
Graphical Representation of
Explanation of Solution
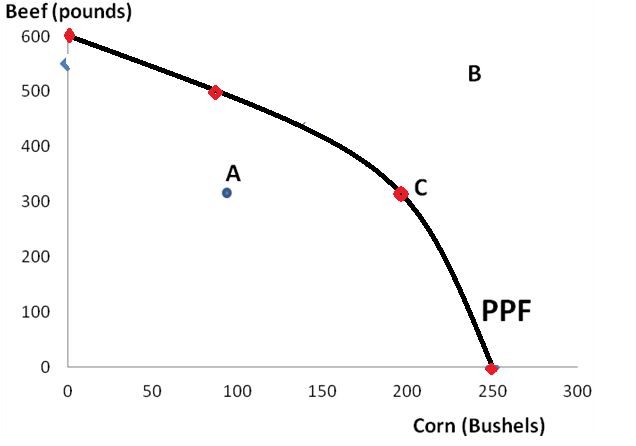
Inefficient points are those in which resources are not fully utilized or are wasted. Economy is producing output inside Production possibility curve. Point A is inefficient as 300 pounds of beef and 100 bushel of corn is produced. At this point, resources are wasted.
Unattainable combinations are such which lie outside PPF curve. These are the combination of output production which cannot be produced as resources are not available for such combination. Point B in unattainable point in the above figure.
Efficient Point: Production is said to be efficient at which an economy can produce maximum output using its existing resources. There is no scope of increasing production, only alteration can be done. Resources are fully employed and attainable. Point C is efficient point.
Concept Introduction:
Production efficiency is the level of optimum level at which am economy can produce maximum output using its existing resources. There is no scope of increasing production, only alteration can be done.
An inefficient output is one in which more output of one good is produced without reducing the other good's output.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Foundations of Economics, Student Value Edition (8th Edition)
- 1. Imagine a society that produces military goods and consumer goods, which we'll call "guns" and "butter." a. Draw a production possibilities frontier for guns and butter. Using the concept of opportunity cost, explain why it most likely has a bowed-out shape. b. Show a point that is impossible for the economy to achieve. Show a point that is feasible but inefficient. c. Imagine that the society has two political parties, called the Hawks (who want a strong military) and the Doves (who want a smaller military). Show a point on your production possibilities frontier that the Hawks might choose and a point the Doves might choose. d. Imagine that an aggressive neighboring country reduces the size of its military. As a result, both the Hawks and the Doves reduce their desired production of guns by the same amount. Which party would get the bigger "peace dividend," measured by the increase in butter production? Explain.arrow_forwardA health study tracked a group of persons for five years. At the beginning of the study, 20%were classified as heavy smokers, 30% as light smokers, and 50% as nonsmokers. Resultsof the study showed that light smokers were twice as likely as nonsmokers to die duringthe five-year study, but only half as likely as heavy smokers.A randomly selected participant from the study died during the five-year period. Calculatethe probability that the participant was a heavy smokerarrow_forwardConsider two assets with the following returns: State Prob. of state R₁ R2 1 23 13 25% 5% 2 -10% 1% Compute the optimal portfolio for an investor having a Bernoulli utility of net returns u(r) = 2√√r+ 10. Compute the certainty equivalent of the optimal portfolio. Do the results change if short-selling is not allowed? If so, how?arrow_forward
- In the graph at the right, the average variable cost is curve ☐. The average total cost is curve marginal cost is curve The C Cost per Unit ($) Per Unit Costs A 0 Output Quantity Barrow_forwardWhat are some of the question s that I can ask my economic teacher?arrow_forwardAnswer question 2 only.arrow_forward
- 1. A pension fund manager is considering three mutual funds. The first is a stock fund, the second is a long-term government and corporate fund, and the third is a (riskless) T-bill money market fund that yields a rate of 8%. The probability distributions of the risky funds have the following characteristics: Standard Deviation (%) Expected return (%) Stock fund (Rs) 20 30 Bond fund (RB) 12 15 The correlation between the fund returns is .10.arrow_forwardFrederick Jones operates a sole proprietorship business in Trinidad and Tobago. His gross annual revenue in 2023 was $2,000,000. He wants to register for VAT, but he is unsure of what VAT entails, the requirements for registration and what he needs to do to ensure that he is fully compliant with VAT regulations. Make reference to the Vat Act of Trinidad and Tobago and explain to Mr. Jones what VAT entails, the requirements for registration and the requirements to be fully compliant with VAT regulations.arrow_forwardCan you show me the answers for parts a and b? Thanks.arrow_forward
- What are the answers for parts a and b? Thanksarrow_forwardWhat are the answers for a,b,c,d? Are they supposed to be numerical answers or in terms of a variable?arrow_forwardSue is a sole proprietor of her own sewing business. Revenues are $150,000 per year and raw material (cloth, thread) costs are $130,000 per year. Sue pays herself a salary of $60,000 per year but gave up a job with a salary of $80,000 to run the business. ○ A. Her accounting profits are $0. Her economic profits are - $60,000. ○ B. Her accounting profits are $0. Her economic profits are - $40,000. ○ C. Her accounting profits are - $40,000. Her economic profits are - $60,000. ○ D. Her accounting profits are - $60,000. Her economic profits are -$40,000.arrow_forward

 Brief Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Cours...EconomicsISBN:9781337091985Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Brief Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Cours...EconomicsISBN:9781337091985Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning
Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning







