Ch. 3 - Duration Here are the prices of three bonds with...Ch. 3 - Prob. 16PSCh. 3 - Prob. 17PSCh. 3 - Spot interest rates and yields A 6% six-year bond...Ch. 3 - Spot interest rates and yields Is the yield on...Ch. 3 - Prob. 20PSCh. 3 - Prob. 21PSCh. 3 - Duration Find the spreadsheet for Table 3.4 in...Ch. 3 - Prob. 23PSCh. 3 - Prob. 25PSCh. 3 - Prob. 26PSCh. 3 - Prob. 27PSCh. 3 - Prob. 28PSCh. 3 - Prob. 29PSCh. 3 - Prices and yields If a bonds yield to maturity...Ch. 3 - Prob. 31PSCh. 3 - Price and spot interest rates Find the arbitrage...Ch. 3 - Prob. 33PSCh. 3 - Prices and spot interest rates What spot interest...Ch. 3 - Prices and spot interest rates Look one more time...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, finance and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Question 6 A five-year $50,000 endowment insurance for (60) has $1,000 underwriting expenses, 25% of the first premium is commission for the agent of record and renewal expenses are 5% of subsequent premiums. Write the gross future loss random variable: Presuming a portfolio of 10,000 identical and independent policies, the expected loss and the variance of the loss of the portfolio are given below (note that the premium basis is not given or needed): E[L] = 10,000(36,956.49 - 3.8786P) V[L] 10,000 (50,000 + 14.52P)². 0.00095 Find the premium that results in a 97.5% probability of profit (i.e. ¹ (0.975) = 1.96). Premium: Please show your work belowarrow_forwardWhat corporate finance?? can you explain this? fully no aiarrow_forwardWhat is corporate finance? how this is usefull?arrow_forward
- Pam and Jim are saving money for their two children who they plan to send to university.The eldest child will enter university in 5 years while the younger will enter in 7 years. Each child is expected spend four years at university. University fees are currently R20 000 per year and are expected to grow at 5% per year. These fees are paid at the beginning of each year.Pam and Jim currently have R40 000 in their savings and their plan is to save a fixed amount each year for the next 5 years. The first deposit taking place at the end of the current year and the last deposit at the date the first university fees are paid.Pam and Jim expect to earn 10% per year on their investments.What amount should they invest each year to meet the cost of their children’s university fees?arrow_forwardPam and Jim are saving money for their two children who they plan to send to university.The eldest child will enter university in 5 years while the younger will enter in 7 years. Each child is expected spend four years at university. University fees are currently R20 000 per year and are expected to grow at 5% per year. These fees are paid at the beginning of each year.Pam and Jim currently have R40 000 in their savings and their plan is to save a fixed amount each year for the next 5 years. The first deposit taking place at the end of the current year and the last deposit at the date the first university fees are paid.Pam and Jim expect to earn 10% per year on their investments.What amount should they invest each year to meet the cost of their children’s university fees?arrow_forwardYou make a loan of R100 000, with annual payments being made at the end of each year for the next 5 years at a 10% interest rate. How much interest is paid in the second year?arrow_forward
- Dr Z. Mthembu is the owner of Mr Granite, a business in the Western Cape. After more than 28 years of operation, the business is thinking about taking on a new project that would provide a profitable new clientele. With only R1.5 million in resources, the company is now working on two competing projects. The starting costs for Project X and Project Y are R625,000 and R600000, respectively. These projected are estimated for the next 7 years timeframe. According to SARS, the tax rate is 28%, and a discount rate of 11.25% is applied.Projects X Project YProject X Project Y129000 145000154000 145000312000 145000168000 14500098250 14500088750 14500016050 145000arrow_forwardDr Z. Mthembu is the owner of Mr Granite, a business in the Western Cape. After more than 28 years of operation, the business is thinking about taking on a new project that would provide a profitable new clientele. With only R1.5 million in resources, the company is now working on two competing projects. The starting costs for Project X and Project Y are R625,000 and R600000, respectively. These projected are estimated for the next 7 years timeframe. According to SARS, the tax rate is 28%, and a discount rate of 11.25% is applied.Projects X Project YProject X Project Y129000 145000154000 145000312000 145000168000 14500098250 14500088750 14500016050 145000arrow_forwardDr Z. Mthembu is the owner of Mr Granite, a business in the Western Cape. After more than 28 years of operation, the business is thinking about taking on a new project that would provide a profitable new clientele. With only R1.5 million in resources, the company is now working on two competing projects. The starting costs for Project X and Project Y are R625,000 and R600000, respectively. These projected are estimated for the next 7 years timeframe. According to SARS, the tax rate is 28%, and a discount rate of 11.25% is applied.Projects X Project YProject X Project Y129000 145000154000 145000312000 145000168000 14500098250 14500088750 14500016050 145000arrow_forward
- Dr Z. Mthembu is the owner of Mr Granite, a business in the Western Cape. After more than 28 years of operation, the business is thinking about taking on a new project that would provide a profitable new clientele. With only R1.5 million in resources, the company is now working on two competing projects. The starting costs for Project X and Project Y are R625,000 and R600000, respectively. These projected are estimated for the next 7 years timeframe. According to SARS, the tax rate is 28%, and a discount rate of 11.25% is applied.Projects X Project YProject X Project Y129000 145000154000 145000312000 145000168000 14500098250 14500088750 14500016050 145000arrow_forwardAn investor buys 100 shares of a $40 stock that pays an annual cash dividend of $2 a share (a 5 percent dividend yield) and signs up for the DRIP. a. If neither the dividend nor the price changes, how many shares will the investor have at the end of 10 years? How much will the position in the stock be worth? Answer: 5.000 shares purchased in year 1 5.250 shares purchased in year 2 6.078 shares purchased in year 5 62.889 total shares purchased b. If the price of the stock rises by 6 percent annually but the dividend remains at $2 a share, how many shares are purchased each year for the next 10 years? How much is the total position worth at the end of 10 years? Answer: 4.717 shares purchased in year 1 4.592 shares in year 3 3.898 shares in year 10 Value of position: $10,280 c. If the price of the stock rises by 6 percent annually but the dividend rises by only 3 percent annually, how many shares are purchased each year for the next 10 years? How much is the total position worth at the…arrow_forwardDr Z. Mthembu is the owner of Mr Granite, a business in the Western Cape. After more than 28 years of operation, the business is thinking about taking on a new project that would provide a profitable new clientele. With only R1.5 million in resources, the company is now working on two competing projects. The starting costs for Project X and Project Y are R625,000 and R600000, respectively. These projected are estimated for the next 7 years timeframe. According to SARS, the tax rate is 28%, and a discount rate of 11.25% is applied.Projects X Project YProject X Project Y129000 145000154000 145000312000 145000168000 14500098250 14500088750 14500016050 145000 Calculate the IRR for the two proposed Projectsarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Essentials Of InvestmentsFinanceISBN:9781260013924Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Essentials Of InvestmentsFinanceISBN:9781260013924Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

 Foundations Of FinanceFinanceISBN:9780134897264Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. WilliamPublisher:Pearson,
Foundations Of FinanceFinanceISBN:9780134897264Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. WilliamPublisher:Pearson, Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...FinanceISBN:9781337395250Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. HoustonPublisher:Cengage Learning Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...FinanceISBN:9780077861759Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...FinanceISBN:9780077861759Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Essentials Of Investments
Finance
ISBN:9781260013924
Author:Bodie, Zvi, Kane, Alex, MARCUS, Alan J.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,



Foundations Of Finance
Finance
ISBN:9780134897264
Author:KEOWN, Arthur J., Martin, John D., PETTY, J. William
Publisher:Pearson,

Fundamentals of Financial Management (MindTap Cou...
Finance
ISBN:9781337395250
Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Joel F. Houston
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Corporate Finance (The Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series i...
Finance
ISBN:9780077861759
Author:Stephen A. Ross Franco Modigliani Professor of Financial Economics Professor, Randolph W Westerfield Robert R. Dockson Deans Chair in Bus. Admin., Jeffrey Jaffe, Bradford D Jordan Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
The U.S. Treasury Markets Explained | Office Hours with Gary Gensler; Author: U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=uKXZSzY2ZbA;License: Standard Youtube License